Hair Loss in Women: Causes, Impacts and Solutions

Summary
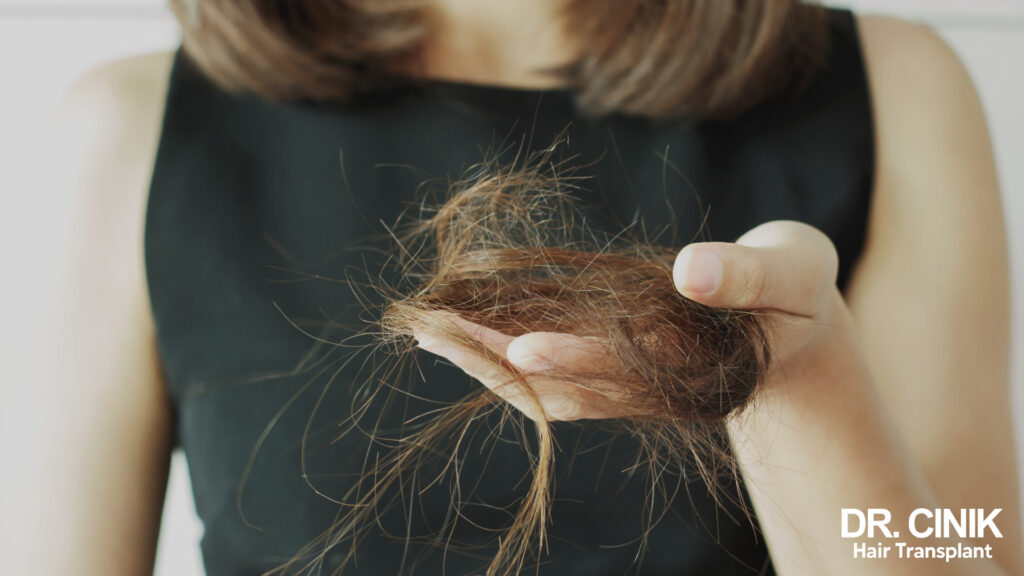
Hair is often considered an asset of attraction and a symbol of femininity. However, many women face hair loss at some point in their lives. Although common, this phenomenon remains rather taboo and can have a considerable impact on self-esteem. Female hair loss is a complex problem with multiple origins, affecting almost 40% of women after menopause and up to 50% of women aged 79.

A Problem More Widespread Than We Think
Contrary to popular belief, hair loss isn’t just a bloke’s problem. In reality, this phenomenon affects many women, often silently. It’s quite normal to lose between 50 and 100 hairs per day. Beyond that, we can talk about abnormal hair loss.
Hair loss in women can occur at any age, but it becomes more common over time. Statistics show that:
- About 12% of women start losing their hair by the age of 29
- 25% of women are affected around the age 49
- Nearly 41% of women notice a decrease in hair density around age 69
- By age 79, more than 50% of women experience some form of hair loss
These figures, reported in a study published in the International Journal of Women’s Dermatology, underline the scale of the problem and the need to talk openly about it to understand better and address it.

The Multiple Origins of Female Hair Loss
Hormonal Changes, Major Hair Disruptors
Hormones play a crucial role in the health of our hair, and hormonal fluctuations can, therefore, significantly impact our locks. Pregnancy, menopause, and thyroid disorders are key periods for women’s hair health.
For example, pregnancy is when hair is generally more beautiful and thicker. However, after giving birth, many women experience temporary hair loss. This phenomenon, called postpartum telogen effluvium, is due to the sudden drop in oestrogen.
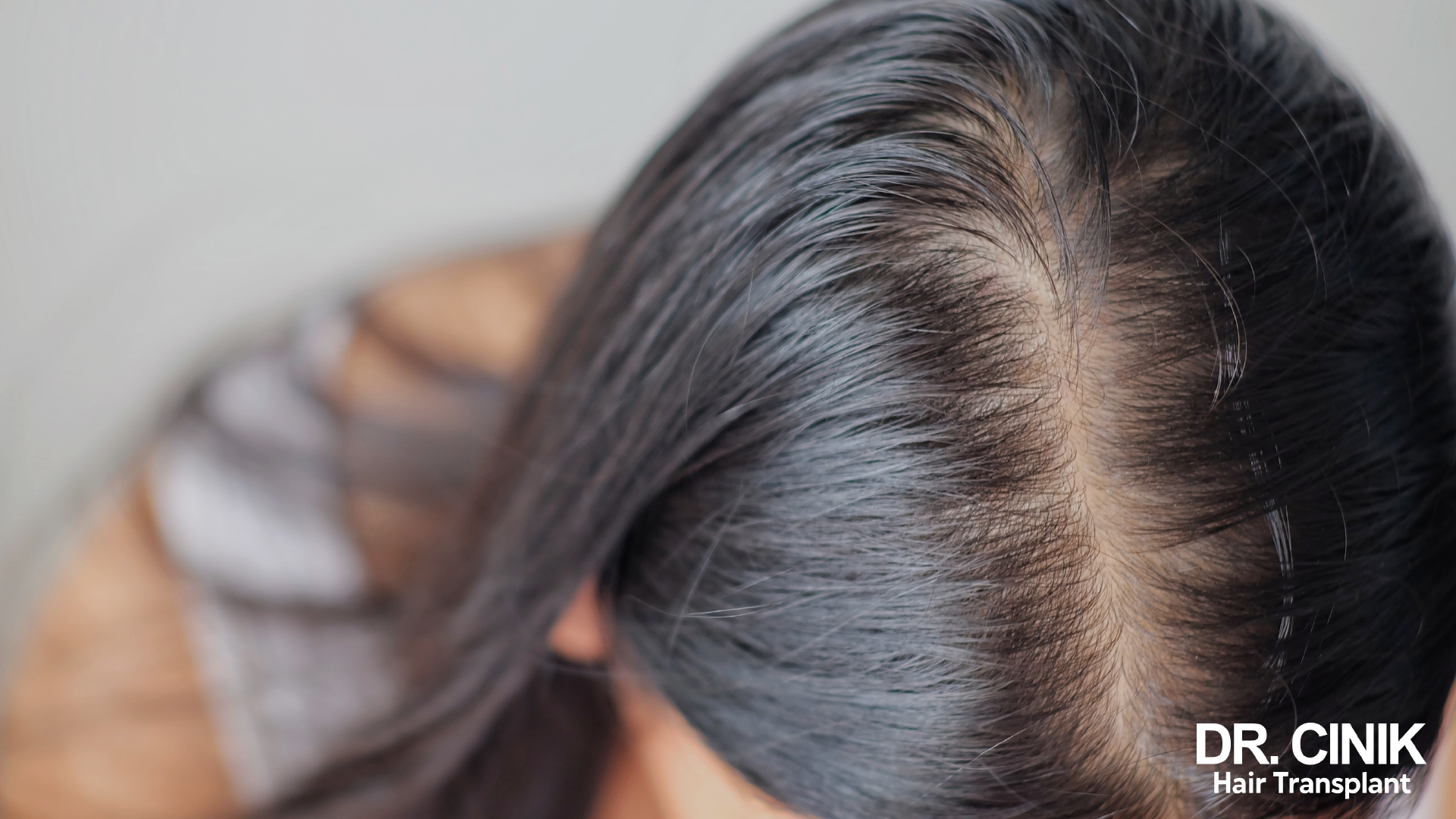

Menopause is another pivotal period for hair health. The decline in oestrogen and the relative preponderance of androgens can lead to progressive hair thinning. This is called female androgenetic alopecia, a form of female pattern baldness.
Thyroid disorders, whether hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, can also affect hair health. Hypothyroidism can cause diffuse hair loss, while hyperthyroidism can cause hair thinning.
Stress the number one enemy of our hair
Intense or chronic stress can cause sudden hair loss. In a state of alert, the body redirects its resources towards vital functions, thus neglecting hair growth.
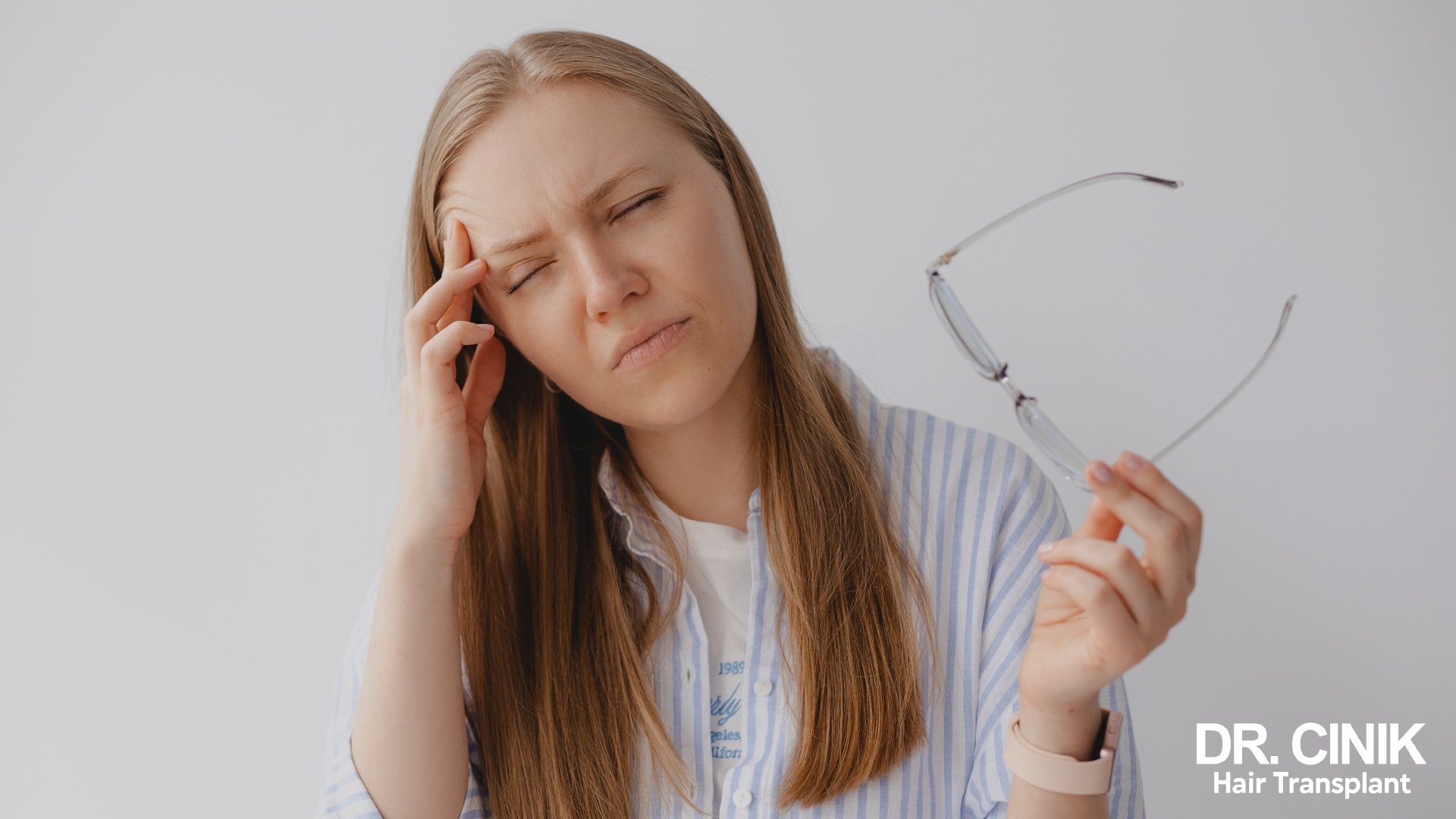

Stress can trigger three types of hair loss, as explained in a review published in Cureus:
- Telogen effluvium: diffuse hair loss that occurs 2 to 3 months after a stressful event.
- Alopecia areata: An autoimmune disease that causes hair loss in patches.
- Trichotillomania: an obsessive-compulsive disorder characterised by repetitive hair pulling.
Stress management is, therefore, essential to maintaining healthy hair. Meditation, yoga, or regular exercise can help reduce stress and improve hair health.
Nutritional Deficiencies, An Often Overlooked Factor
A balanced diet is essential to maintaining healthy hair. Iron, zinc, and B vitamin deficiencies can lead to hair loss, especially for women on restrictive diets or with eating disorders.

Iron plays a crucial role in hair growth. Iron deficiency, or anaemia, is a common cause of hair loss in women, especially those who have heavy periods or follow a vegetarian or vegan diet.
Zinc is also important for hair health. It helps in protein production and cell division, two processes essential for hair growth.
B vitamins, especially biotin (vitamin B7), are essential for healthy hair. Biotin deficiency can lead to hair loss, although this deficiency is rare in people eating a balanced diet.
Autoimmune Diseases and Other Pathologies
Certain illnesses can cause hair loss. Alopecia areata, for example, is an autoimmune disease that causes hair loss in patches. It affects around 2% of the population and can occur at any age.
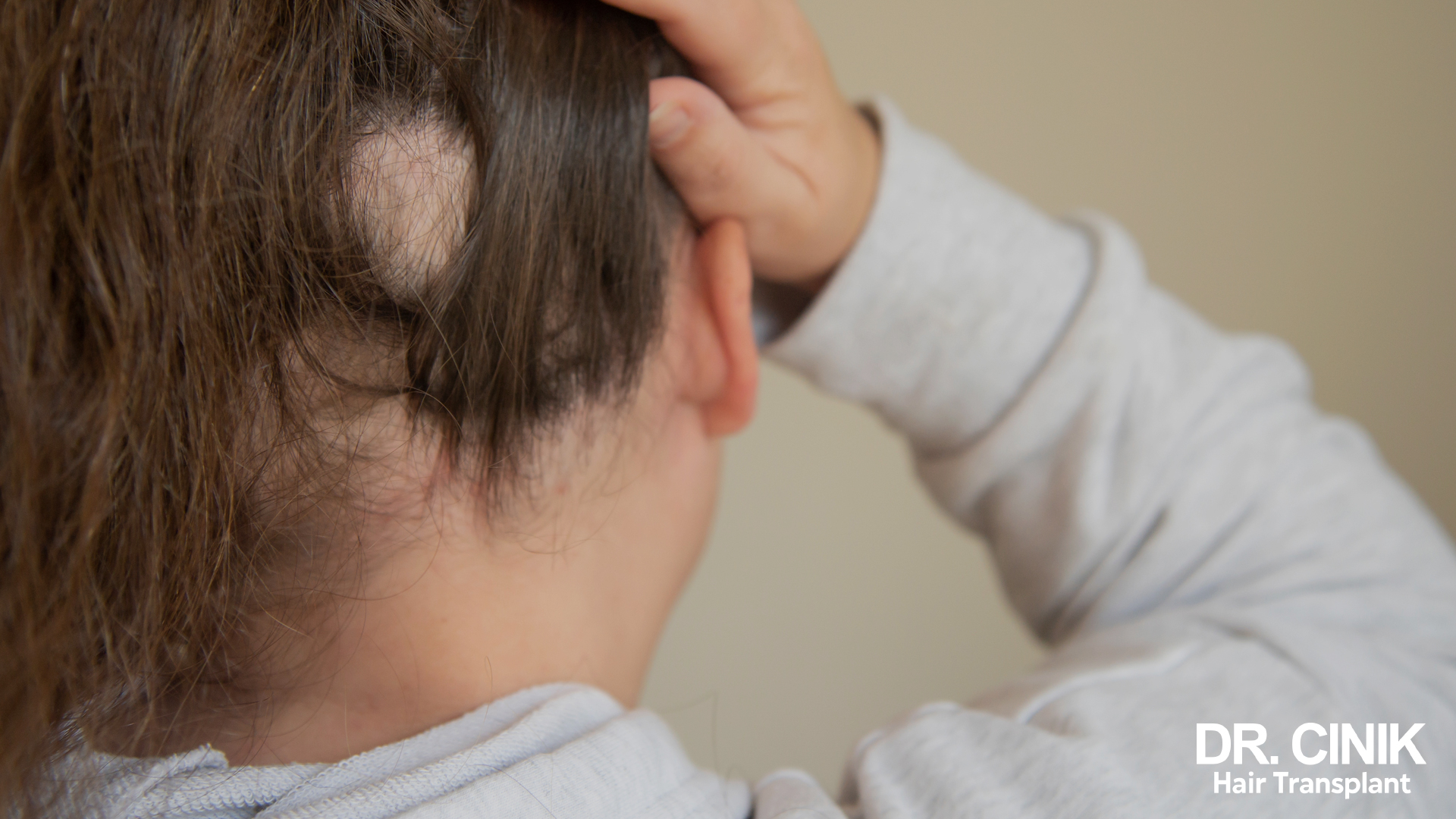
Systemic lupus erythematosus is another autoimmune disease that can cause hair loss. In this case, hair loss is often accompanied by other symptoms like rashes, fatigue, and joint pain.
Thyroid problems, whether hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, can also affect hair health. A thyroid test is often recommended in cases of unexplained hair loss.
Medical Treatments and Their Side Effects
Specific medical treatments, such as chemotherapy, are known to cause hair loss. However, other medications, less known for this side effect, can also be involved. This is the case with certain antidepressants, anticoagulants or acne treatments.
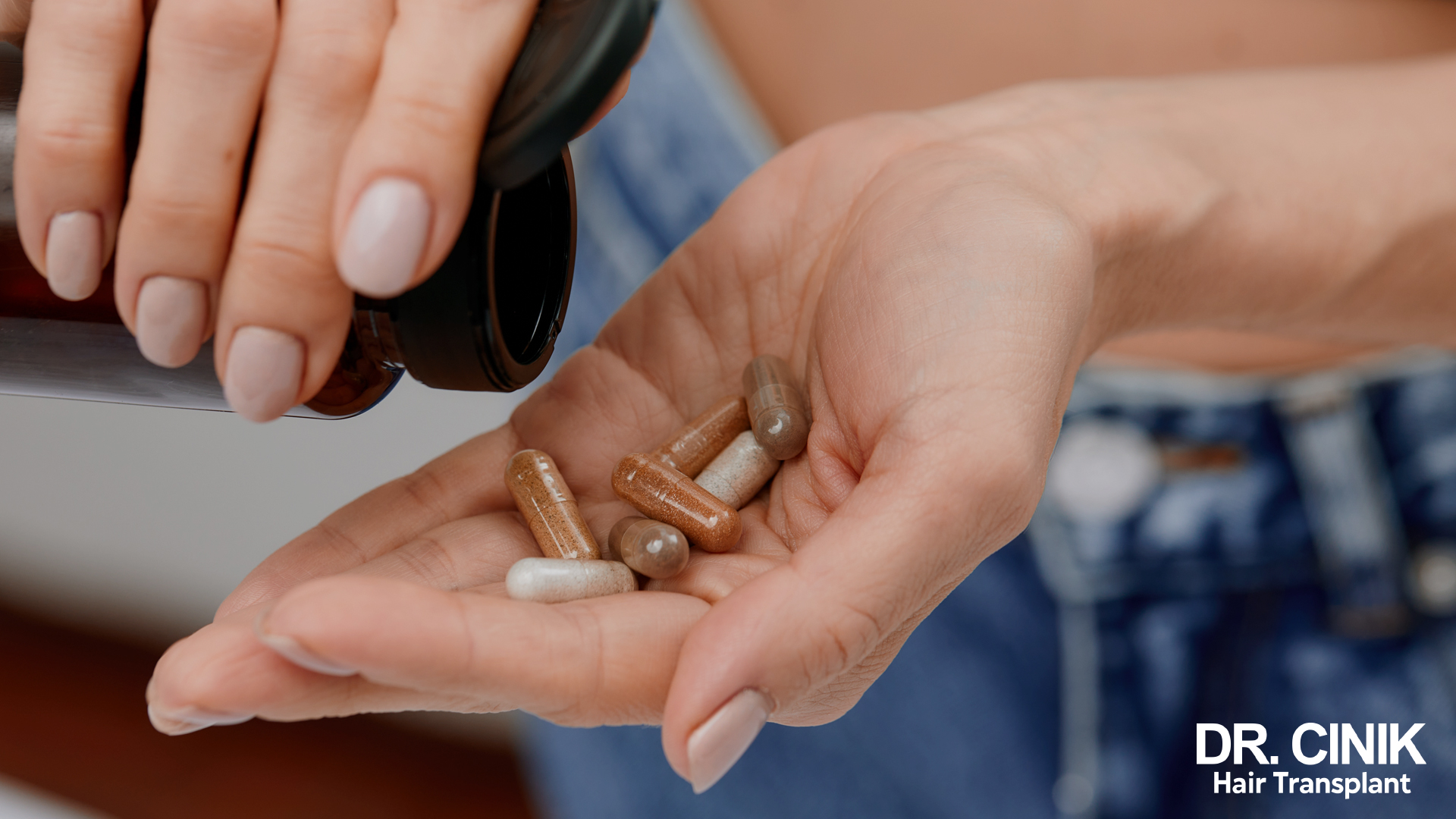

Chemotherapy is the most common medical treatment for hair loss. It targets fast-growing cells, including hair cells. Fortunately, this hair loss is usually temporary, and the hair will grow back once treatment is complete.
Other medications can also cause hair loss:
- Anticoagulants
- Certain antidepressants
- Acne medications based on vitamin A
- Certain medications for arthritis
- Beta-blockers used to treat hypertension
It’s important to note that stopping birth control treatment can also cause temporary hair loss due to hormonal changes.
The Psychological Impact of Hair Loss in Women
Hair loss can have a significant impact on women’s psychological well-being. In a society where appearance plays an important role, hair loss can be experienced as a loss of femininity and attractiveness. This can lead to lowered self-esteem, anxiety, and even depression.
The emotional impact of hair loss on women is often underestimated. A study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology found that 55% of women suffering from hair loss had symptoms of depression. Additionally, 89% of women surveyed said their hair loss hurt their self-esteem.
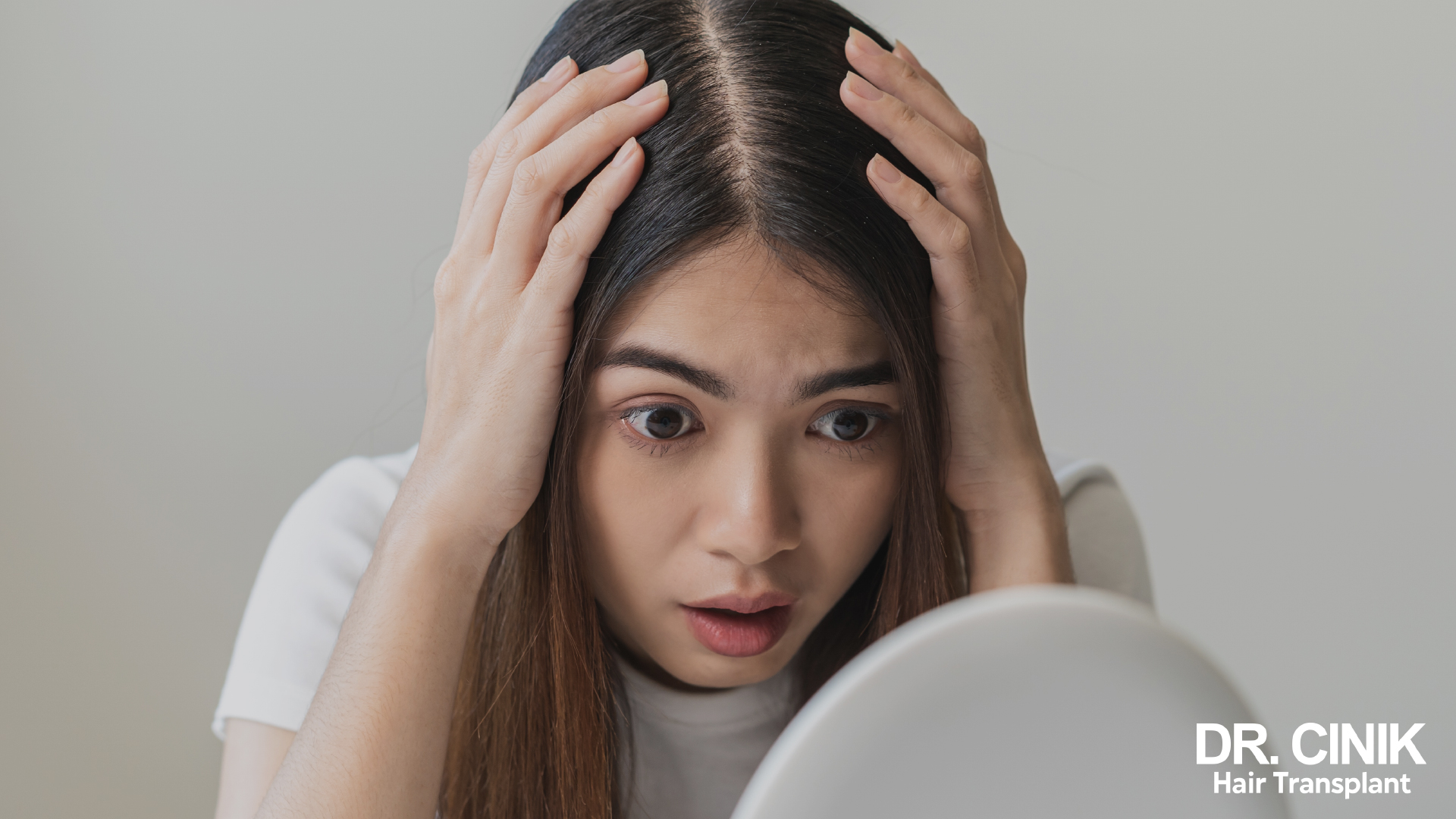

Hair loss can affect many aspects of a woman’s life:
- Self-confidence: Losing hair can seriously undermine self-confidence since it is often considered a symbol of femininity and youth.
- Social relationships: Some women may feel embarrassed in public and avoid social interactions.
- Professional life: Loss of confidence can affect work performance and career opportunities.
- Intimate relationships: Hair loss can affect self-image and intimate life.
When treating hair loss, this psychological aspect must be considered. Psychological support can be essential to helping women overcome this ordeal. Online or in-person support groups can also be beneficial, allowing women to share their experiences and feel less isolated.
Solutions to Combat Hair Loss
Fortunately, today, there are many solutions to hair loss in women. The treatment choice will depend on the underlying cause and severity of the hair loss.
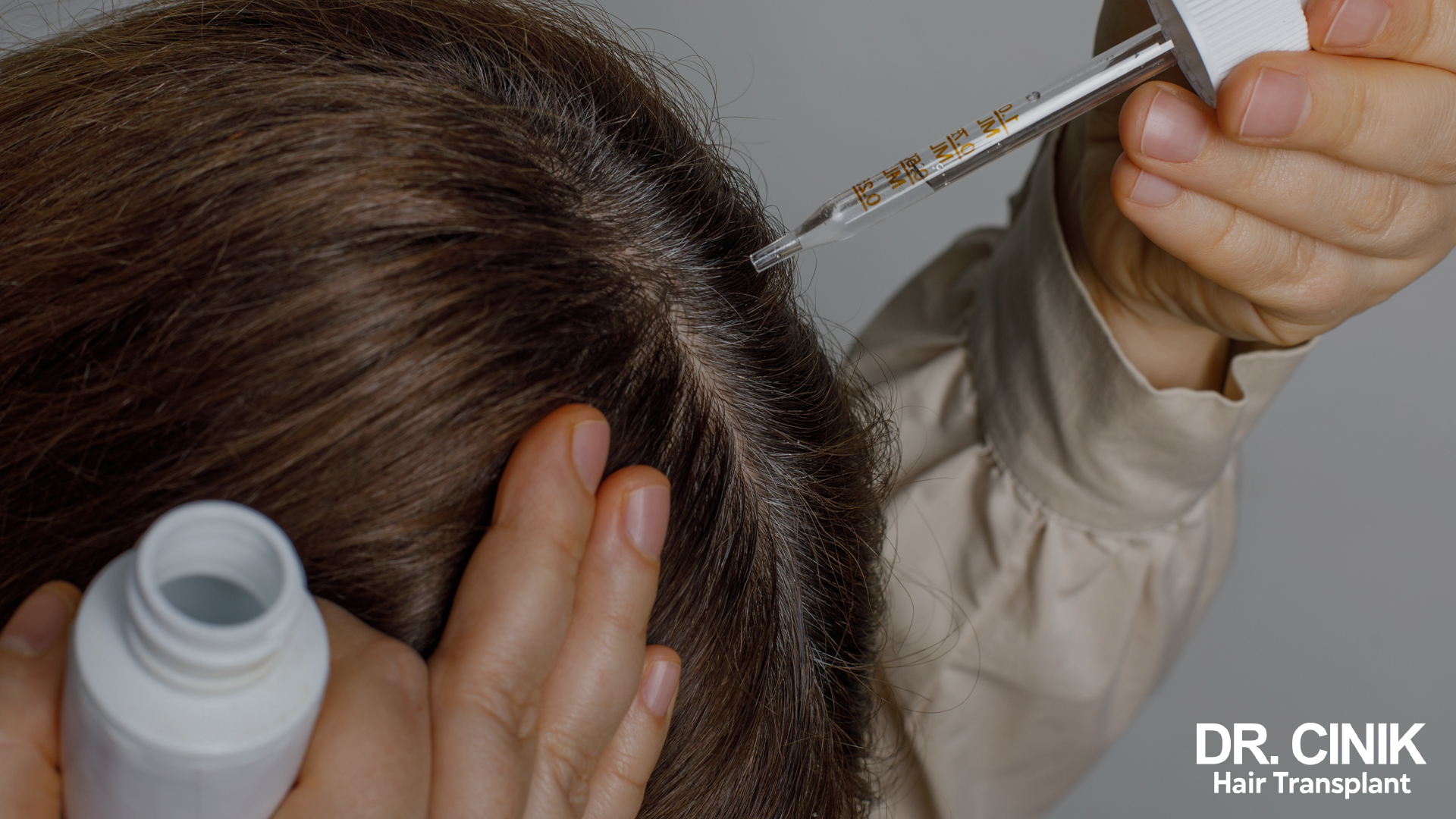
Drug Treatments
Minoxidil is the reference treatment for female androgenetic alopecia. Applied locally, it stimulates hair growth and slows hair loss. Available over the counter, it exists in a 2% or 5% solution for women. Results are usually visible after 3 to 6 months of regular use.
Other treatments, such as anti-androgens, may be prescribed in some cases. Finasteride, commonly used in men, is generally not recommended for women of childbearing age due to its potential effects on the foetus.

Food Supplements
Iron, zinc or vitamin supplements can be beneficial in cases of deficiencies. Biotin, in particular, is often recommended to strengthen hair and nails. However, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional before starting supplementation, as excess nutrients can be just as harmful as a deficiency.
Suitable Hair Care
The right hair products can help maintain a healthy scalp and strengthen existing hair. A dermatologist or trichologist may recommend specific shampoos and lotions. These products may contain ingredients such as keratin, panthenol, or plant extracts known for their strengthening properties.
It’s also important to adopt good hair practices:
- Avoid aggressive chemical treatments (colouring, straightening)
- Limit the use of heating tools (hair dryers, straighteners)
- Opt for a soft brush and avoid brushing wet hair
- Massage the scalp regularly to stimulate blood circulation

Camouflage Techniques
Powders, sprays, and hair fibres give the illusion of fuller hair for women wishing to camouflage mild to moderate hair loss. These products are particularly useful for masking thinning areas or visually widening the hair part.
Hair extensions and hairpieces can also be an option for women wanting to regain volume quickly. However, it’s important to choose quality products and apply them by a professional to avoid further damage to existing hair.
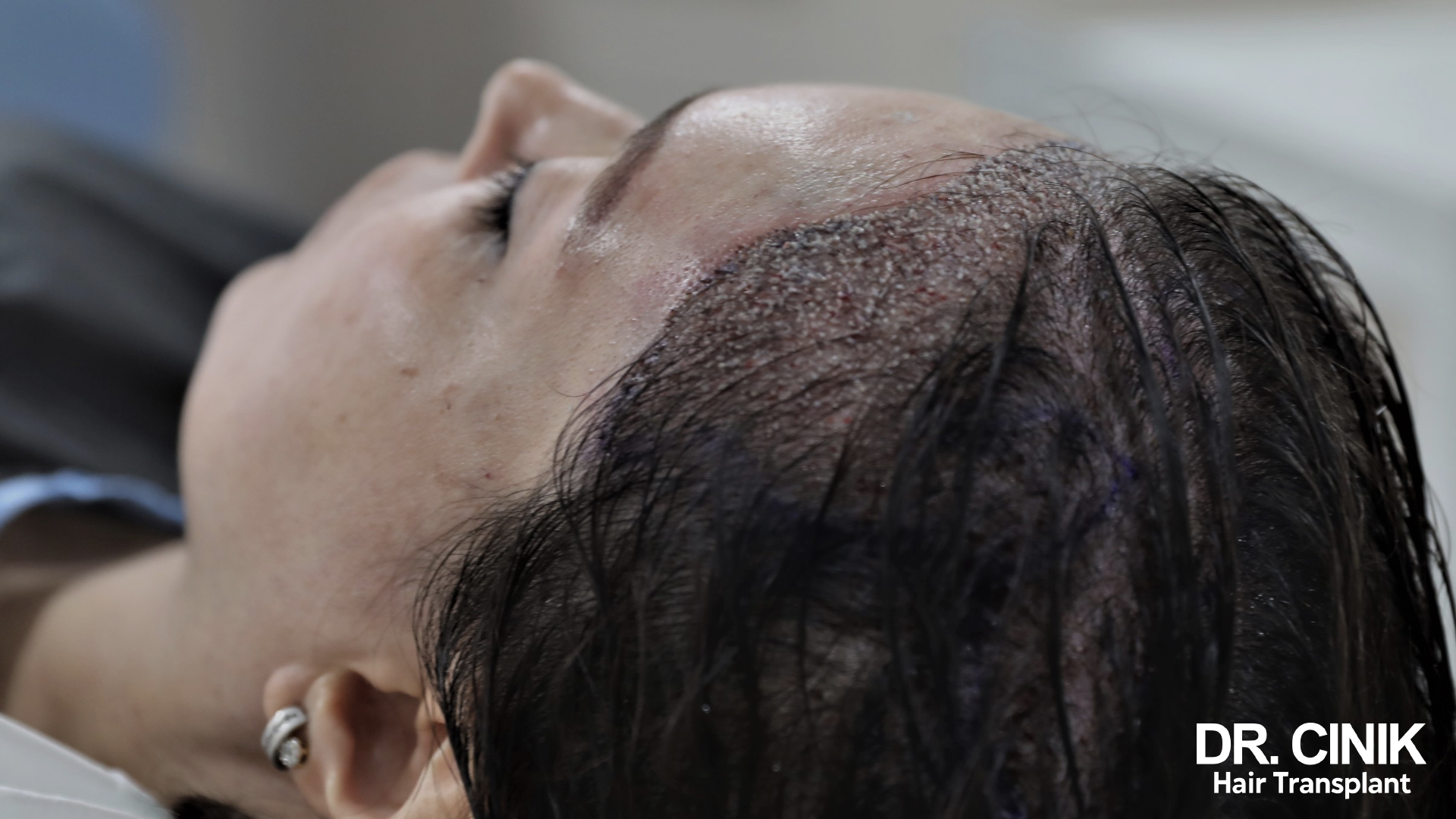

Hair Transplantation, A Lasting Solution
Hair transplantation can be considered for cases of more advanced hair loss. This technique, long reserved for men, is increasingly practised among women with excellent results. Dr. Cinik, a hair transplant expert in Istanbul, offers modern techniques such as FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) and DHI (Direct Hair Implantation), which are particularly suitable for women.
The FUE hair transplant technique involves taking individual follicular units from the donor area (usually the back of the head) and re-implantation into areas affected by hair loss. This method does not leave a linear scar and allows for faster recovery.
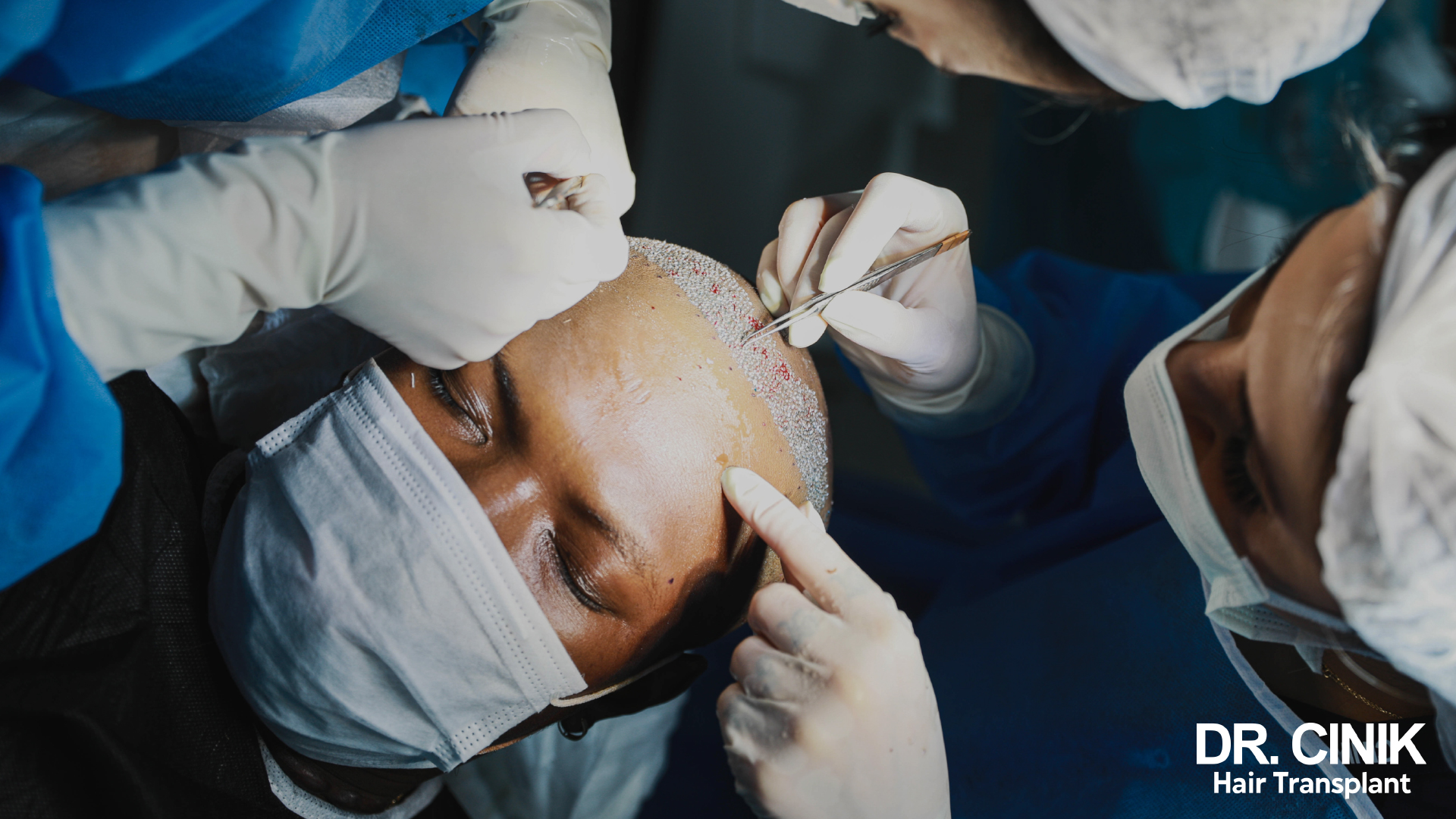
The DHI hair transplant technique is an advanced variant of FUE. It uses a special instrument called a Choi implanter that allows the grafts to be extracted and implanted in one step. This method provides increased precision and achieves higher density.
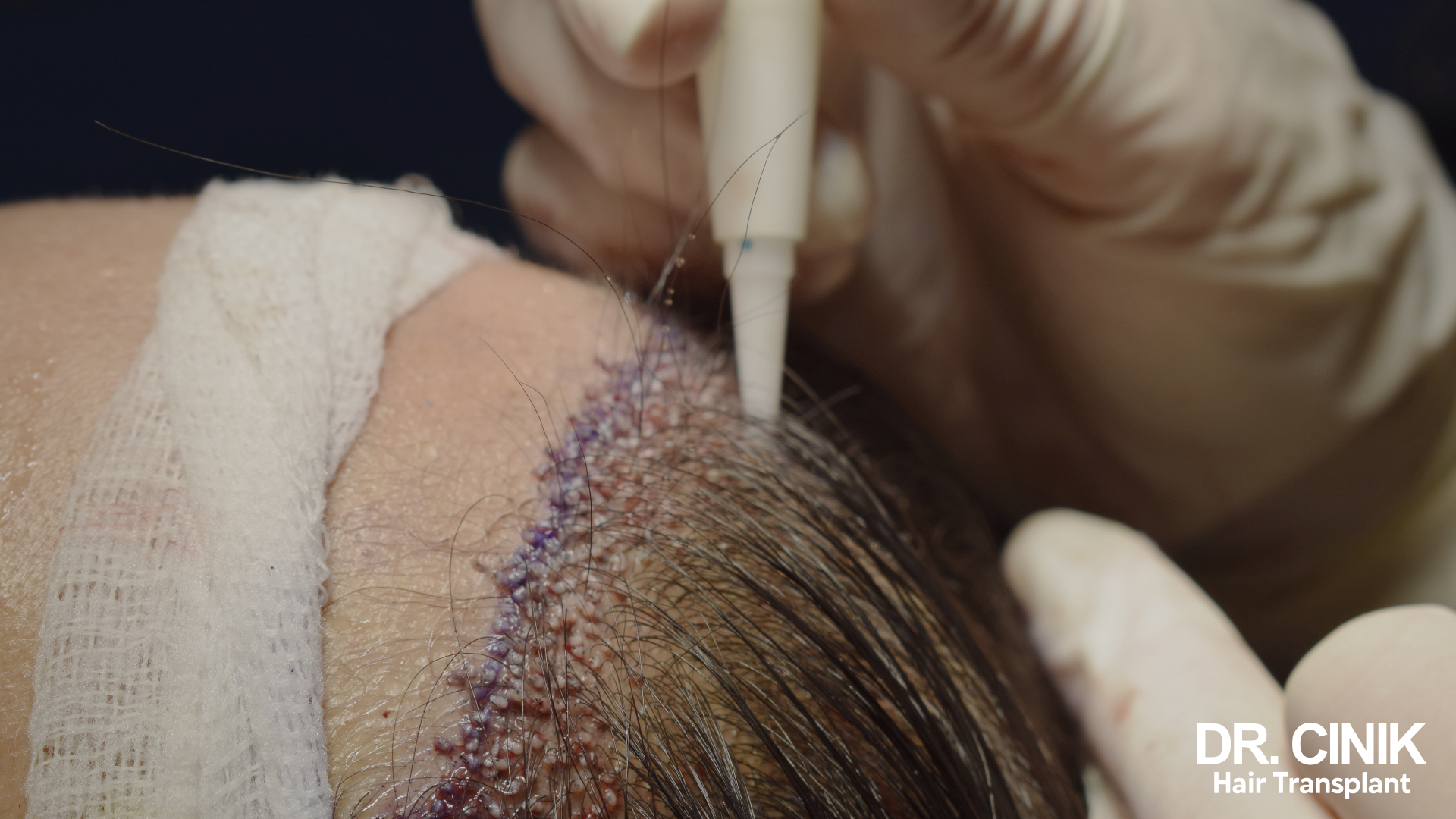
These techniques allow you to obtain natural and long-lasting results, giving women back dense hair and newfound confidence. Turkey, particularly Istanbul, has become a destination of choice for hair transplants, offering quality care at competitive prices.
It’s important to note that hair transplantation is not suitable for all types of hair loss. A consultation with a specialist like Dr Cinik is essential to determine if this option is appropriate.
PRP Treatment, An Effective Complement
PRP (platelet-rich plasma) treatment is often used in addition to hair transplantation or as a stand-alone treatment to stimulate hair growth. This technique involves injecting a concentrate of platelets obtained from the patient’s blood into the scalp 3.
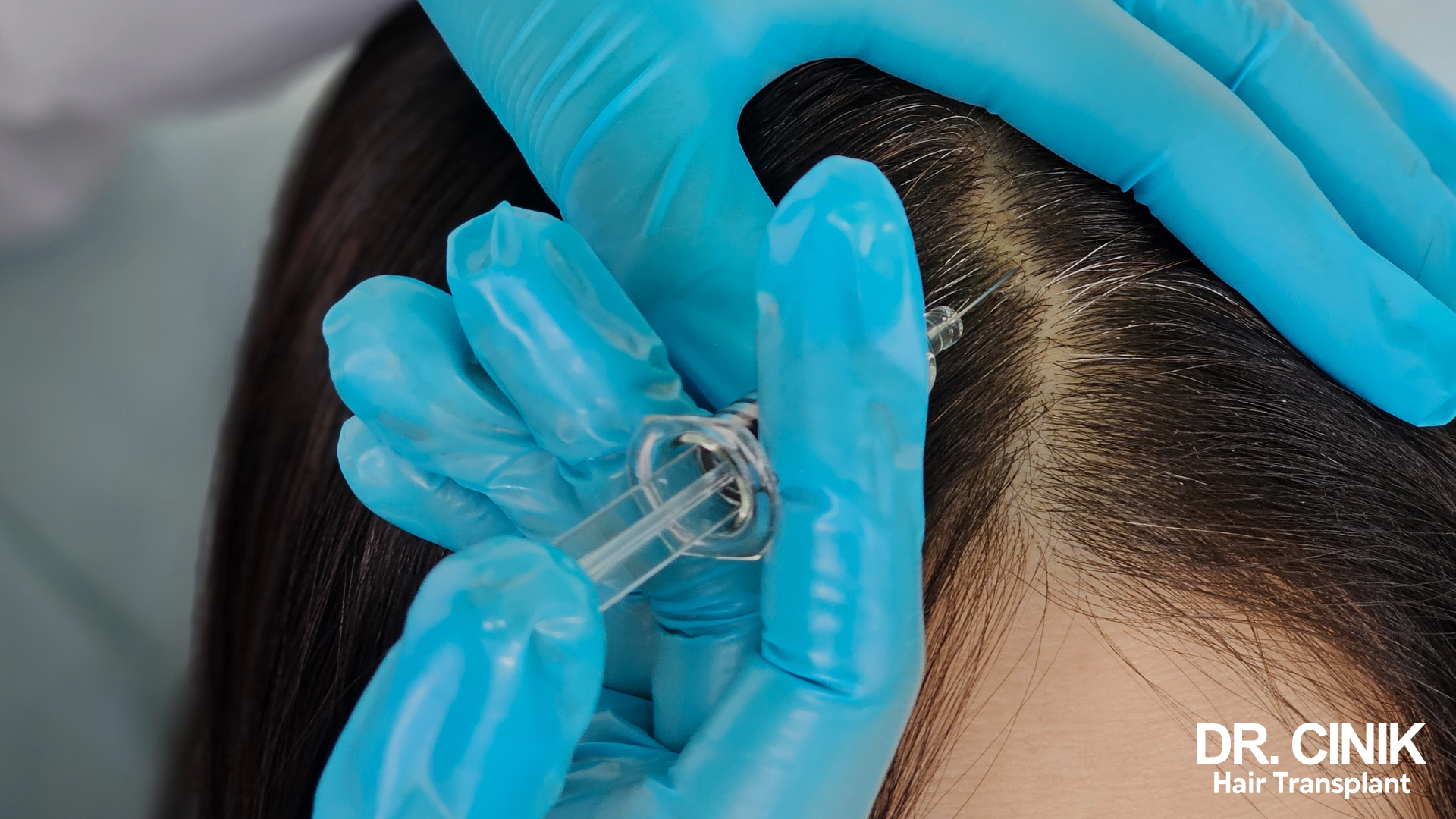
PRP is rich in growth factors that stimulate cell regeneration and promote hair growth. It may be particularly beneficial for women suffering from androgenetic alopecia or traction alopecia.
Prevention Rather Than Cure
Although some causes of hair loss are unavoidable, it’s possible to adopt habits that promote hair health:
A Balanced Diet
A diet rich in protein, iron and vitamins is essential for hair health. Particularly beneficial foods include:
- Lean proteins (chicken, fish, eggs)
- Leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale)
- Nuts and seeds
- Fruits rich in vitamin C (citrus fruits, berries)
- Foods rich in omega-3 (salmon, flax seeds)

Studies have shown that iron deficiency may be associated with hair loss, particularly in women 2. Iron is crucial in producing haemoglobin, which carries oxygen to cells, including hair follicles. Iron supplementation can benefit women with a proven deficiency, but it’s important to consult a doctor before starting any supplementation, as excess iron can be harmful.
Good Stress Management
Chronic stress can significantly impact hair health. Stress management techniques like meditation, yoga, or regular exercise can help maintain healthy hair. A study published in the journal PLoS One showed that chronic stress can affect hair growth by inhibiting the production of proteins needed for hair follicle formation 4.
Gentle Hair Care
Avoid harsh hair treatments and overly tight hairstyles that can damage the hair and scalp. Opt for gentle products suited to your hair type. Excessive use of chemicals, heat, or tight hairstyles can lead to hair loss called traction alopecia.

Regular Medical Monitoring
Regular check-ups can help quickly detect and treat any health problems affecting hair growth. This includes hormonal assessments and testing for nutritional deficiencies. For example, undiagnosed thyroid problems can contribute to hair loss and are easily detected with a simple blood test 1.
Promising New Approaches and Research
Research into hair loss and its treatments continues to advance. Here are some recent developments and promising avenues:
Stem Cell Therapy
Research is underway into using stem cells to regenerate hair follicles. A study published in the journal Nature showed that stem cells grown in the laboratory could be used to create new hair follicles in mice. Although this technique has not yet been tested in humans, it offers hope for future baldness treatment 3.
Prostaglandin D2 Inhibitors
Researchers have found that high levels of prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) in the scalp are associated with male pattern baldness. Drugs that block the PGD2 receptor are currently in development and may offer a new treatment option for androgenetic alopecia 3.

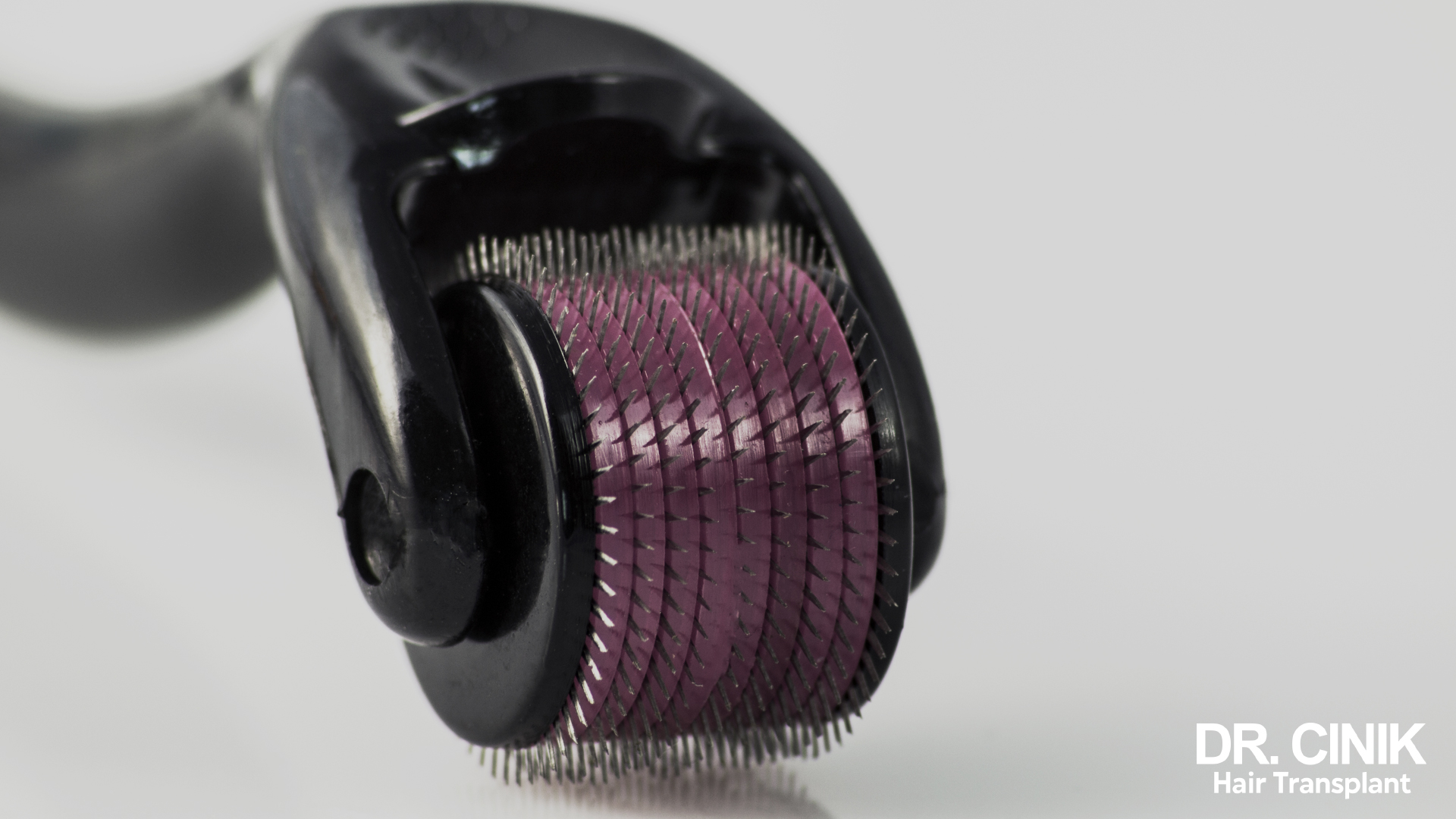
Microneedling
Microneedling is a technique that involves using a needle roller to create tiny punctures in the scalp’s skin. This method could improve the absorption of topical treatments and stimulate collagen production, thereby promoting hair growth. Preliminary studies have shown promising results, particularly when this technique is combined with treatments like minoxidil 3.

Conclusion
Hair loss in women is a complex problem with multiple origins. Although it can be a source of distress, it’s important to know that there are solutions. Whether through medical treatments, lifestyle changes or advanced surgical techniques like those proposed by Dr. Cinik, it’s possible to regain healthy, abundant hair.
Don’t hesitate to consult a health professional if you notice abnormal hair loss. An early diagnosis will allow more effective treatment and help you regain confidence in yourself and your image. Remember that you’re not alone in this problem and that with the right care and support, it’s possible to overcome this ordeal and regain hair that you’ll be proud of.
Research continues to advance in this area, providing new insights and hope for hair loss patients. A holistic approach combining a healthy diet, good stress management, appropriate hair care, and, if necessary, medical or surgical treatments can help maintain or regain healthy hair.
Remember that beauty is about more than just physical appearance. Although hair loss can be challenging to live with, it doesn’t define your worth. The important thing is to take care of your overall physical and mental health and surround yourself with people who support you on your journey.
For more information on the treatments available and a personalised consultation, don’t hesitate to contact Dr. Cinik. His expertise in hair transplantation and his personalised approach can help you find the solution best suited to your situation.
Sources
- Phillips TG, Slomiany WP, Allison R. Hair Loss: Common Causes and Treatment. Am Fam Physician. 2017;96(6):371-378. https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2017/0915/p371.html
- Guo EL, Katta R. Diet and hair loss: effects of nutrient deficiency and supplement use. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2017;7(1):1-10. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5315033/
- Fabbrocini G, Cantelli M, Masarà A, Annunziata MC, Marasca C, Cacciapuoti S. Female pattern hair loss: A clinical, pathophysiologic, and therapeutic review. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2018;4(4):203-211. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6322157/
- Asghar F, Shamim N, Farooque U, Sheikh H, Aqeel R. Telogen Effluvium: A Review of the Literature. Cureus. 2020;12(5):e8320. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7320655/




