Menopause Hair Loss: causes and possible treatments

Summary
Menopause is a phase that usually starts around 50 in a woman’s life. This phase is distinguished by a gradual decrease in the production of certain reproductive hormones, notably oestrogen and progesterone. These hormonal changes can provoke several effects, such as hot flashes, mood alterations, insomnia, weight increase, and even hair loss.
Post-Menopausal Alopecia: A Primary Reason for Hair Loss in Women

The Influence of Menopause-Related Hormonal Shifts
During menopause, there’s a drop in the levels of estrogen and progesterone, which in turn can cause hair loss. These two hormones are vital for promoting hair growth as they help maintain the strength of the hair follicles on the scalp. As their production decreases, it leads to thinner hair that grows more slowly. This condition is commonly referred to as post-menopausal alopecia.
Deficiencies
Hair loss and a lack of shine can often result from a deficiency in vitamin D. In such cases, the hair follicles become weaker, and hair growth may be impaired. Similarly, a lack of iron can lead to hair loss, given that iron is fundamental for the production of blood – a necessary element for hair growth. If blood supply is compromised, hair loss is often the consequence.

Zinc is another vital nutrient, essential for synthesising keratin and collagen, substances integral to the health and texture of hair. If zinc levels are insufficient, there may be an increased risk of alopecia and premature hair ageing. B vitamins are also crucial as they strengthen hair and promote optimal hair health. They help stimulate keratin production, a protein vital for hair and nail formation.
Environmental factors
Several factors can lead to a decline in hair quality. One prominent factor is a lifestyle marked by high stress. In such situations, hormonal imbalances can occur, including reduced oestrogen production. This may result in mood fluctuations, anxiety, depression, and even hair loss.
Overusing heat stylings tools, like straightening irons and hair dryers, can also cause significant hair damage, leading to hair breakage and loss. Similarly, overexposure to the sun can negatively affect hair health and strength.
Symptoms of postmenopausal alopecia, when to worry?
Hair loss following menopause tends to occur gradually, characterised by a slow hairline recession at a rate of about one millimetre per month. This hair loss can also affect other areas, including the eyelashes and eyebrows. This condition is generally irreversible and is often associated with the emergence of red pimples in the area where the hairline is receding.
How common is hair loss during the menopause?
Hair loss or alopecia is not a rare occurrence after menopause. It affects more than two-thirds of women during this phase. The degree of post-menopausal alopecia tends to be determined by genetic predisposition. If a close relative has dealt with this issue during menopause, there’s a strong possibility that other family members may also encounter the same situation.
What treatments are available for post-menopausal alopecia?
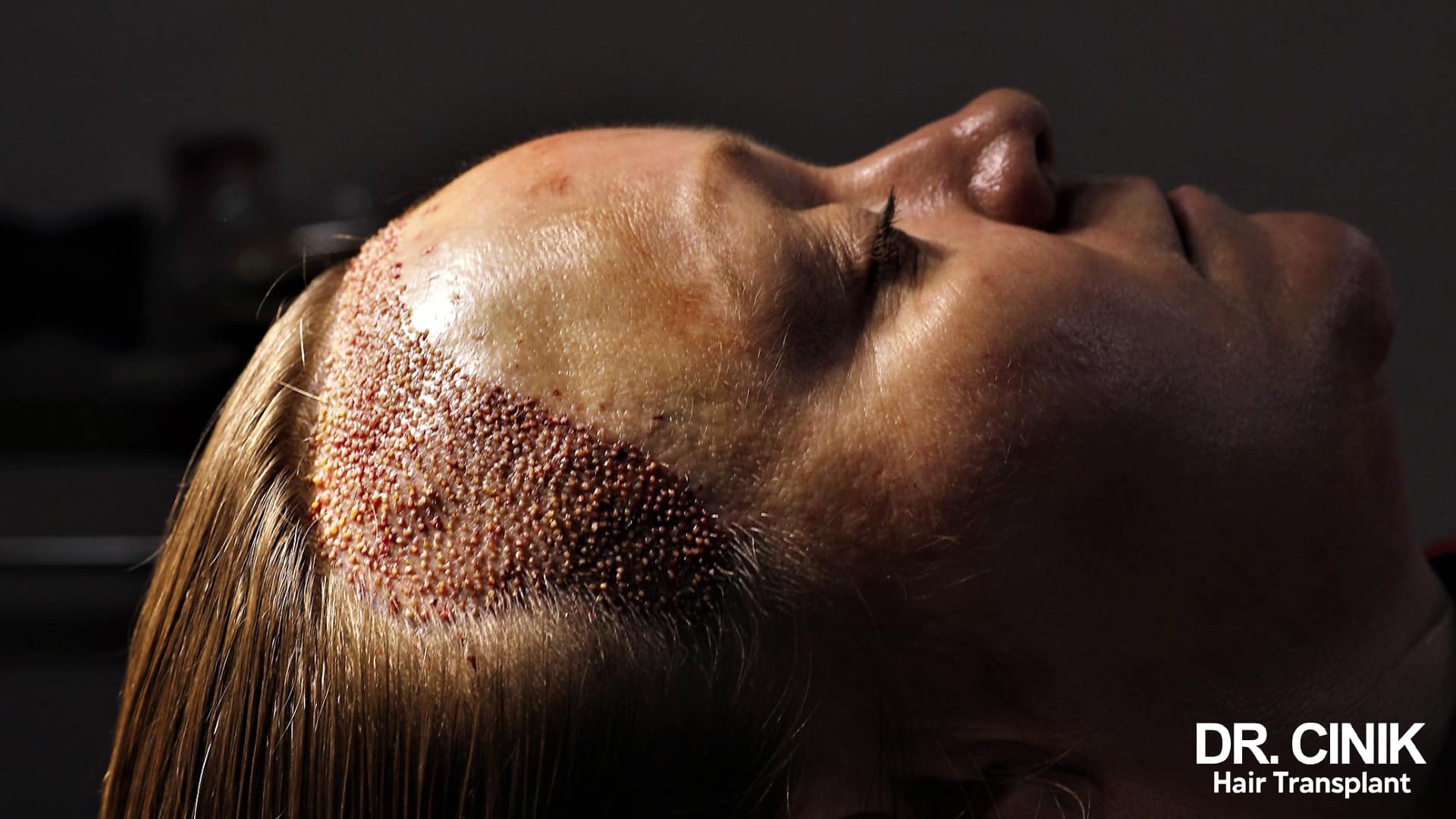
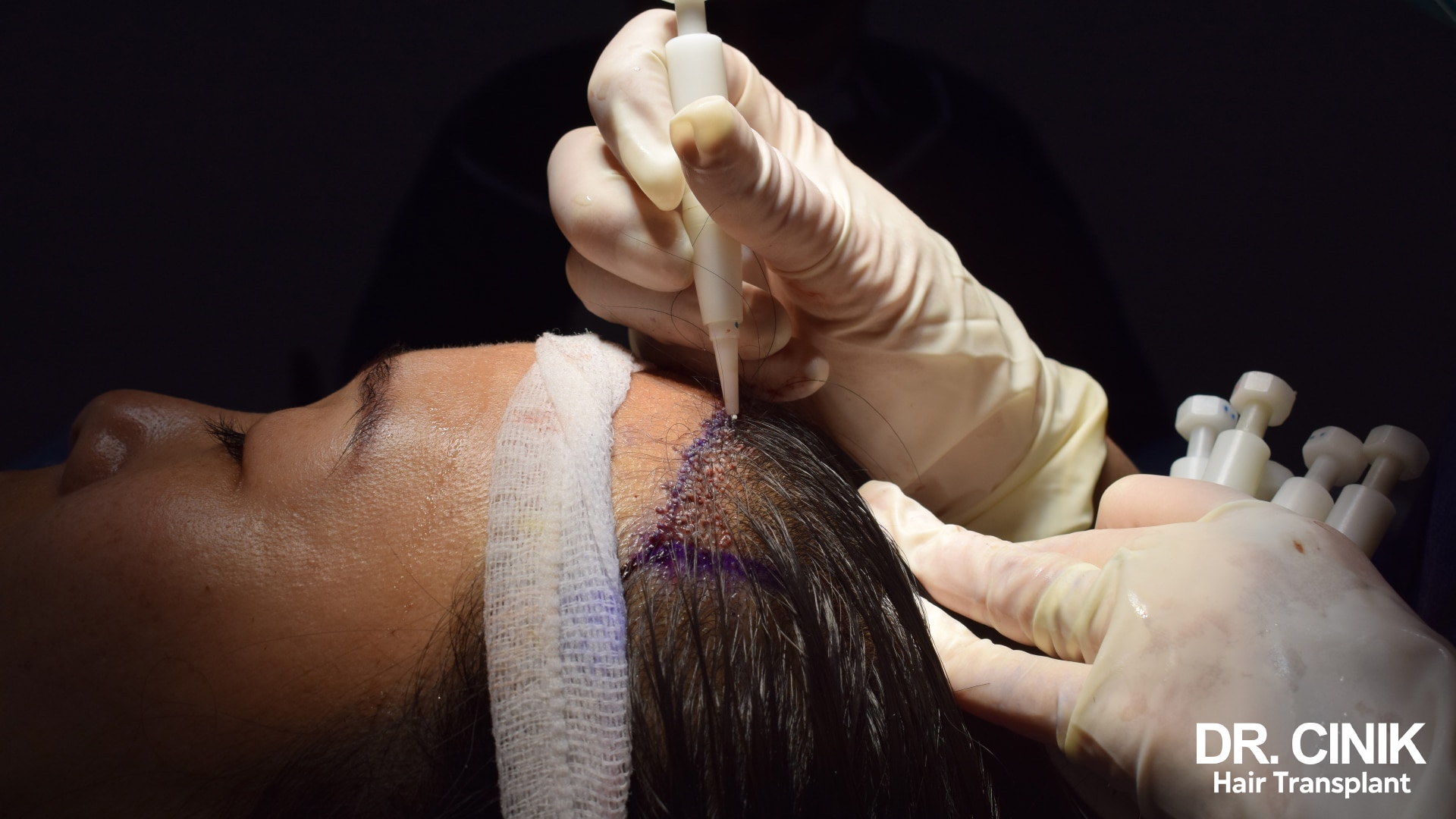
DHI hair transplantation
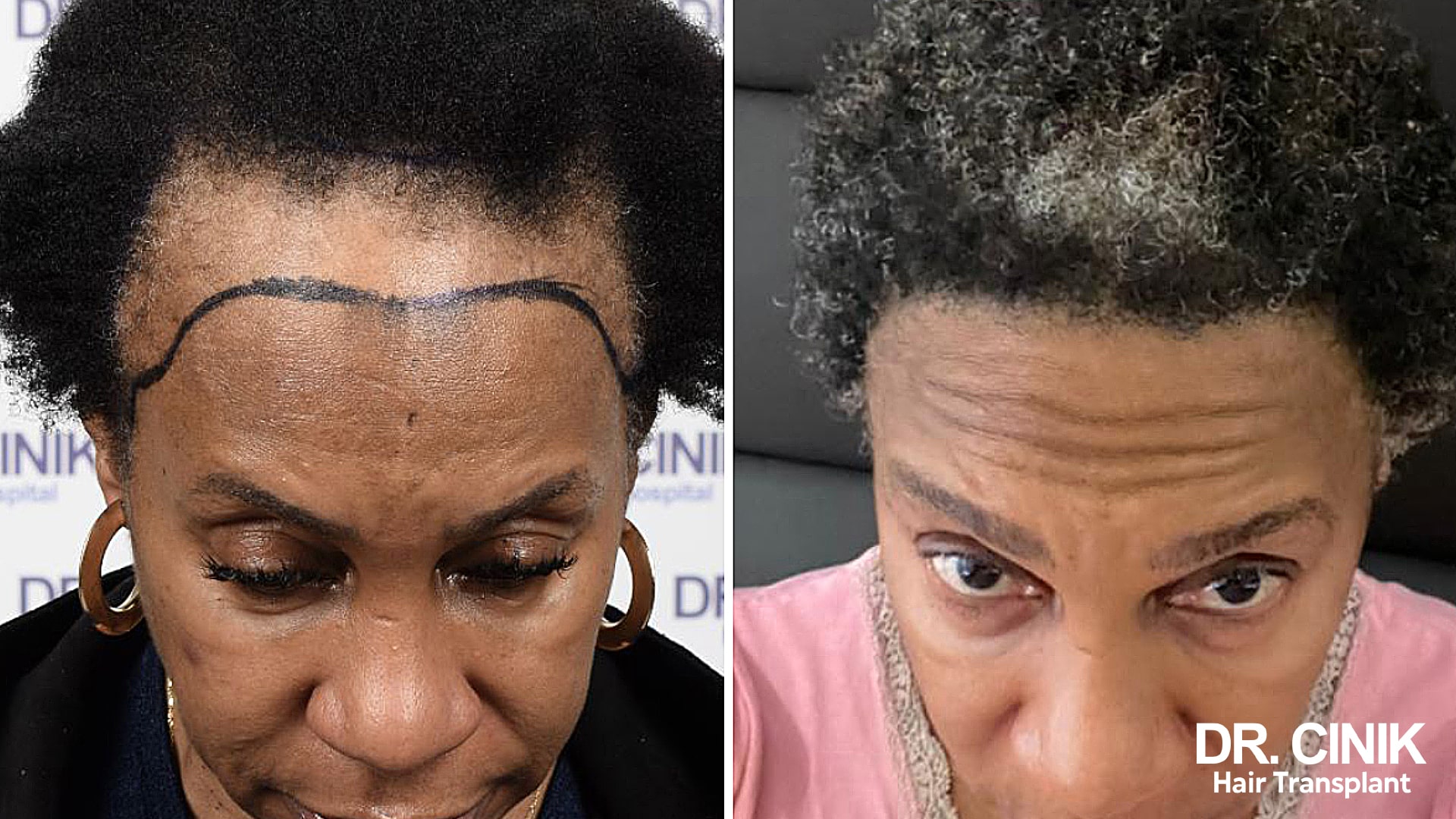
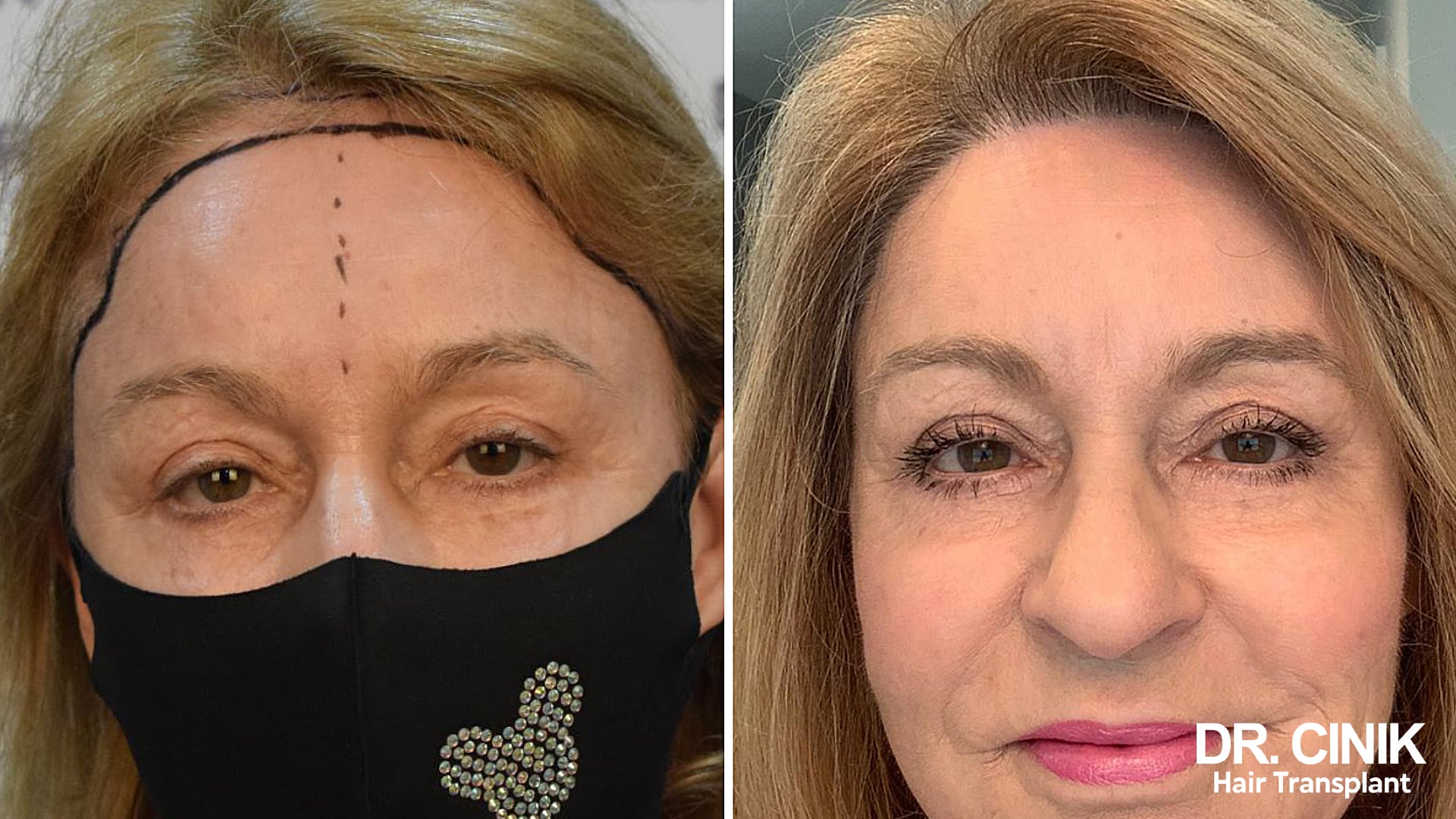
Among the various techniques available for hair transplant for women, the Direct Hair Implantation (DHI) method stands out as one of the most advanced and frequently used, especially when addressing post-menopausal alopecia. This technique, derivative of the Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) method, notably uses a CHOI Implanter Pen instead of a blade for the grafting process. The DHI method allows for each hair graft to be implanted with remarkable precision, thereby ensuring a natural-looking outcome. In some instances, this method allows for hair transplantation with only partial shaving. Moreover, this approach doesn’t result in noticeable scars in either the donor or recipient area. This technique demands significant skill from the hair transplant surgeon, as they need to implant the hair follicles at a precise angle, direction, depth, and density to recreate the patient’s natural hair growth pattern. For an affordable yet expert hair transplant in Turkey, consider reaching out to Dr Cinik and benefit from his extensive experience and expertise.
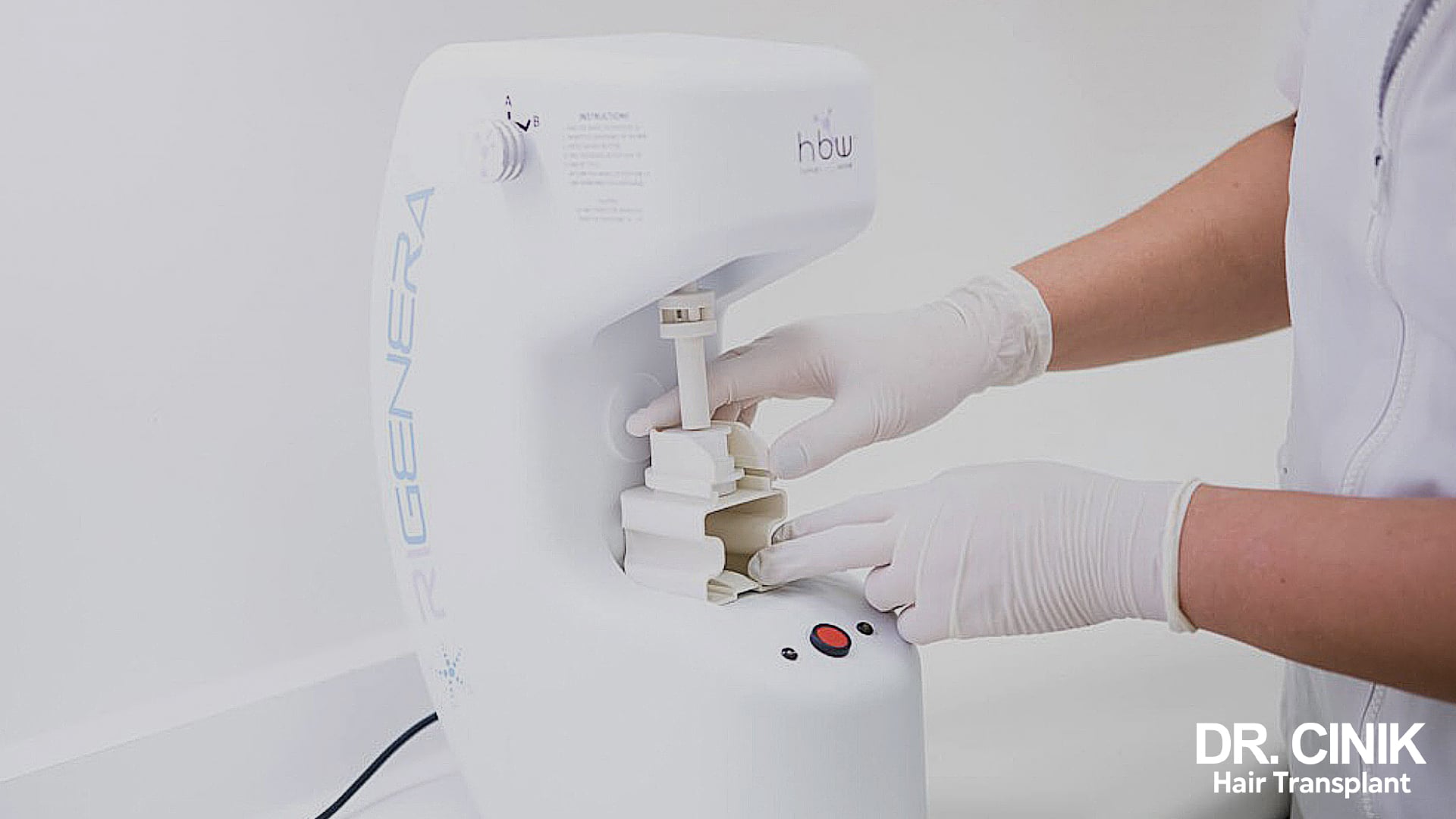
Regenera Activa hair mesograft
The innovative Regenera Activa stem cells hair transplant is designed to normalise hair loss and stimulate hair growth. It uses mesenchymal stem cells, which are extracted from the scalp. These cells will improve the loss of irrigation of the grafts.
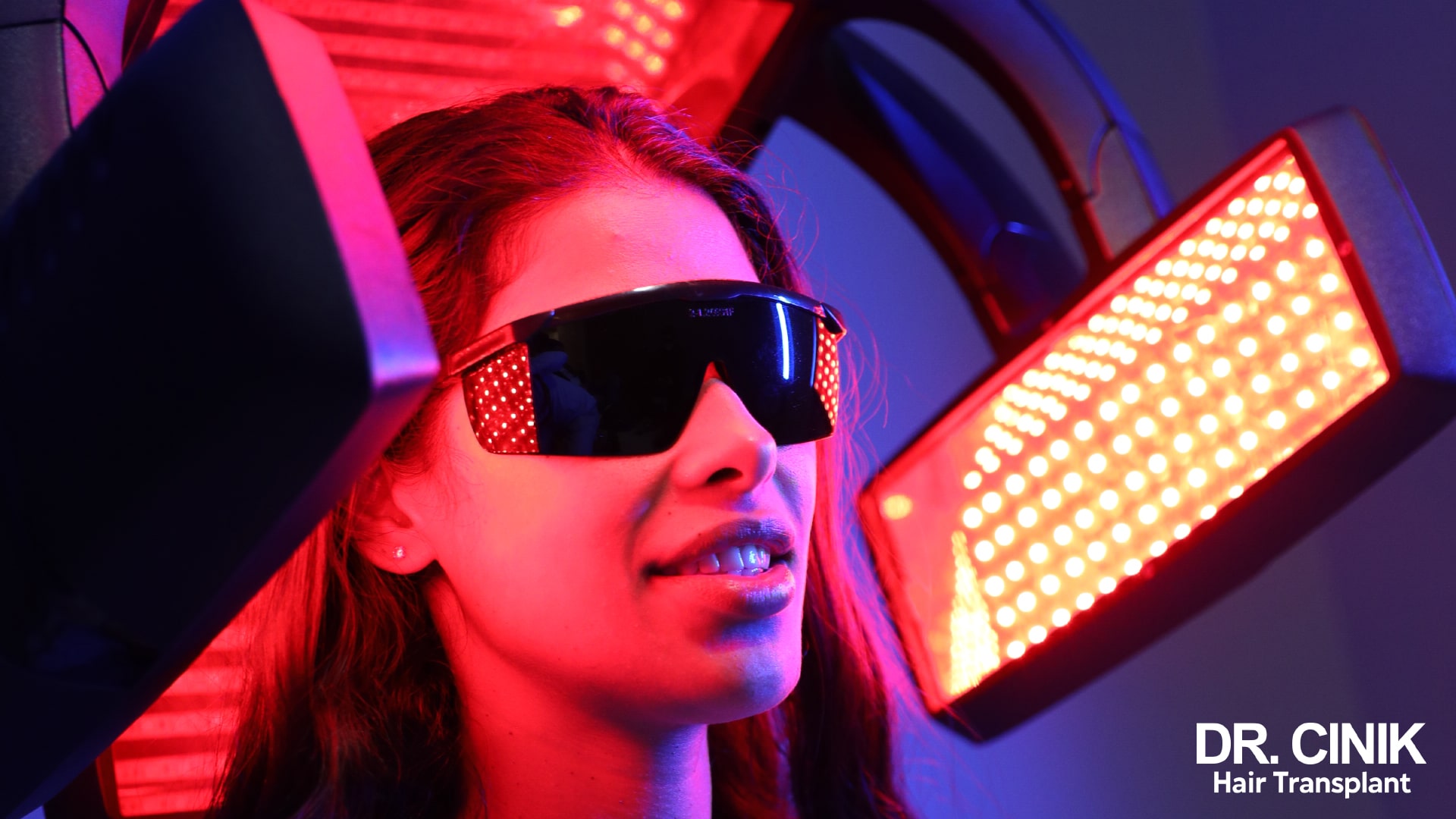
Laser hair treatment
Laser hair treatment can be used to remedy the problem of hair volume loss. The use of a low-intensity laser characterises this method, the purpose of which is to promote cell activation in the hair follicles. Based on the principle of photobiomodulation, the method reproduces the photosynthesis model of plants. Photobiomodulation provides the energy necessary for the hair follicles to regenerate.

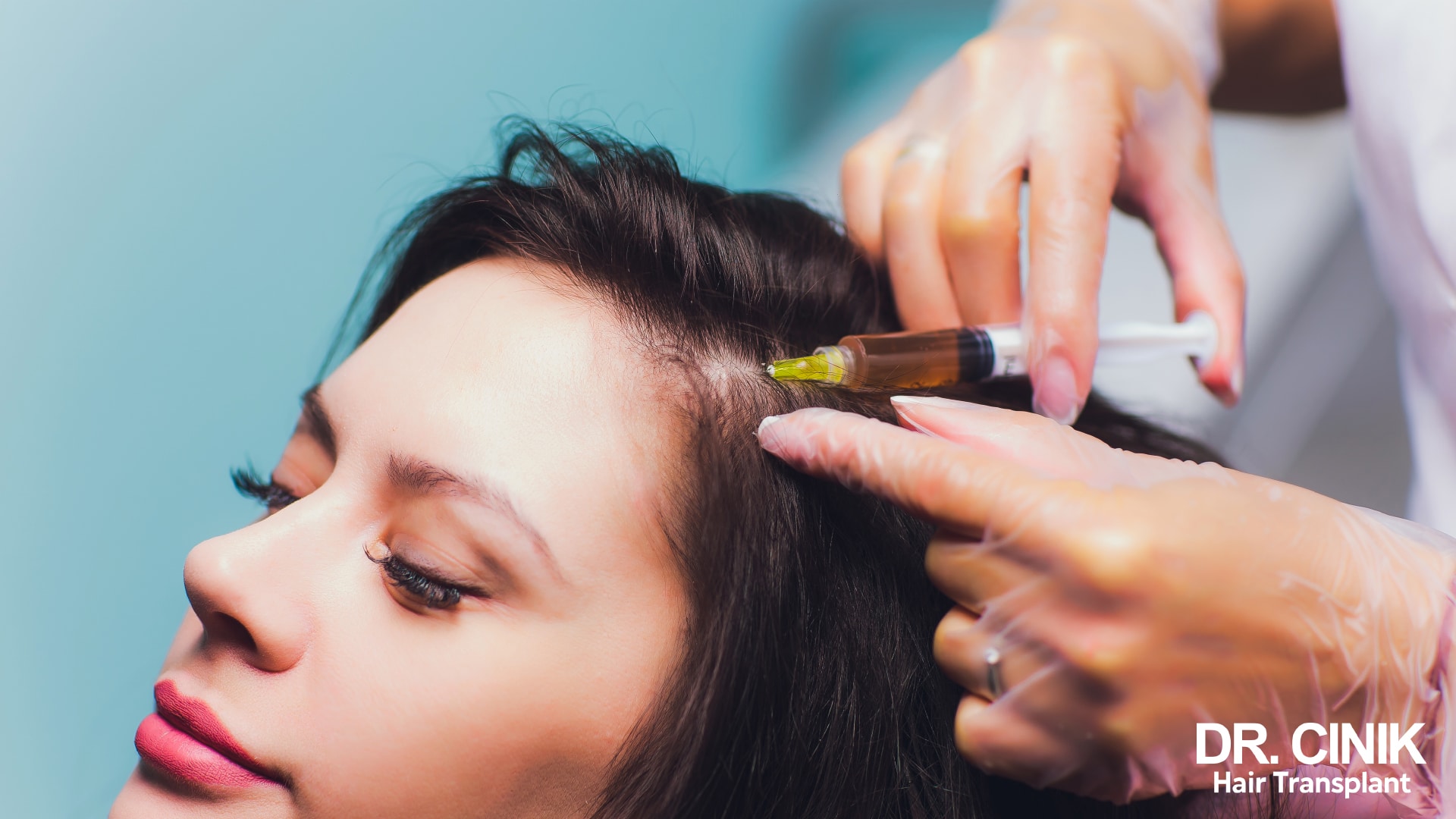
The PRP (Platelet Rich Plasma) injection method
To support the hair growth process, PRP injections can be used on the scalp. This technique is a non-invasive therapy that injects blood platelets into the scalp. This results in the regeneration of hair follicle cells and the nourishment of multipotent stem cells. The microcirculation of the scalp can also be activated.

Tips to prevent or slow down postmenopausal alopecia
There are several strategies to can employ to minimise the effects of post-menopausal alopecia.. Opting for a shorter, layered hairstyle, can create an illusion of thicker, more voluminous hair.
Stress management is also essential, and engaging in activities like yoga can be beneficial in achieving this. Additionally, maintaining a balanced, low-fat diet is advisable for managing post-menopausal alopecia.

Food and food supplements that can help strengthen hair
Protein-rich foods are beneficial in limiting hair loss. Hair is largely composed of keratin, a protein formed from amino acids in the diet. Beans, fish, eggs, milk and red meat provide sufficient protein.
Vitamin C is also essential as it helps to remove accumulated minerals. The hair then benefits from more effective hydration. Vitamin A is also very important, as it helps to moisturise the hair and reduce breakage. Its role is to accelerate cell regeneration.
Appropriate hair care
In addition to vitamins, hair products can counteract hair loss. Some products are specifically designed to increase hair texture and provide protection against hair breakage. These treatments are usually available in several variants to allow adaptation to the hair colour.
The case of postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia or PFFA
Postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia is a dermatological condition known as lichen planopilaris. While this disease primarily impacts post-menopausal women, it can also occur in younger women and, in some cases, men.




