Scalp psoriasis: understanding and managing this skin disease
Sommaire
Scalp psoriasis is a specific form of psoriasis that affects the skin on the head. This chronic inflammatory disease is characterised by the appearance of red patches covered with white or silver scales. Contrary to popular belief, psoriasis is not a simple skin condition but a complex autoimmune disease that can significantly impact the quality of life of those affected.
What is scalp psoriasis?
Scalp psoriasis is a manifestation of psoriasis that specifically affects the skin of the head. In this condition, the immune system goes into overdrive and accelerates the renewal of skin cells. Instead of renewing themselves every 28 to 30 days, as is normally the case, skin cells regenerate in just 3 to 7 days. This acceleration causes an accumulation of dead cells on the surface of the scalp, thus forming the plaques characteristic of psoriasis.
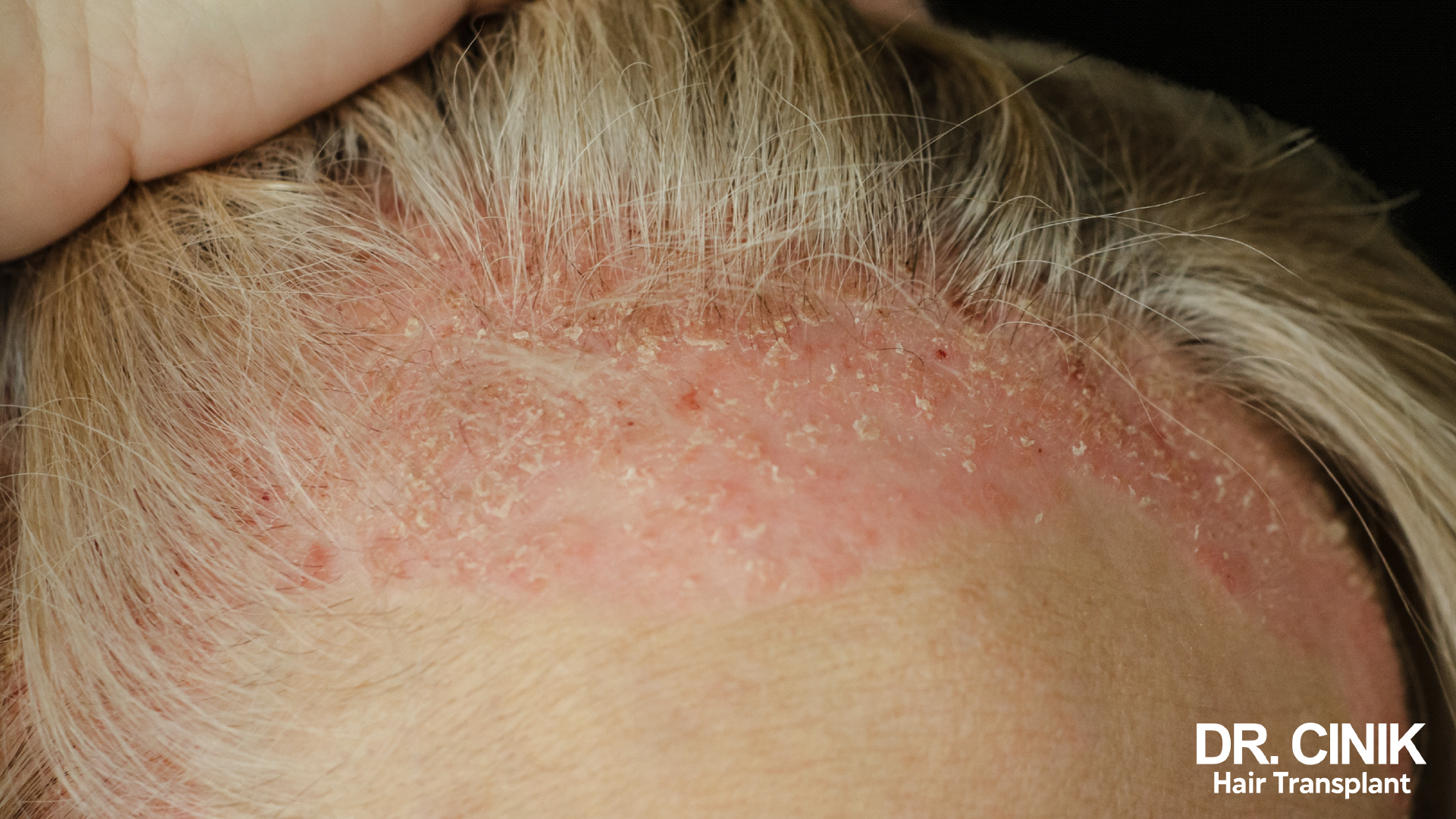
It is important to emphasise that scalp psoriasis is not contagious. This clarification is essential because many people with psoriasis unfortunately suffer from the stigma associated with their condition.
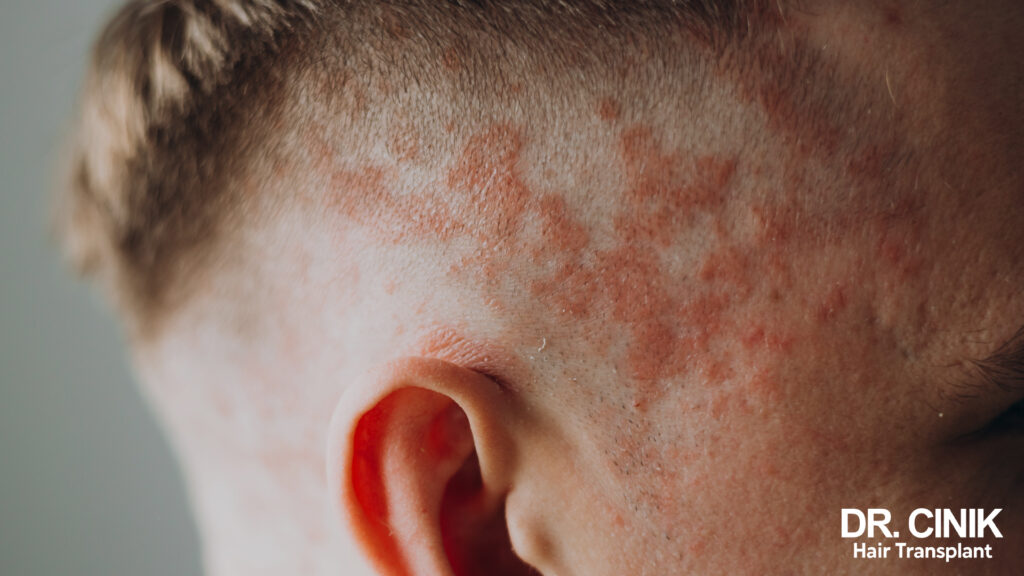
Symptoms of scalp psoriasis
The most common signs of scalp psoriasis include:
- Well-demarcated red patches on the scalp
- White or silver scales that come off easily
- Intense itching, sometimes accompanied by burning sensations
- Dry scalp
- In some cases, slight temporary hair loss
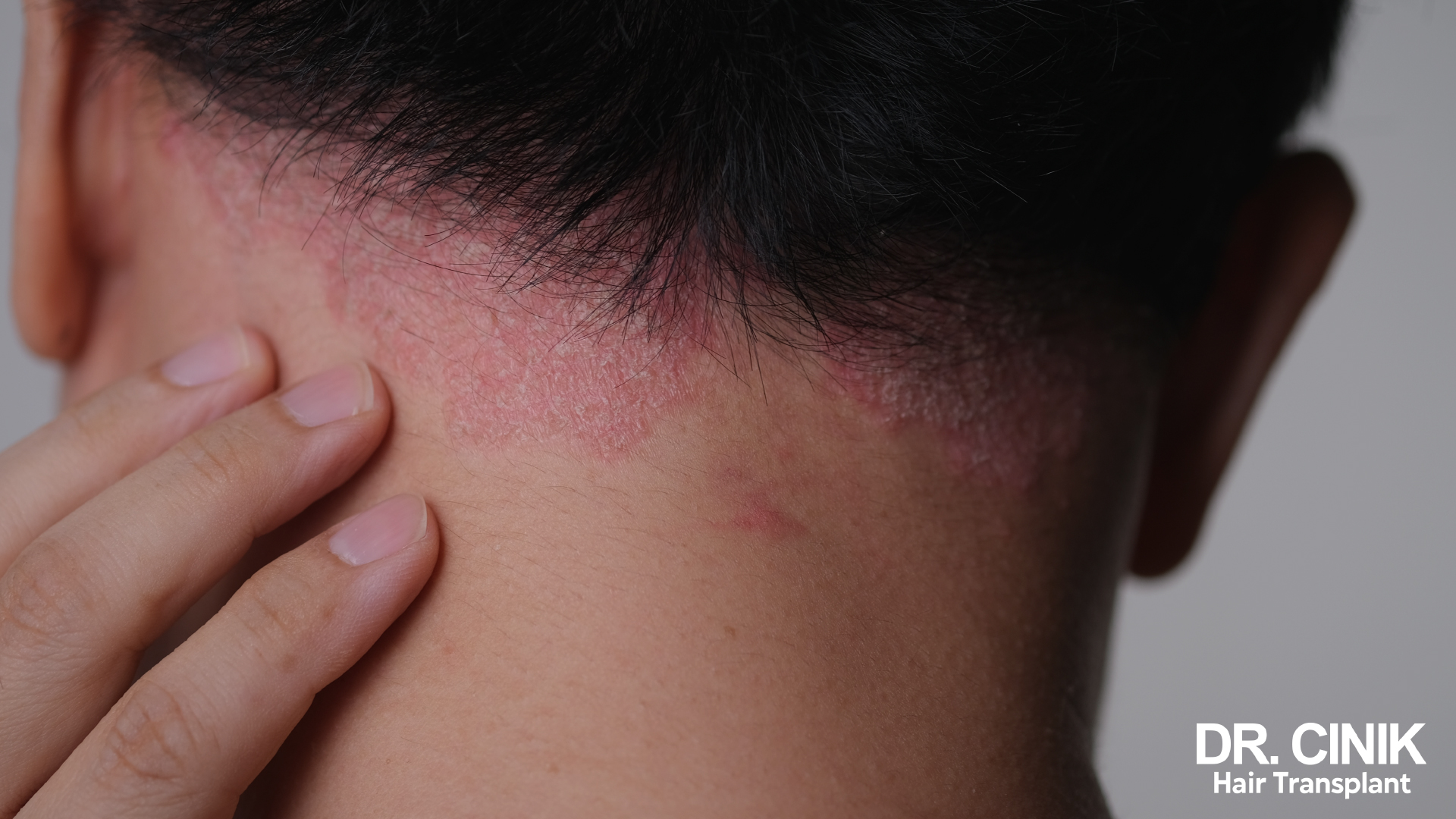
Scalp psoriasis appears around the edge of the forehead, the back of the neck and behind the ears. In more severe cases, it can form a “psoriatic helmet”, covering the entire scalp.
Causes of scalp psoriasis
Although the exact mechanisms of psoriasis are not yet fully understood, several factors contribute to its appearance:
- Genetic predisposition: Psoriasis has a hereditary component. Recent studies have identified several genes involved in psoriasis, including the HLA-Cw6 gene present in approximately 60% of affected people.
- Immune dysfunction: In psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, causing inflammation and accelerated cell proliferation. T lymphocytes play a key role in this inflammatory process.
- Environmental factors: Certain external elements, such as stress, infections, certain medications, or even skin trauma, can trigger or worsen psoriasis.
- Hormones: Hormonal changes, particularly during puberty, pregnancy or menopause, can influence the appearance or progression of psoriasis.
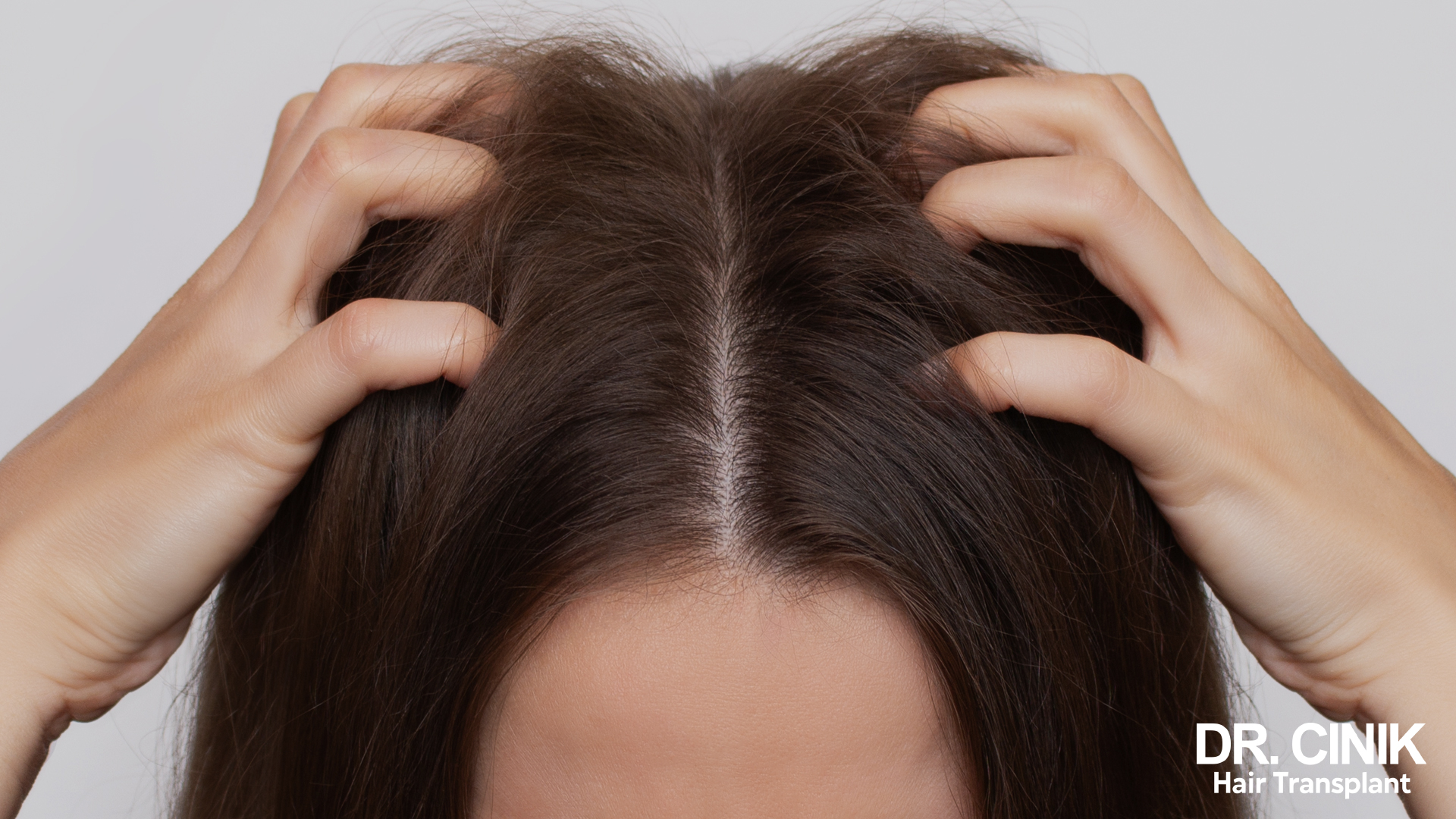

The link between scalp psoriasis and hair loss
Scalp psoriasis can indirectly contribute to temporary hair loss in several ways:
- Excessive scratching: Intense itching can lead to scratching, which can damage hair follicles and cause hair loss.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation of the scalp can disrupt the hair growth cycle. Pro-inflammatory cytokines produced during psoriasis flare-ups can affect the normal function of hair follicles.
- Aggressive treatments: Certain treatments used for psoriasis, if misapplied, can weaken the hair.
It is important to emphasise that this hair loss is usually temporary. Once psoriasis is under control, hair tends to grow back normally. However, in severe and chronic psoriasis cases, scarring alopecia can sometimes develop, leading to permanent hair loss in certain areas.
Treatments for scalp psoriasis
There are many options for treating scalp psoriasis. The main goals are to reduce inflammation, relieve symptoms, and slow the excessive proliferation of skin cells.
- Topical treatments: Corticosteroids are often the first treatment prescribed. They reduce inflammation and quickly relieve symptoms. Vitamin D analogues, such as calcipotriol, help slow the growth of skin cells and are often used in combination with corticosteroids for increased effectiveness.
- Medicated shampoos: Coal tar shampoos have long been used to treat psoriasis. Salicylic acid shampoos help remove flakes, preparing the scalp for further treatments.
- Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to UVB rays can help reduce inflammation and slow cell growth. A study showed that UVA1 phototherapy may be more effective than narrow-spectrum UVB for treating scalp psoriasis, with faster improvement in symptoms and quality of life.
- Systemic treatments: Oral or injectable medications may be prescribed for severe cases. Biotherapies, such as TNF-α inhibitors or anti-interleukins, specifically target the molecules involved in the inflammation of psoriasis.
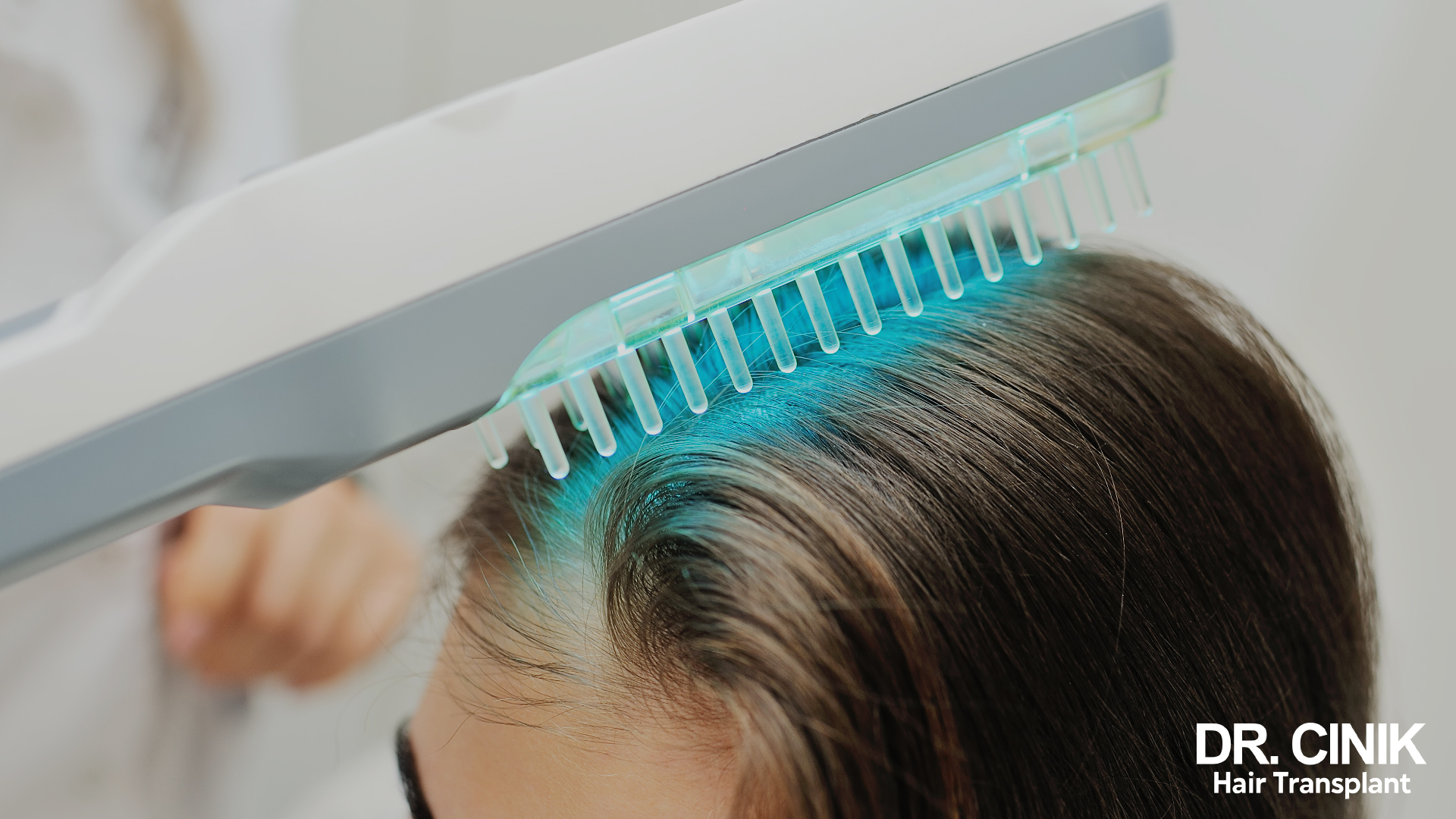

A recent study showed that tofacitinib, a JAK inhibitor, may effectively treat scalp psoriasis, body psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
Consult a dermatologist to obtain an accurate diagnosis and a treatment plan tailored to your situation.
Hair transplantation and scalp psoriasis
A hair transplant is generally not recommended as a direct treatment for scalp psoriasis. However, in certain specific cases, a hair transplant may be considered:
- When psoriasis is well controlled and in remission for a prolonged period.
- To treat permanent hair loss due to scarring alopecia caused by severe psoriasis.
- To restore hair in areas not affected by psoriasis.
A case study published in the Journal of Hair Transplant Forum International showed that hair transplantation can be performed successfully in patients with psoriasis, provided the disease is well-controlled during the procedure. However, the authors emphasise the importance of careful assessment and careful follow-up to prevent any exacerbation of psoriasis after transplantation.
If you are considering a hair transplant despite a history of scalp psoriasis, it is crucial to consult an experienced specialist. Experts like Dr Cinik, a surgeon specialising in hair transplantation, can evaluate your case and determine if a transplant is appropriate and safe for you.
Living with scalp psoriasis: practical advice
Here are some tips to better manage scalp psoriasis daily:
- Maintain good hair hygiene using gentle shampoos specially formulated for sensitive scalps.
- Moisturise your scalp regularly with suitable oils or creams.
- Identify and avoid the triggers for your psoriasis flare-ups.
- Manage your stress through relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in omega-3 and antioxidants.
- Be gentle with your hair by avoiding tight styles and harsh chemical treatments.
- Inform your hairdresser of your condition so that he can adapt his actions and products.

Innovations in the treatment of scalp psoriasis
Research on psoriasis is constantly progressing, offering new treatment perspectives:
- New targeted biotherapies, such as IL-23 or IL-17 inhibitors, are showing promising results.
- Research into gene therapy is underway to target genes involved in psoriasis specifically.
- The study of the scalp microbiome opens new avenues for understanding and treating psoriasis.
- Using nanotechnology to deliver drugs more efficiently is a promising avenue of research.

Conclusion
Scalp psoriasis is a chronic condition that can be difficult to live with. Still, with continued medical advances and a better understanding of the disease, treatment options are becoming more effective. Whether you opt for conventional treatments or consider solutions like hair transplantation, the main thing is maintaining hope. Appropriate medical monitoring and a comprehensive approach to your health can effectively control scalp psoriasis and significantly improve your quality of life.
Sources :
- Vaggu, A. K., et al. (2012). Should hair transplantation be performed in psoriasis? Hair Transplant Forum International, 22(4), 124-126. https://www.ishrs-htforum.org/content/22/4/124
- Todberg, T., et al. (2020). Improvement of Psoriasis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and Alopecia Universalis during Treatment with Tofacitinib: A Case Report. Case Reports in Dermatology, 12(2), 150-154. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7506247/
- Mosca, M., et al. (2021). Scalp Psoriasis: A Literature Review of Effective Therapies and Updated Recommendations for Practical Management. Dermatology and Therapy, 11(3), 769-797. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8163911/
Zhou, J., et al. (2018). Efficacy assessment of UVA1 and narrowband UVB for treatment of scalp psoriasis. Lasers in Medical Science, 33(9), 1979-1982. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29915975/



