Crown hair transplant: principles, techniques, prices and results
Sommaire
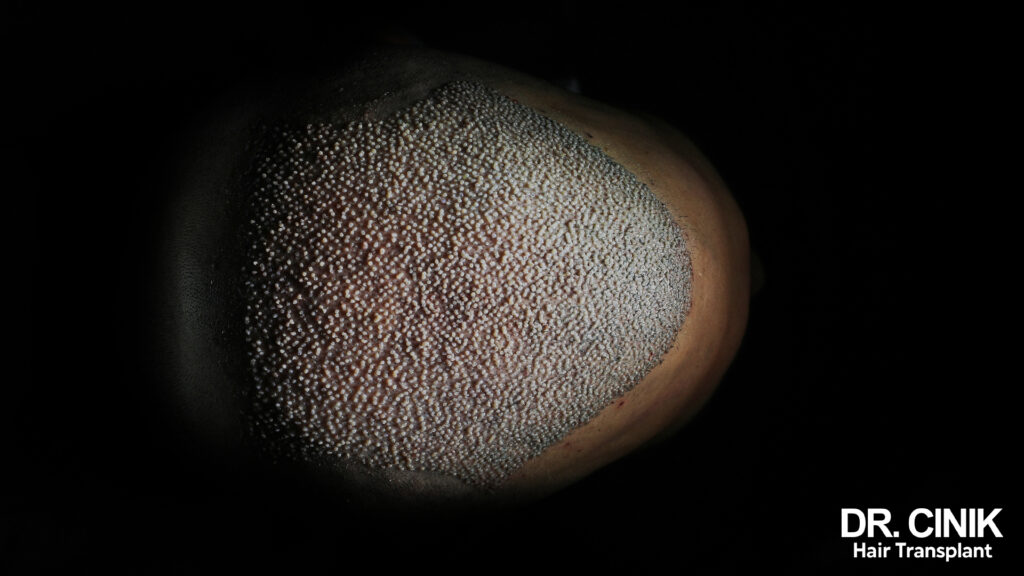
The crown, located at the top of the head, is a crucial area that greatly influences a hairstyle’s overall appearance and balance. It’s a highly visible spot, especially when seen from above, making it a key factor in achieving a harmonious and attractive look. However, many people experience hair loss or thinning in the crown region, which can be a source of self-consciousness and frustration. This is where a crown hair transplant is a specialised procedure designed to restore volume and density to the crown area.
By targeting hair restoration efforts on the crown, individuals can enjoy a more youthful, fuller head of hair that looks natural and complements their facial features. A crown hair transplant can be a game-changer for those seeking to improve their appearance and boost their self-esteem.

Causes of crown hair loss
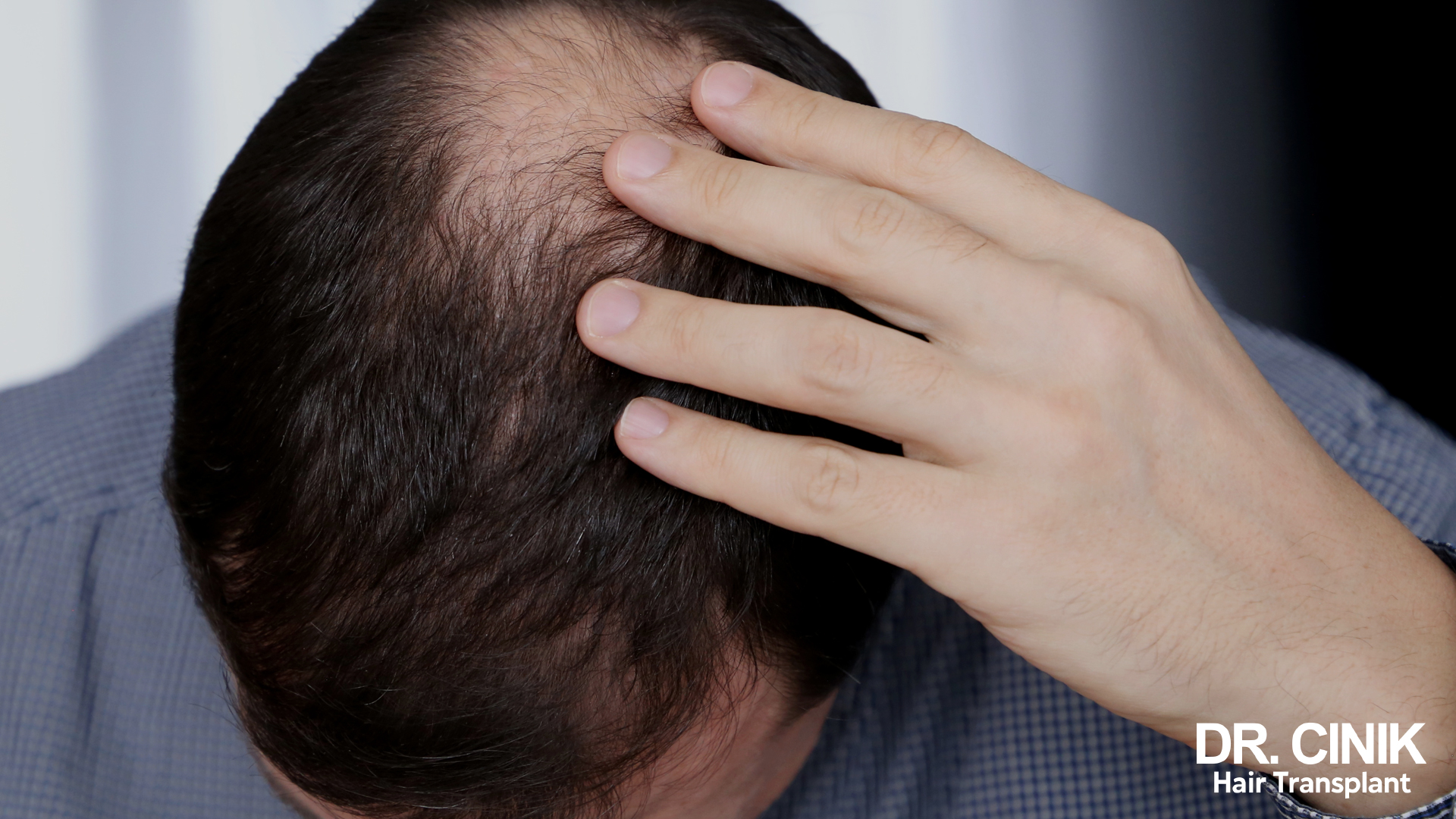
Crown hair loss is primarily caused by androgenetic alopecia, which leads to predictable balding patterns. Specialists often use the Norwood Hamilton scale to assess the extent of this hereditary male pattern baldness. From stage III onwards on this scale, significant hair loss can usually be observed in the crown area.
However, the severity of hair loss in the crown varies greatly from person to person. Some men may experience only mild thinning, while others may have much more noticeable hair loss. This variation is largely due to genetic factors. Heredity determines the sensitivity of hair follicles to androgens, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is the main culprit behind follicle miniaturisation and subsequent hair loss. The specific balding pattern in the crown is thought to be related to an individual’s unique skull shape.

In addition to genetics, other factors can contribute to crown hair loss. Stress, for instance, is known to accelerate hair loss. Smoking can also worsen the situation by impairing blood circulation and damaging hair follicles. It’s the combination of these environmental and lifestyle factors, along with genetic predisposition, that ultimately determines the extent and progression of crown hair loss in each individual.
Hair Transplant Techniques for the Crown
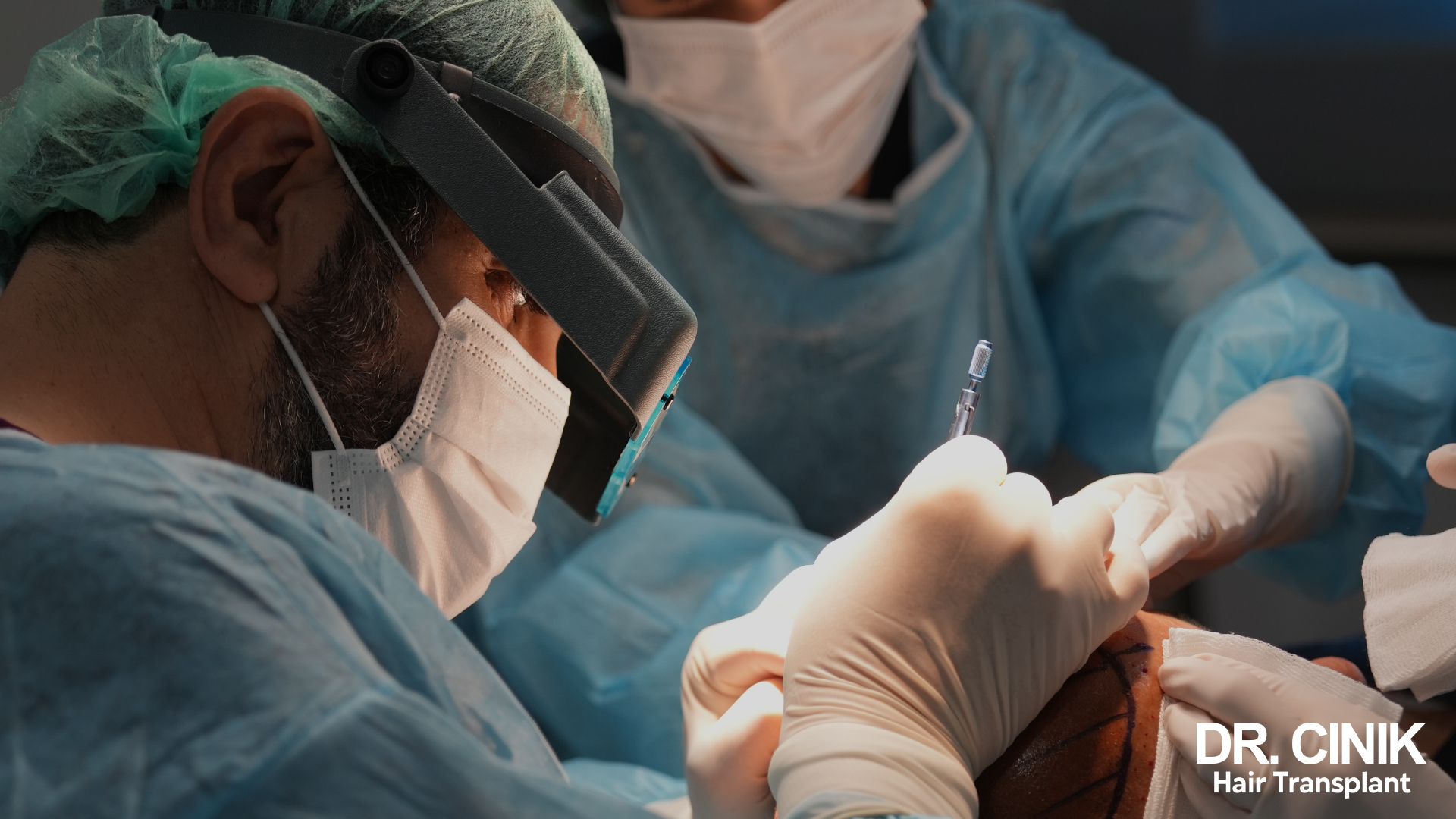
While there are no specific grafting techniques exclusively for the crown, hair restoration professionals adapt their approach to this delicate area. They must consider the natural hair density, the unique orientation of the follicles forming a swirl pattern, and anticipate the progression of hair loss around the transplanted area.
The FUE Technique
The Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) technique is a state-of-the-art hair transplantation method that is particularly effective in treating advanced stages of androgenetic alopecia affecting the crown. Unlike older techniques such as Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), which involves removing a strip of hair-bearing skin from the back of the scalp, FUE offers a more targeted and less invasive approach.
The FUE process starts with the precise extraction of individual hair follicles from the donor area, typically located at the back and sides of the head. Using a specialized instrument called a punch, the surgeon makes tiny circular incisions around each follicular unit, which usually contains 1 to 4 hairs. These units are then carefully extracted one by one, preserving their integrity and maximising the chances of successful graft survival.
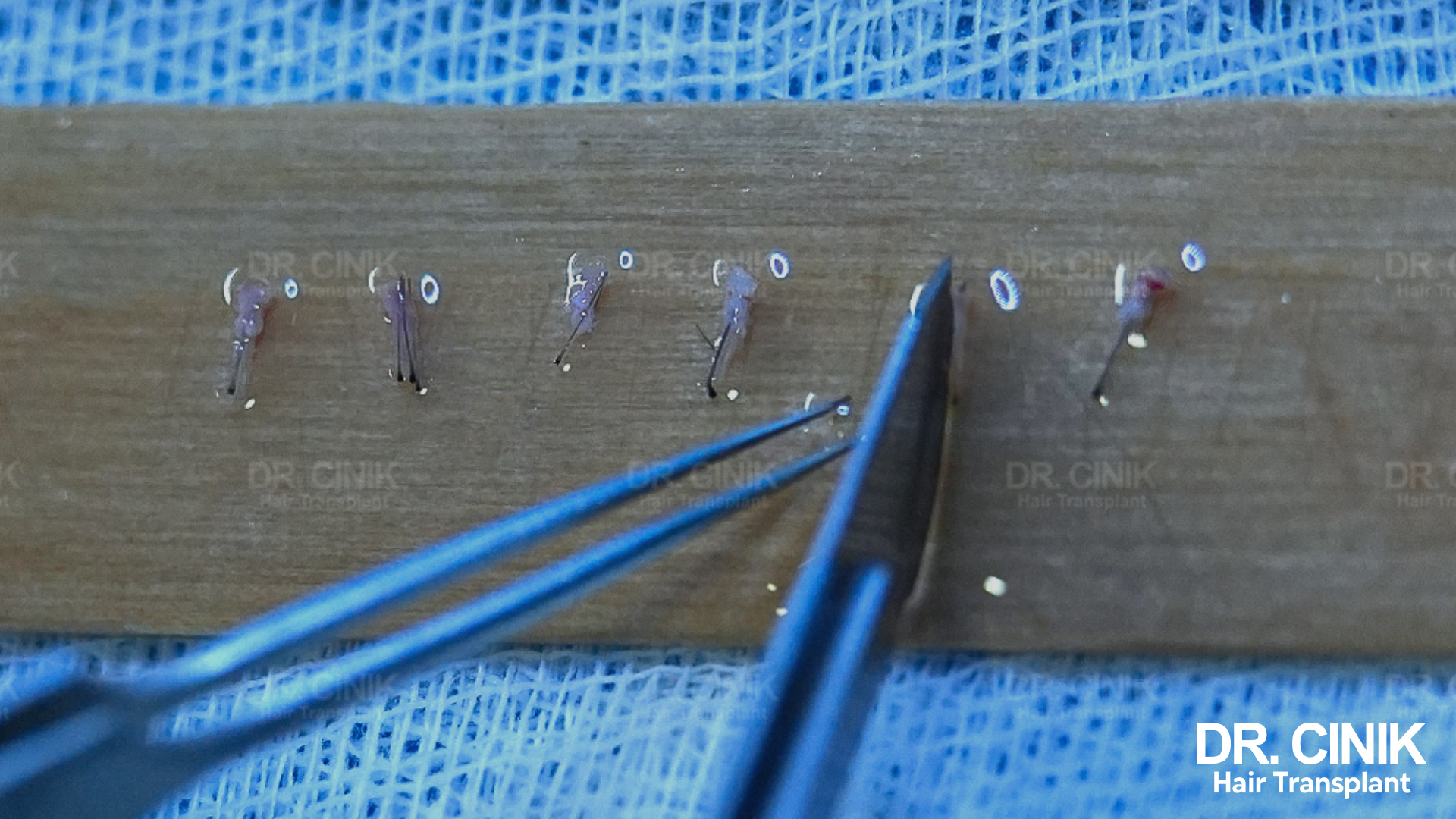
One of the significant benefits of FUE is its minimally invasive nature. The technique leaves minimal, barely noticeable scars, allowing patients to wear very short hairstyles without revealing signs of the procedure. Additionally, the recovery period following an FUE procedure is generally shorter and less uncomfortable than traditional methods.
After harvesting the precious follicles, the next step involves meticulous preparation for reimplantation. The follicles are sorted, counted, and kept in optimal conditions until the time of transplantation. The surgeon then creates micro-incisions in the previously bald crown area, taking great care to respect the natural angle and density of the hair to achieve the most realistic final result.
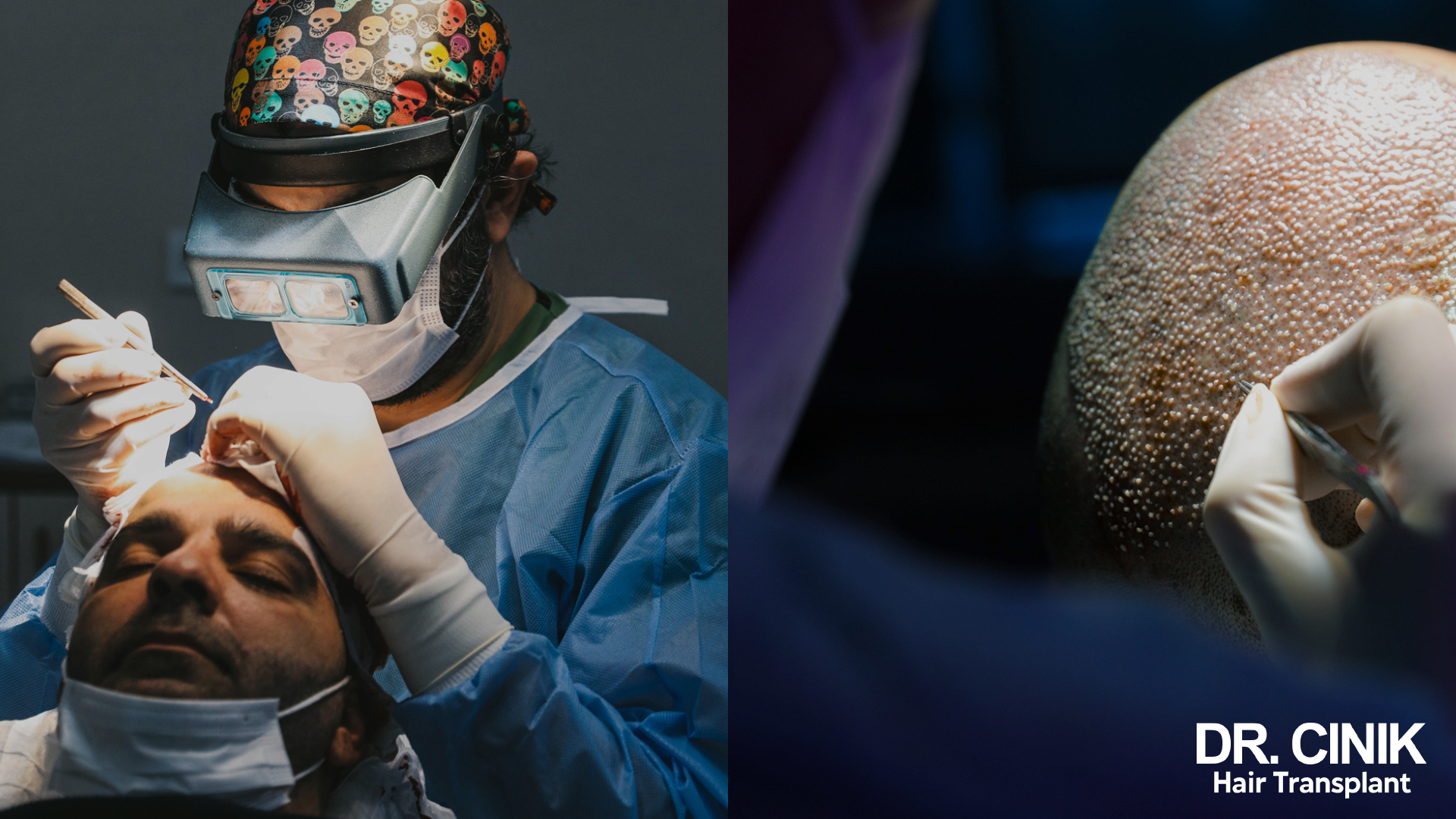
This ability to precisely target the problematic crown area makes FUE a preferred option for advanced stages of male pattern baldness. By optimally utilizing the available follicles from the donor area, this technique offers remarkable, long-lasting results, providing patients with a denser, more natural-looking head of hair, even in the most challenging cases of androgenetic alopecia.
The DHI Technique
Direct Hair Implantation (DHI) is a hair transplant technique that stands out for its precision and effectiveness. Derived from the FUE method (Follicular Unit Extraction), DHI allows for denser and more precise implantation of the grafts, making it particularly beneficial for individuals who have not yet reached an advanced stage of hair loss but notice significant balding around the crown area.
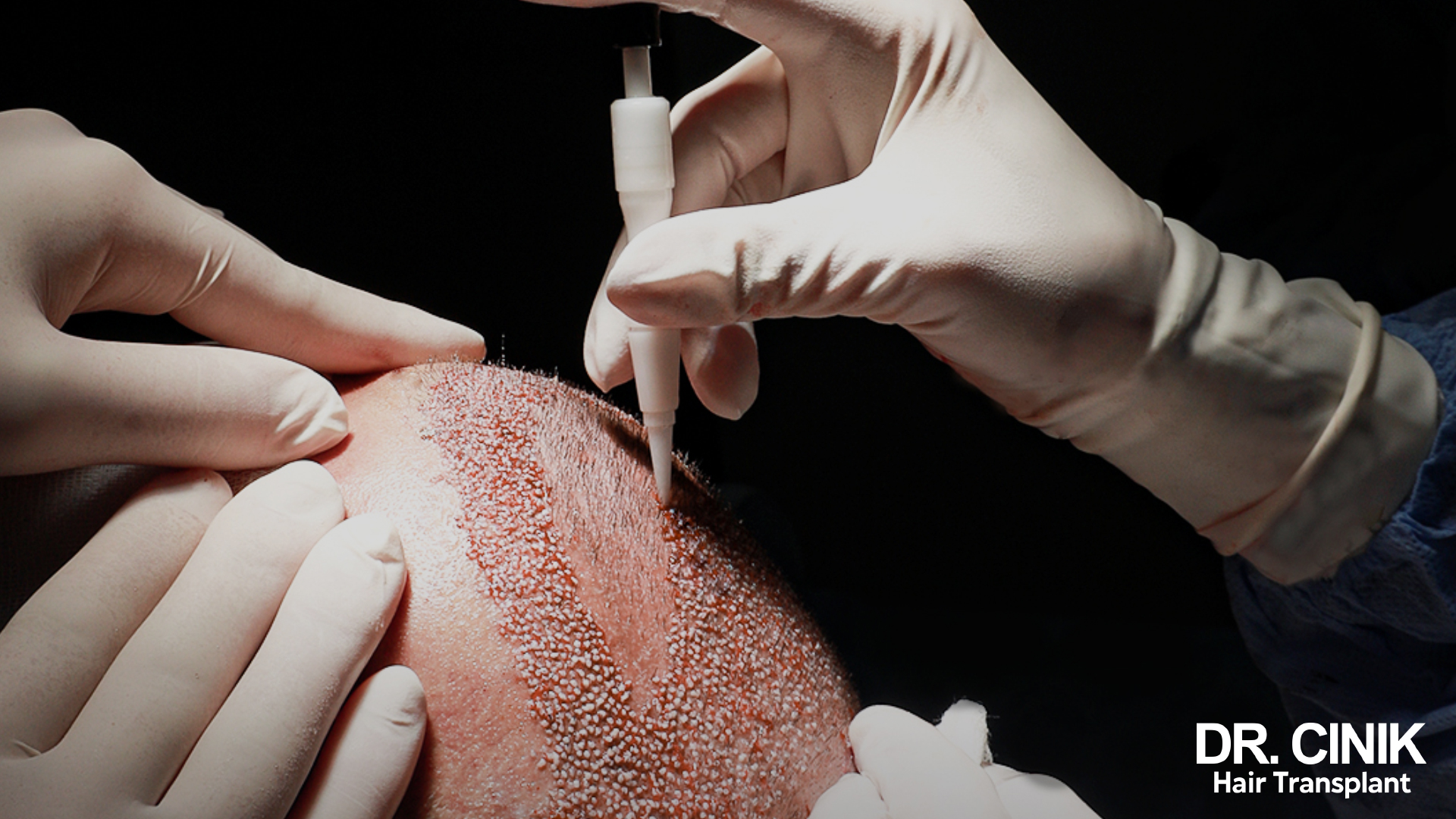
The unique feature of DHI is the use of a specialized instrument called the Choi implanter pen. Unlike conventional FUE, where follicles are first extracted and then implanted via incisions, the Choi pen enables follicles to be extracted and implanted in a nearly simultaneous manner. The advantage of this approach is that the grafts remain outside the scalp for a shorter duration, increasing their chances of successful transplantation.
DHI also provides the surgeon with great precision, as they can perfectly control the depth, angle, and direction of each implanted graft. This level of precision is a significant advantage for achieving a natural-looking result, particularly in visible areas such as the crown. Moreover, this precision ensures a denser and more evenly distributed hair coverage, which is ideal for patients seeking a full and uniform head of hair.
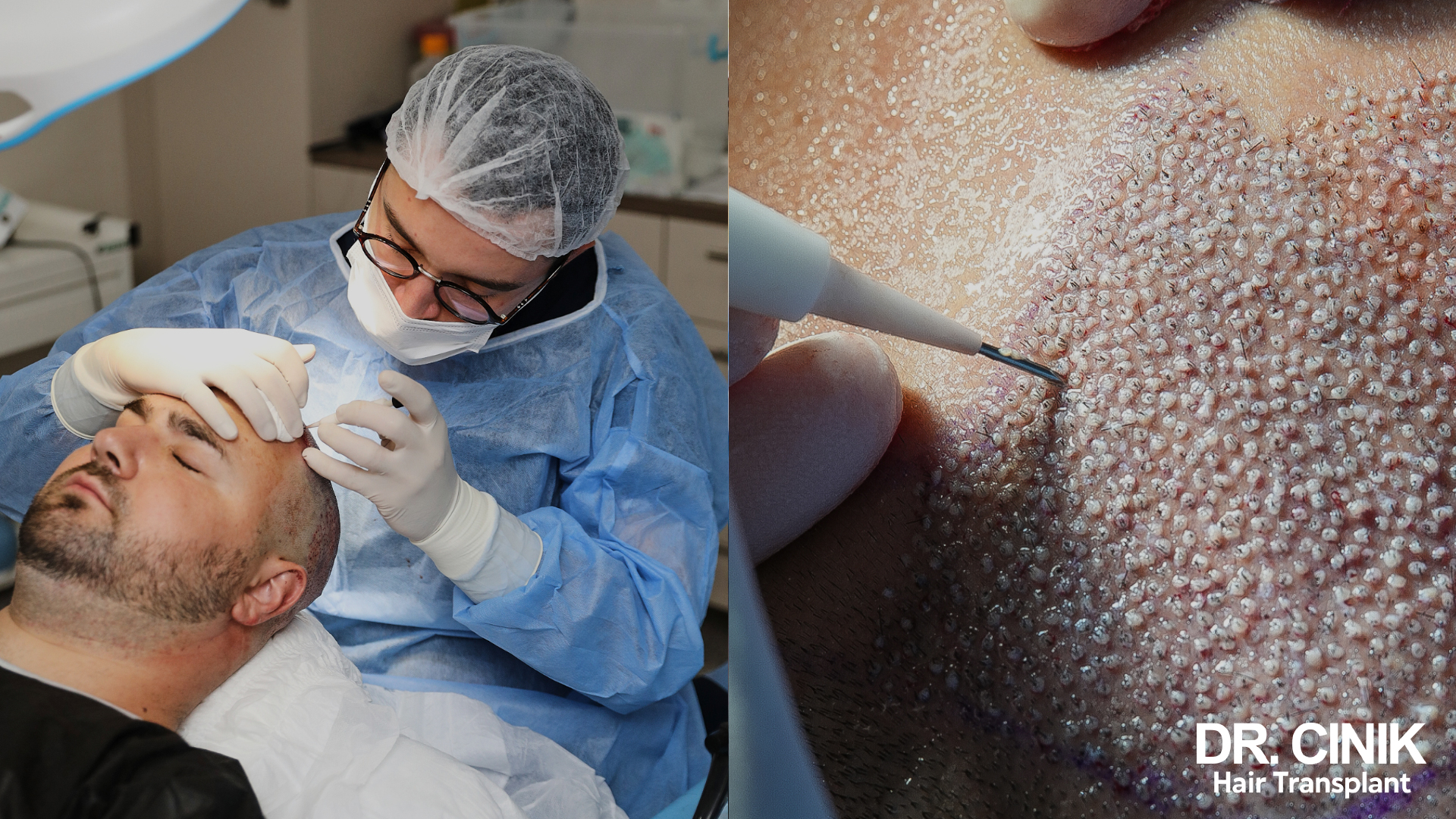
However, it’s important to note that DHI is often more expensive than other grafting techniques due to the expertise required and the longer operation time compared to FUE for the same number of grafts. Despite the higher cost, patients who choose this method generally benefit from a shorter recovery time and highly aesthetic results.
The FUT Technique
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) is a hair transplantation method that, although once popular, is now considered outdated. With the development of more advanced surgical techniques, FUT is being used less frequently, primarily because of the linear scar it leaves at the back of the scalp.
The FUT process involves the extraction of a strip of scalp, usually from the back of the head. This strip is then meticulously dissected into small fragments, each containing a few grafts. These grafts are then transplanted into sparse or balding areas, such as the crown. While this method allows for a large number of grafts to be harvested in a single session, the linear scarring it generates has significant drawbacks.
The scar resulting from FUT is permanent and may pose a problem for patients who desire to wear their hair short, as the scar is likely to be visible. Post-operative management of the scar and patient comfort is more complex, leading to a longer recovery time compared to FUE and DHI techniques.
How many grafts are needed to cover the entire crown?
The number of grafts needed to completely cover the crown varies depending on several factors specific to each individual. There is no one-size-fits-all figure that applies to all cases. The required number of grafts will depend on the extent of hair loss, the patient’s natural hair density, and their personal aesthetic goals.
Generally speaking, to achieve satisfactory coverage of the crown, between 1,500 and 3,000 grafts are needed. This is a relatively wide range because it encompasses very different situations. For example, a patient with limited hair loss and naturally high hair density will require fewer grafts compared to someone with more advanced baldness and naturally finer hair.
What is the average cost of a hair transplant for crown baldness?
The price of a hair transplant to treat crown baldness can vary considerably depending on the country where you choose to have the procedure. Let’s consider an example of a transplant involving 2,000 grafts, which is a common number for this type of operation. The average prices charged in different countries vary significantly:
| Country | Price for 2000 Grafts |
| UK | £7,000 |
| Ireland | €8,000 |
| USA | $10,000 |
| Canada | C$12,000 |
| Turkey | €2,300 |
As you can see, the United States and Canada have the highest prices, with an average cost of $10,000 and C$12,000, respectively, for 2,000 grafts. The United Kingdom and Ireland fall into a slightly lower price range, at around £7,000 and €8,000. However, Turkey stands out with the most competitive prices, offering the same procedure for approximately €2,300 with Dr. Cinik.
 en
en



