How Many Grafts Are Needed for a Hair Transplant?
Sommaire
What is a Graft?
A hair graft, also known as a hair follicle unit, is the basic component of a hair transplant. It consists of a tiny segment of the scalp that typically contains one to four healthy hair follicles. These follicles comprise the hair-producing part, the follicular bulb, and the emerging hair shaft. The grafts are meticulously harvested throughout the transplantation process from the donor area, located on the back and sides of the head. They are carefully re-implanted into the thinning regions to revive the hair’s density naturally and lastingly.
Graft Requirements Based on Baldness Severity Using the Norwood-Hamilton Scale
The Norwood-Hamilton scale is an essential tool for classifying the extent of androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male pattern baldness. It defines seven stages that illustrate the progression of hair loss and helps determine the number of grafts needed for hair transplantation:
- Stage 1: No grafts are required due to insignificant hair loss.
- Stage 2: 500 to 1,000 grafts are suggested to correct minor temple recession.
- Stage 3: 1,000 to 2,000 grafts are recommended for more evident temple recession.
- Stage 4: 2,000 to 3,000 grafts are necessary due to severe temple recession and crown thinning.
- Stage 5: 3,000 to 4,000 grafts are needed to cover larger balding areas.
- Stage 6: 4,000 to 5,000 grafts are essential as the bald spots at the crown and temples begin to merge.
- Stage 7: The extent of baldness is too significant, and transplantation is often not a viable option.

Determinants of Graft Quantity for Harvesting
Several factors influence the quantity of grafts needed for a procedure. Key elements include the density of the donor area, the quality of the grafts, and the strategic planning for their placement.
Donor Area Density
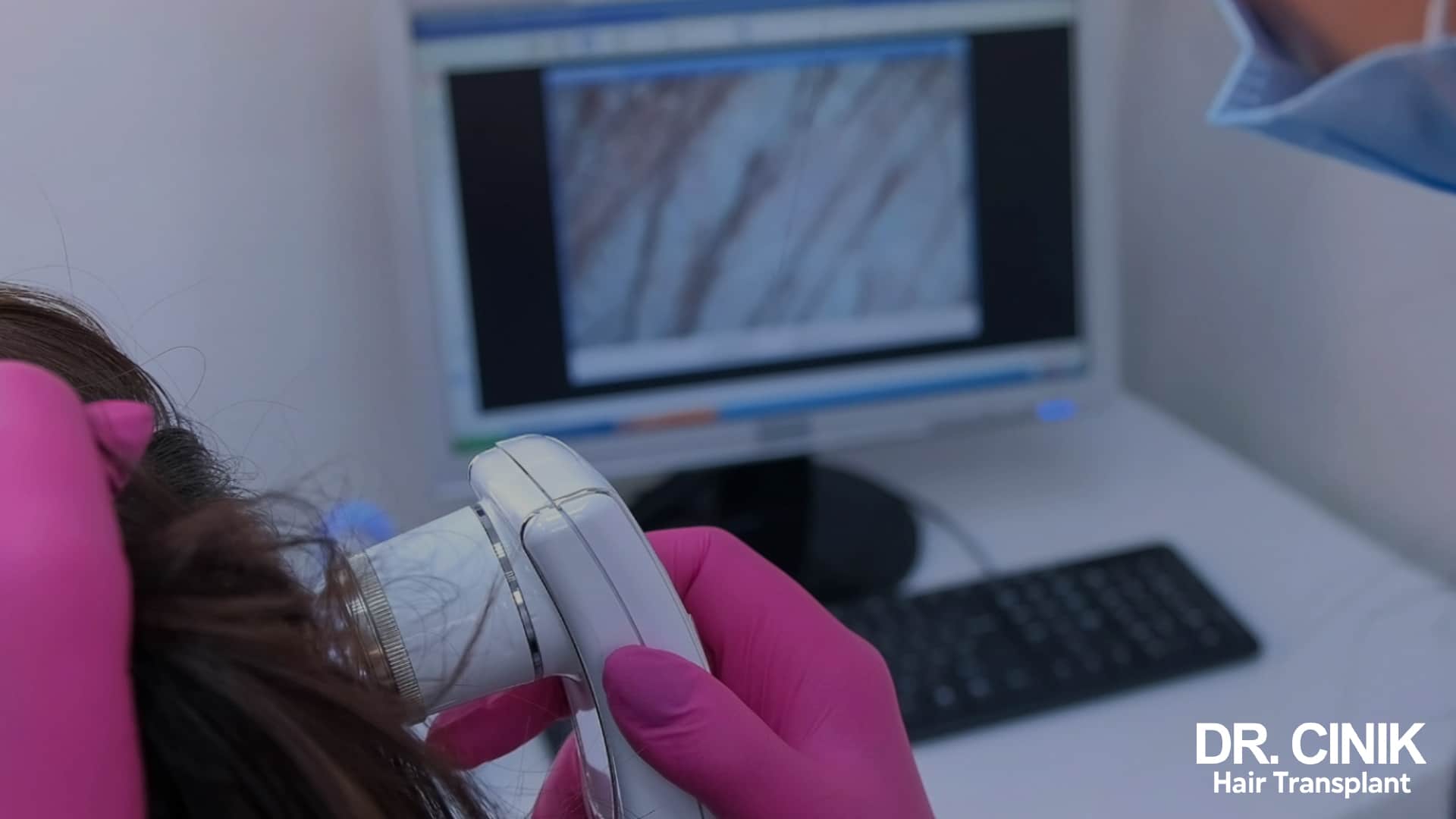
The donor area, where hair grafts are extracted, is strategically situated at the back and sides of the head. This area wasn’t selected randomly; hair follicles here are typically resistant to the hormones that cause androgenetic alopecia. It’s important to note that hair density varies among patients. Individuals with lower density in the donor area may need more grafts to achieve full coverage of balding sections. A thorough diagnosis by the surgeon is vital to pinpoint the viable hair follicle count, which then informs the precise calculation of the necessary number of grafts.

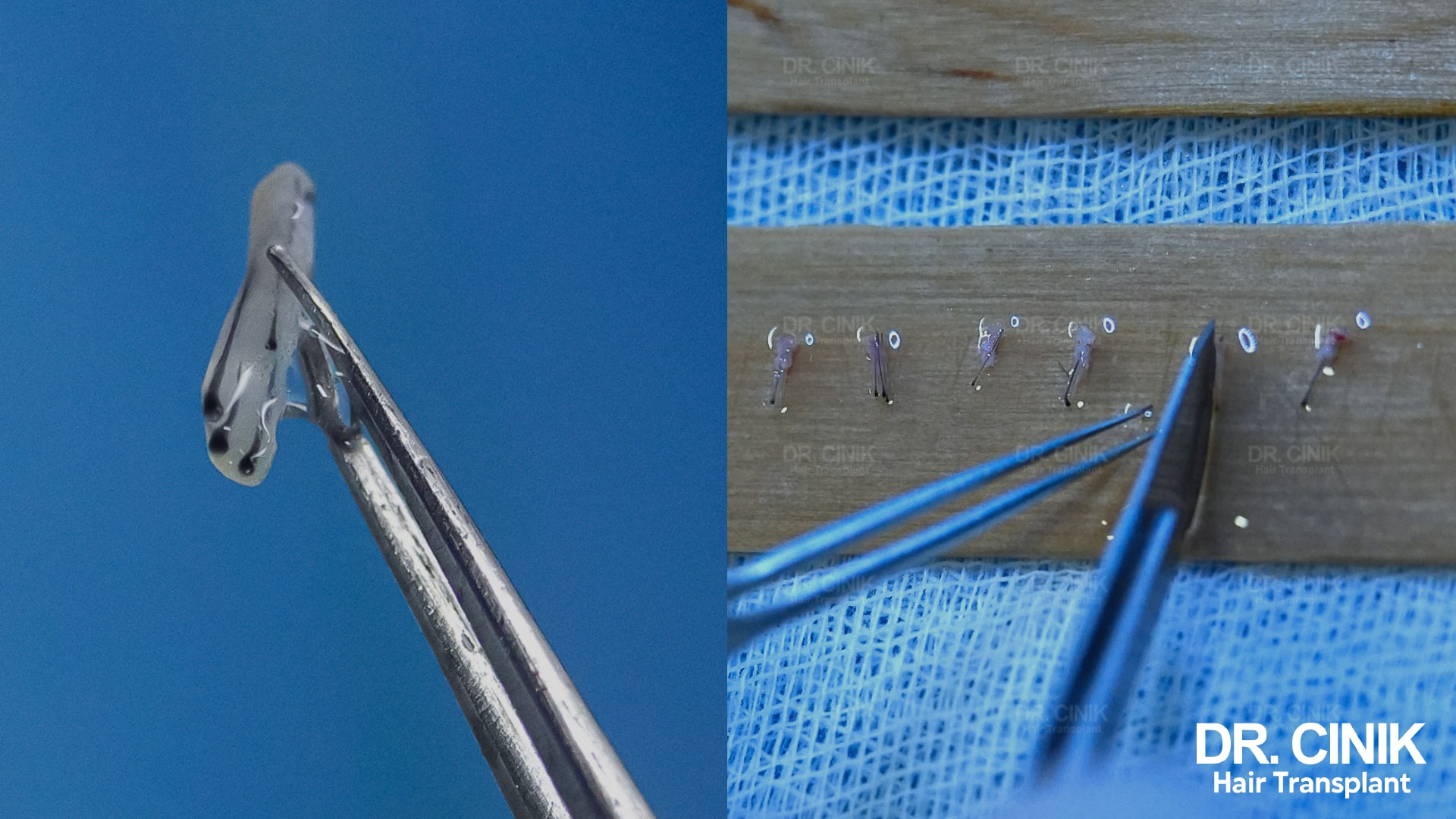
The Quality of Grafts
The quality of the grafts sourced from the donor area plays a pivotal role in their survival rate after transplantation.
If the grafts are of inferior quality, lack sufficient tissue, or possess a damaged follicular bulb, they will likely fail to take root post-implantation.
For this reason, it’s vital for surgeons to thoroughly examine each graft’s quality during the harvest, which, in turn, influences the determination of the total number of grafts needed for the procedure.
The Hair Transplant planning
The hair transplant planning also impacts the number of grafts needed.
The medical team will craft an optimised distribution strategy based on the patient’s requirements, the level of hair loss, and the available donor hair. This includes creating an exact blueprint of the recipient zones that need coverage designating an appropriate number of grafts to each area to achieve the targeted density.
Through this meticulous allocation, every graft harvested is placed precisely, following a plan that ensures the optimal outcome.
 en
en



