Understanding Hair Transplant Infections: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Summary
Hair transplant surgery, a popular method for addressing hair loss, is not without potential complications; infections, although infrequent—manifesting in less than 1% of cases—are a concern due to bacterial exposure within the micro-incisions, compromised healing, or an intense immune response.
This article discusses the origins, warning signs, and remedial options for infections after hair transplantation. Signs such as swelling, redness, itching, fever, pus discharge, and even loss of grafts can indicate an infection. Depending on the severity, treatments may include prescribed antibiotics, meticulous local care, or additional surgical intervention.
The goal is to give patients vital information about these potential complications, ensuring they seek medical advice promptly if any uncertainty arises. Prevention plays a pivotal role—opting for a certified surgeon and scrupulously adhering to post-surgery care guidelines is imperative.
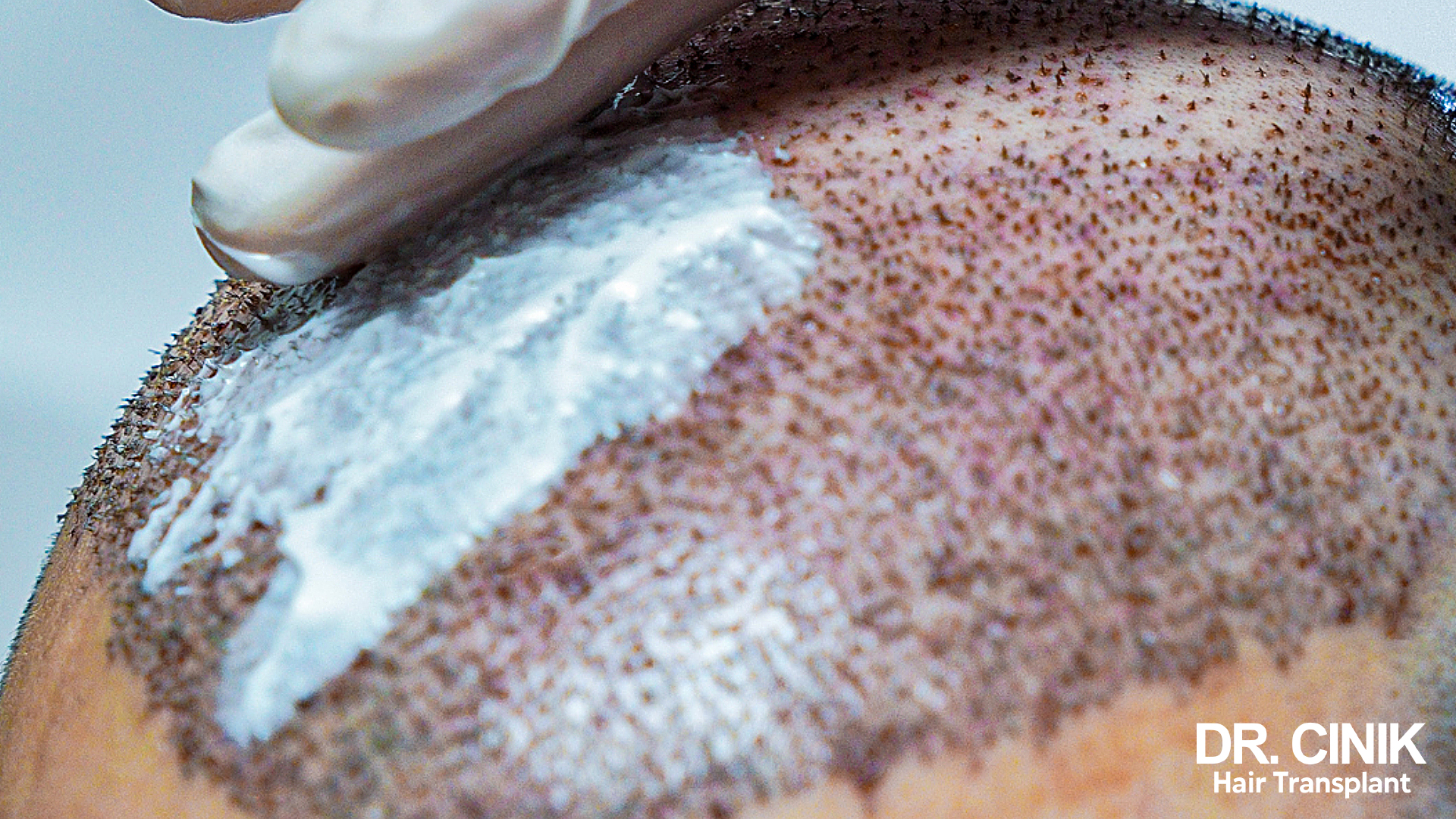

Infection Trigger Factors Post-Hair Transplant
Post-operative infection following a hair transplant could arise from various sources:
- Bacterial contamination during the procedure: If surgical instruments are insufficiently sterilised or if the hygiene standards in the operating room are subpar, bacteria can enter open wounds.
- Inadequate post-surgical care: A failure to clean the transplanted site as instructed can result in bacterial proliferation.
- Surgery in unsanitary conditions: Operations performed in environments that lack proper sterilisation pose an increased infection risk.
- Overly aggressive inflammatory response: This may damage tissues and contribute to infection.
Patients who have diabetes or are immunocompromised are particularly susceptible to such complications.
Effective prevention hinges on rigorous hygiene practices. Ensuring that the donor area and recipient areas are meticulously disinfected is essential.
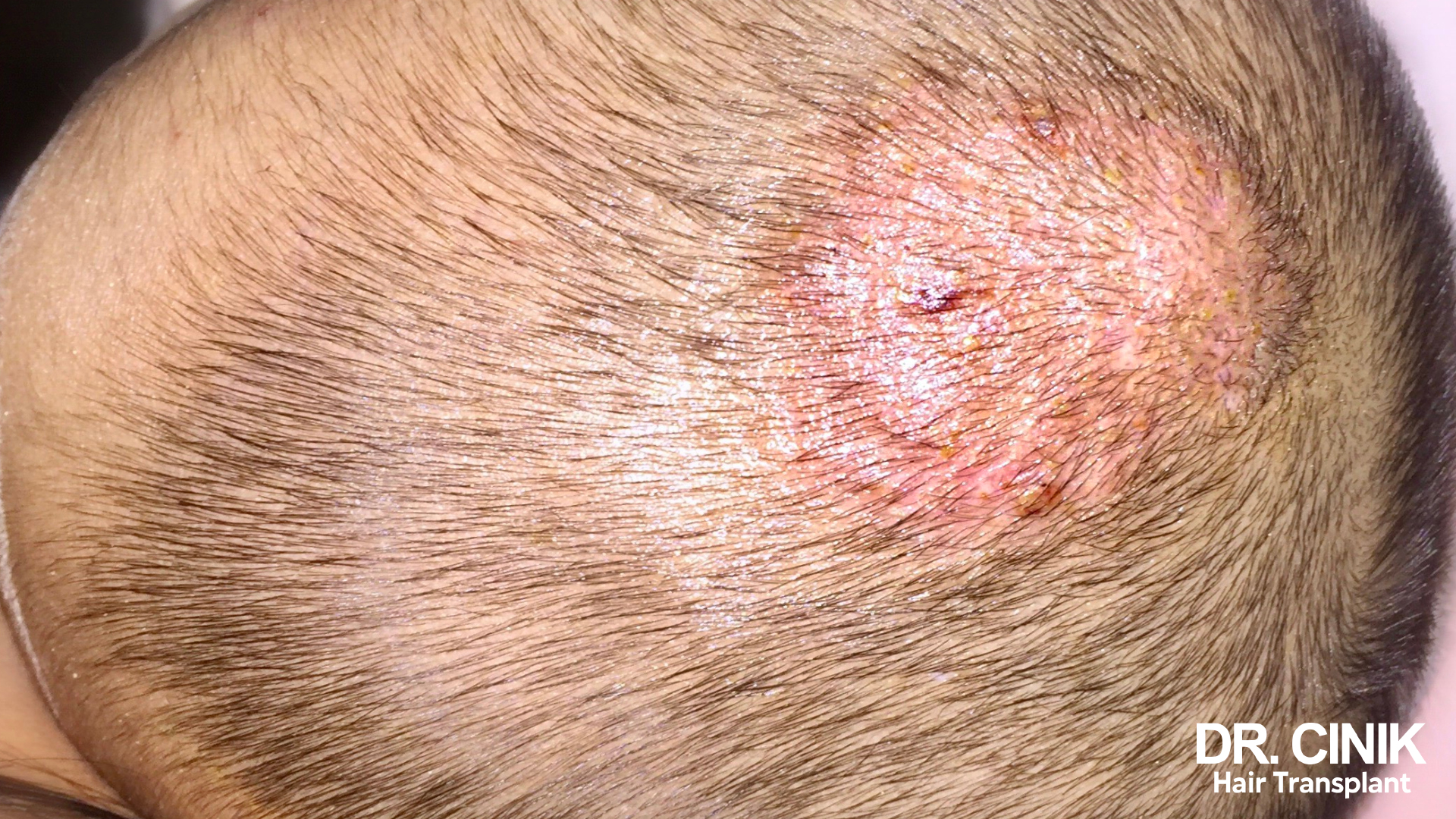
Recognising Scalp Infection Symptoms After a Hair Transplant
Post-transplant infections on the scalp may present with several distinct symptoms indicative of the body’s response to bacterial intrusion. Patients should stay vigilant for the following:
- Redness, swelling, or the emergence of skin rashes around the transplanted sites.
- Severe itching, burning sensations, and pain: These symptoms point to the irritation of the nerve endings due to the infection.
- Discharge of pus or purulent fluid: Such secretions are the hallmark of a secondary bacterial infection.
- Fever, intense headaches, and widespread body aches signaling systemic involvement.
- Loss of grafts: An infection can compromise the successful engraftment and vascularisation of the transplanted follicles.
- Profound fatigue and enlarged lymph nodes: These general symptoms may also manifest as part of the body’s reaction to the infection.
Should these signs occur following your hair restoration procedure, seeking medical attention promptly to confirm the diagnosis and initiate appropriate treatment is imperative.
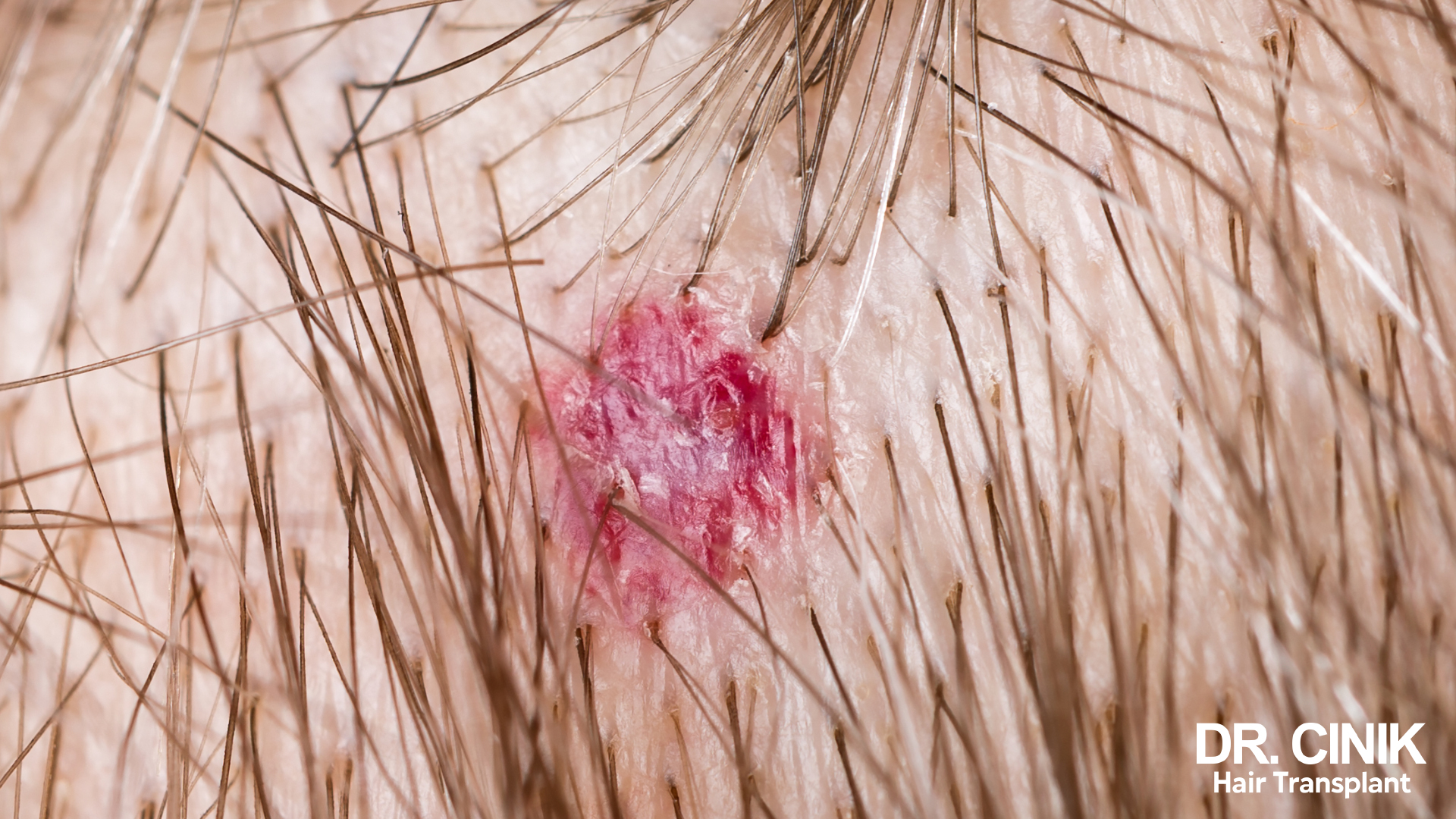
Identifying a Post-Hair Transplant Infection
If you experience any signs of infection, such as fever, pain, purulent discharge, or scalp swelling, you must immediately seek your surgeon’s advice.
The diagnostic process typically includes:
- A meticulous examination of the scalp to check for any signs of redness, inflammation, crusts, lumps, or discharge around the grafted sites.
- An in-depth discussion regarding the progression of any symptoms.
- Blood tests, if needed, to detect signs of an inflammatory response.
- Sample cultures from the wounds to isolate and identify the culprit bacterium, often Staphylococcus aureus.
- Sometimes, a skin biopsy from affected areas is needed for further investigation.
The laboratory results, specifically the bacteria cultures, serve to pinpoint the exact pathogen responsible, thus guiding a targeted antibiotic treatment plan.
Managing Infections After a Hair Transplant
Effective management of infections following a hair transplant hinges on prompt identification of the offending pathogen through bacteriological testing, coupled with swift initiation of treatment:
- Antibiotics, either oral or intravenous, are chosen based on the sensitivity profile derived from the lab’s antibiogram.
- Topical antiseptics such as chlorhexidine or Betadine are used to cleanse the impacted area.
- Rigorous wound management, entailing cleansing, disinfecting, and applying sterile dressings to the affected zones.
- Anti-inflammatory medication like corticosteroids or ibuprofen alleviates inflammation, alongside analgesics to relieve discomfort.
- In specific scenarios, a follow-up surgical procedure may be deemed necessary to address a profound abscess or considerable tissue necrosis by evacuating the infection.
Continual observation of the patient’s clinical response is crucial for gauging the success of the treatment. Should symptoms not improve as anticipated, medical professionals may need to adjust the therapeutic strategy.
Mitigating Infectious Complications Following a Hair Transplant
- Verify the surgeon’s credentials and the clinic’s certification to ensure healthcare quality.
- Complete a comprehensive pre-operative blood workup (including checks for blood sugar levels, blood count, coagulation factors, and infectious disease markers) and confirm with your surgeon that you’re fit for the transplant procedure.
- Address any current infections in the body, such as dental, skin, or urinary tract infections, before undergoing the operation.
- Follow the surgical team’s instructions to shower using an antiseptic solution, like Betadine, on the day before the procedure.
- After the transplant, maintain excellent personal hygiene with regular hand washing and careful management of your scalp and dressings.
- Diligently apply the recommended antiseptic solutions and shampoos to the affected areas.
- Be vigilant for early infection signs, like redness or fever, and seek medical advice within 24 hours.
- Adhere strictly to the prescribed post-operative care plan, including any antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, and pain relief.
- Faithfully follow all post-operative guidelines regarding rest, physical activity, sexual activity, scab care, graft protection, and limits on smoking and alcohol consumption.
In case of any concerns regarding potential complications, contact your surgeon without hesitation.
Academic Sources :




