Hair Transplant: The Ultimate Guide
Sommaire
Baldness, more formally known as “androgenetic alopecia,” affects 50% of men and 35% of women globally. In combatting this concern, many individuals are opting for hair transplants. This surgical remedy entails the removal of hair follicles from a donor site, typically at the back of the head, followed by their repositioning in the balding regions of the scalp. The transplanted hair follicles then take root and grow, leading to a natural and enduring restoration of hair density.
The General Principle of a Hair Transplant
A hair transplant is executed in two main phases:
- The extraction phase, where grafts are harvested from a donor area.
- The implantation phase, during which the grafts are meticulously placed into the targeted bald spots.
Harvesting Grafts from the Donor Area
The donor area, the area from which grafts are sourced is typically situated at the back and sides of the head. Hair follicles in this region are known for their resilience against androgenetic alopecia.
Extraction Techniques
Two primary methods are employed to harvest grafts from the donor area:
The FUE Method
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is the most prevalent technique in use today. This method involves using a punch, ranging from 0.8 to 1 mm in diameter, to meticulously extract individual micrografts, each containing 1 to 4 hairs.
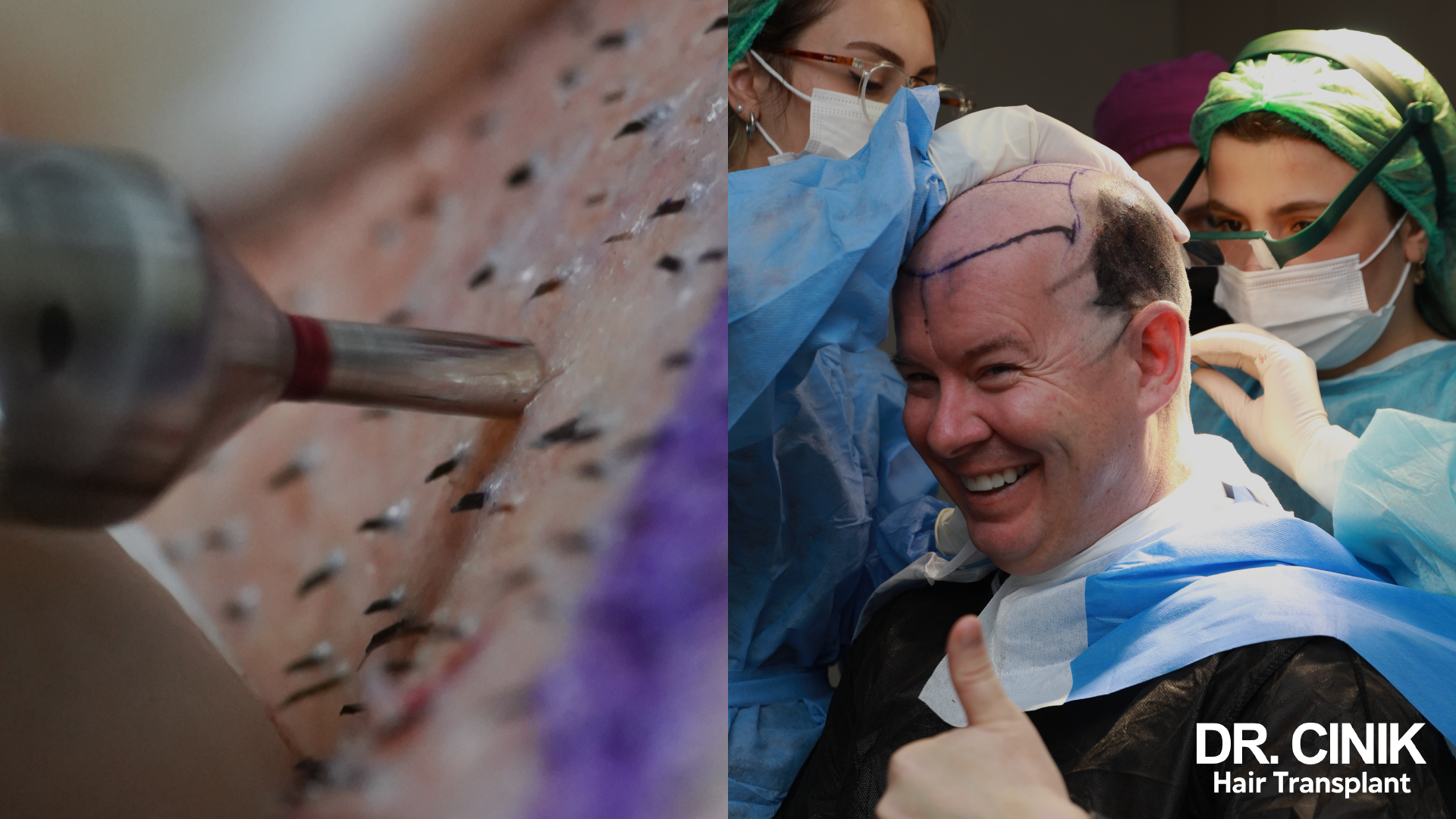

There are two variants:
FUE with Manual Extraction
The surgeon performs This method manually, using a rotary punch device to extract hair follicles.
FUE with Robotic Extraction
This procedure is carried out with the aid of a robotic system equipped with advanced imaging and software that identifies the follicles for extraction.
The FUT Method
FUT, or Follicular Unit Transplantation, involves the surgical removal of a strip of scalp, typically ranging from 15 to 25 cm, from the donor area. The strip is then meticulously dissected under a microscope to isolate the individual micro-grafts. While effective, the FUT method is more invasive than FUE and has become less popular over time.

Implantation of Grafts in Balding Regions
Once harvested through either the FUE or FUT techniques, the grafts are preserved in a nutrient-rich solution at 4°C before being transplanted.
Several methods exist for creating the recipient sites, also known as canals, and for the subsequent placement of the grafts.
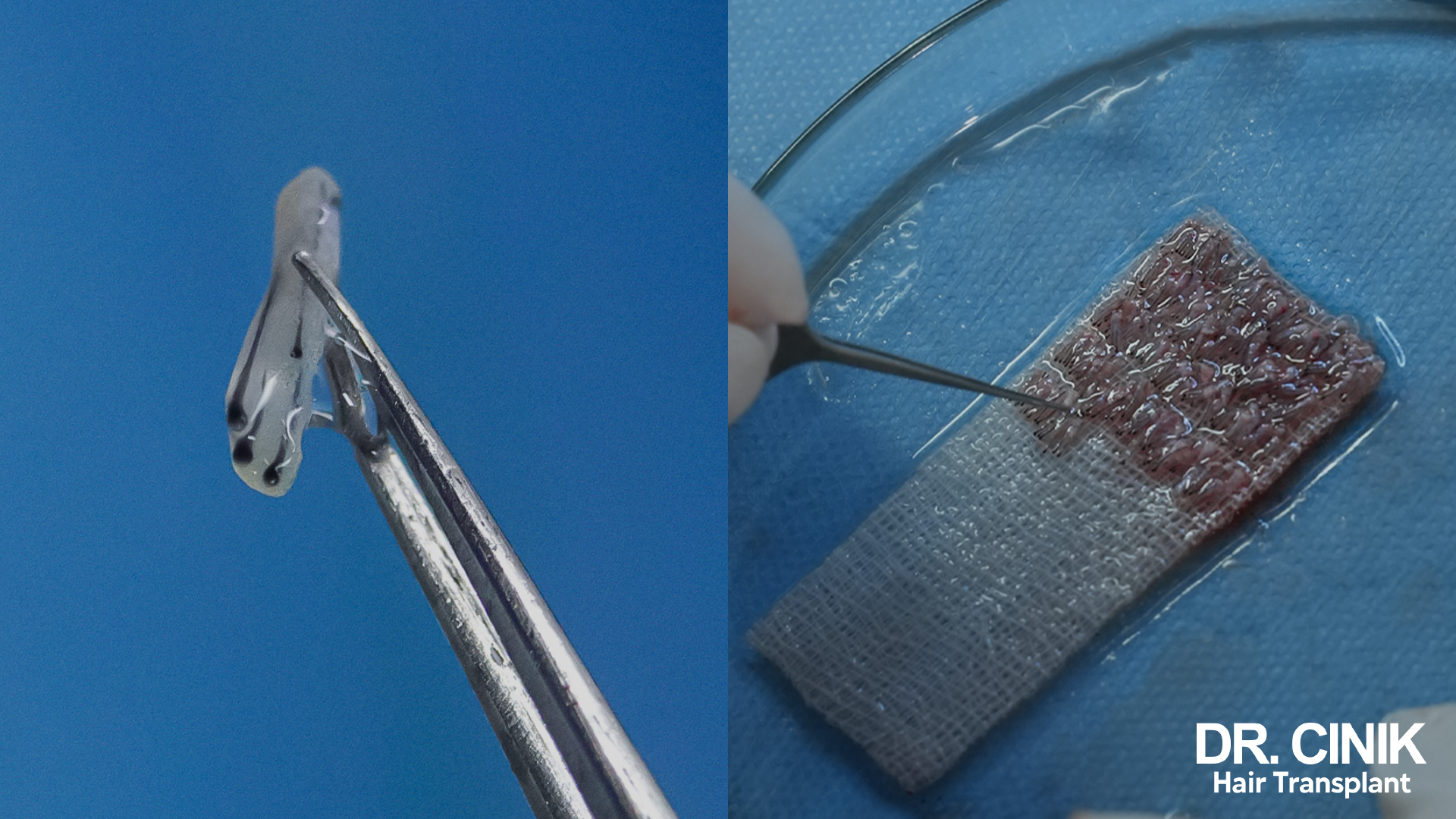
Implantation in Pre-formed Channels
For this technique, micro-channels are crafted within the scalp using microblades—these can be fashioned from either metal or sapphire. Subsequently, the hair grafts are delicately inserted into these channels with the assistance of forceps or a specialised graft holder.
Implantation Using the DHI Technique with the CHOI Implant Pen
The DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) technique employs the specialised CHOI implant pen. This instrument enables simultaneous incision and placement of the graft, eliminating the need to pre-form a canal.

Indications for a Hair Transplant
Not all forms of hair loss can be treated with a hair transplant.
Androgenetic Alopecia
A prevalent source of male baldness, androgenetic alopecia is characterised by a gradual thinning of hair in both volume and diameter, influenced by dihydrotestosterone (DHT)—a byproduct of testosterone. Although pharmacological like Minoxidil or Finasteride solutions may decelerate the progression of this hormonal hair loss, hair transplants are the sole option for achieving long-term, satisfactory hair density.

Traction Alopecia
Traction alopecia is a condition that predominantly impacts women. It results from hairstyles that exert excessive tension, such as overly tight ponytails, hair extensions, or consistent tugging over extended periods. These practices can lead to the gradual destruction of the hair follicles. Hair transplantation offers a solution to recover hair density for those affected by this condition.

Scarring Alopecia
Scarring alopecia arises as a result of physical trauma, such as burns or injuries, leading to the irreversible destruction of hair follicles that are subsequently replaced by scar tissue. Transplanting healthy hair follicles into the affected bald areas can significantly improve hair density and restore appearance.
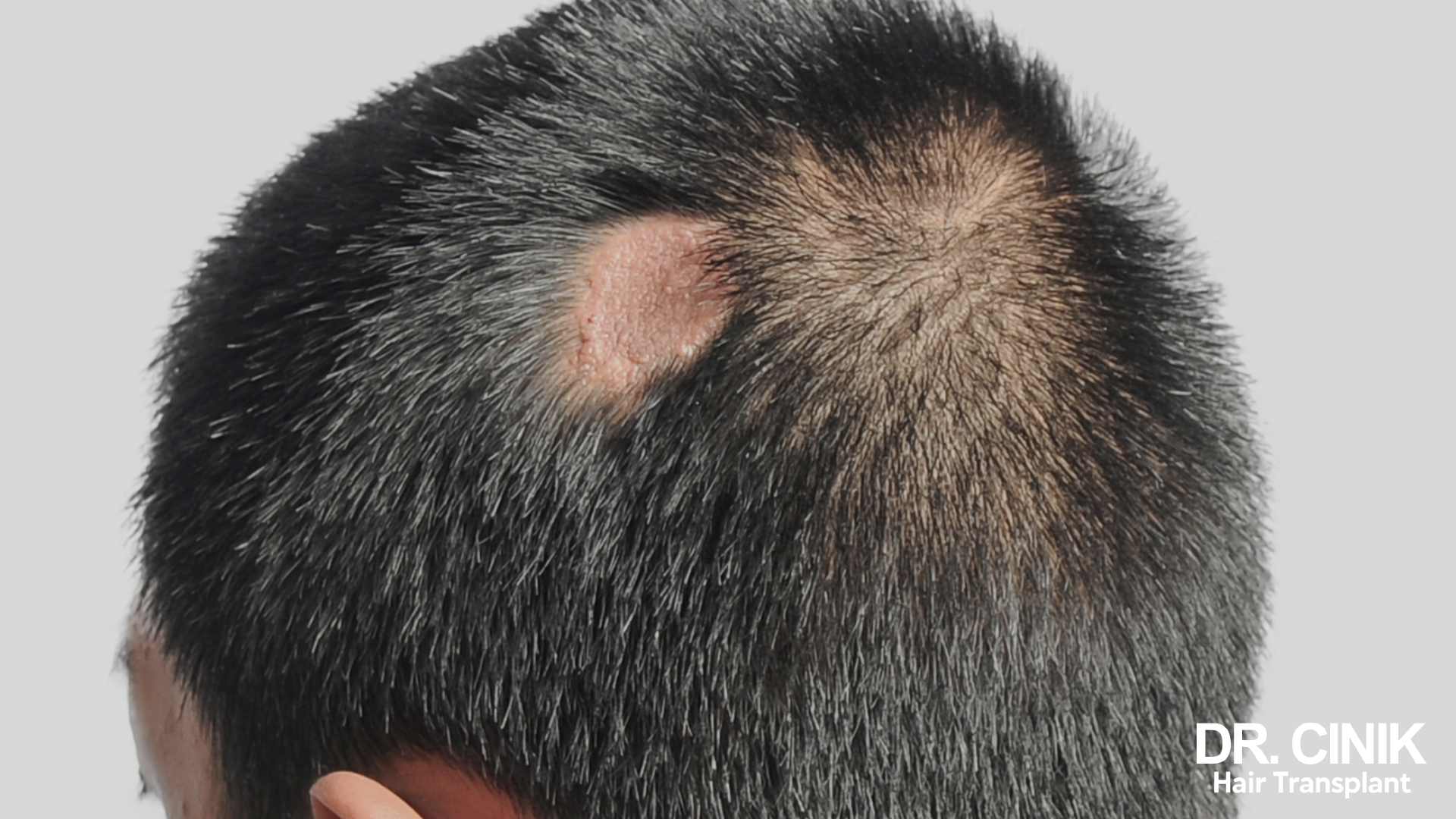
Contraindications to a Hair Transplant
There are specific medical contraindications to undergoing a hair transplant that must be considered.
Autoimmune Diseases
Conditions such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and alopecia areata represent absolute contraindications for hair transplantation. In these cases, the patient’s overactive immune system poses a risk of rejecting the transplanted hair grafts.
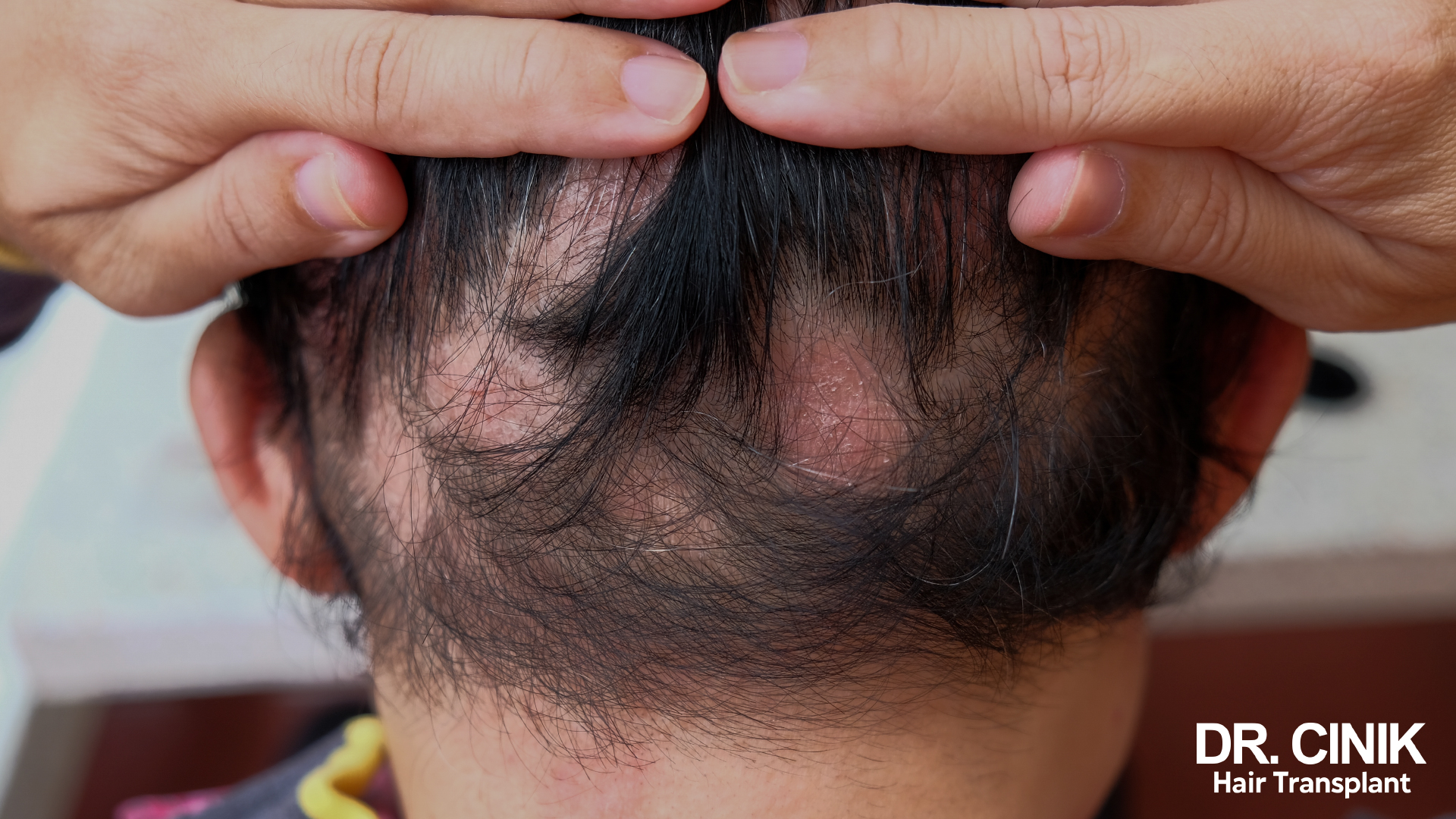
Cancer History Considerations
Patients with a history of cancer, specifically skin or haematological cancers, must observe a waiting period of 12 to 24 months following the completion of anti-cancer treatments before considering hair implantation. This precaution ensures patient safety and the success of the procedure.

Endocrine Disorders
Conditions like uncontrolled diabetes, untreated thyroid disorders, or excess cortisol levels can negatively affect the scalp’s blood supply and the overall healing process. These imbalances may jeopardise the survival of hair grafts due to compromised vascularisation and healing quality.

Heart and Vascular Diseases
Conditions like severe hypertension, heart failure, and a recent history of heart attack or stroke necessitate delaying the hair transplant procedure by several months to ensure patient safety during and after surgery.
Coagulation Disorders
Disorders that result in impaired blood clotting, such as haemophilia, as well as the use of anticoagulant or antiplatelet medications, may constitute contraindications for a hair transplant. Similarly, thrombopathies (an abnormal platelet count) or severe anaemia present a significant haemorrhage risk, making the procedure inadvisable.
Immunocompromised Individuals
For individuals with a significantly reduced CD4 count, such as HIV patients, or those with certain congenital immune deficiencies, the heightened risk of postoperative infections renders hair transplant surgery inadvisable.
Psychological Contraindications
Psychiatric conditions like dysmorphophobia, certain delusional disorders, unstable obsessive-compulsive disorders, severe depression, or addiction to cosmetic surgery necessitate a postponement of the procedure.
Additionally, having unrealistic expectations about the outcome, psychological instability, or a propensity for repetitive cosmetic surgeries are psychological factors that present contraindications to a hair transplant. These must be taken into account before proceeding with the surgery.

Hair Transplant Procedure Overview
Pre-operative Assessment
In the lead-up to the surgery, several consultations with the trichology surgeon are essential. During these sessions, the surgeon will:
- Conduct a detailed examination of the patient’s scalp, assessing bald spots, the quality of remaining hair, and the donor site.
- Perform a hair density evaluation using a trichogram.
- Take photographs from various angles and under different lighting conditions.
- Request additional examinations (such as biopsies or blood tests) if needed.
- Explain the surgical procedure in full detail.
- Offer dietary and lifestyle recommendations for pre-operative preparation.
A few weeks before the surgery, the patient must undergo blood tests that include a complete blood count, screenings for hepatitis B and C, and HIV serology.
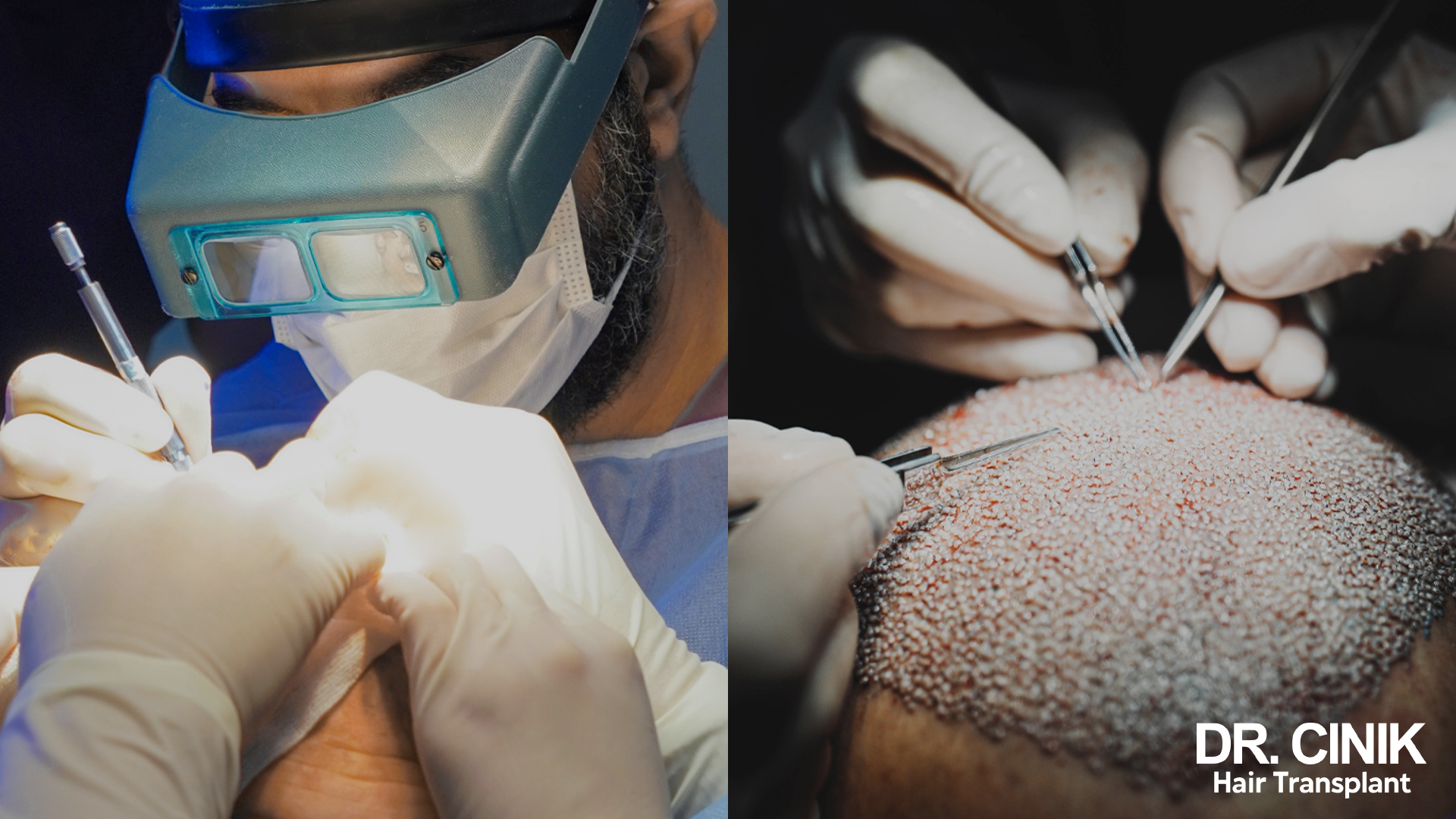
Day of Operation
On the day of the surgery, patients are admitted to the surgical unit and are typically required to fast beforehand. The operation involves four essential steps:
- Administration of local anaesthesia to both the donor and recipient areas of the scalp.
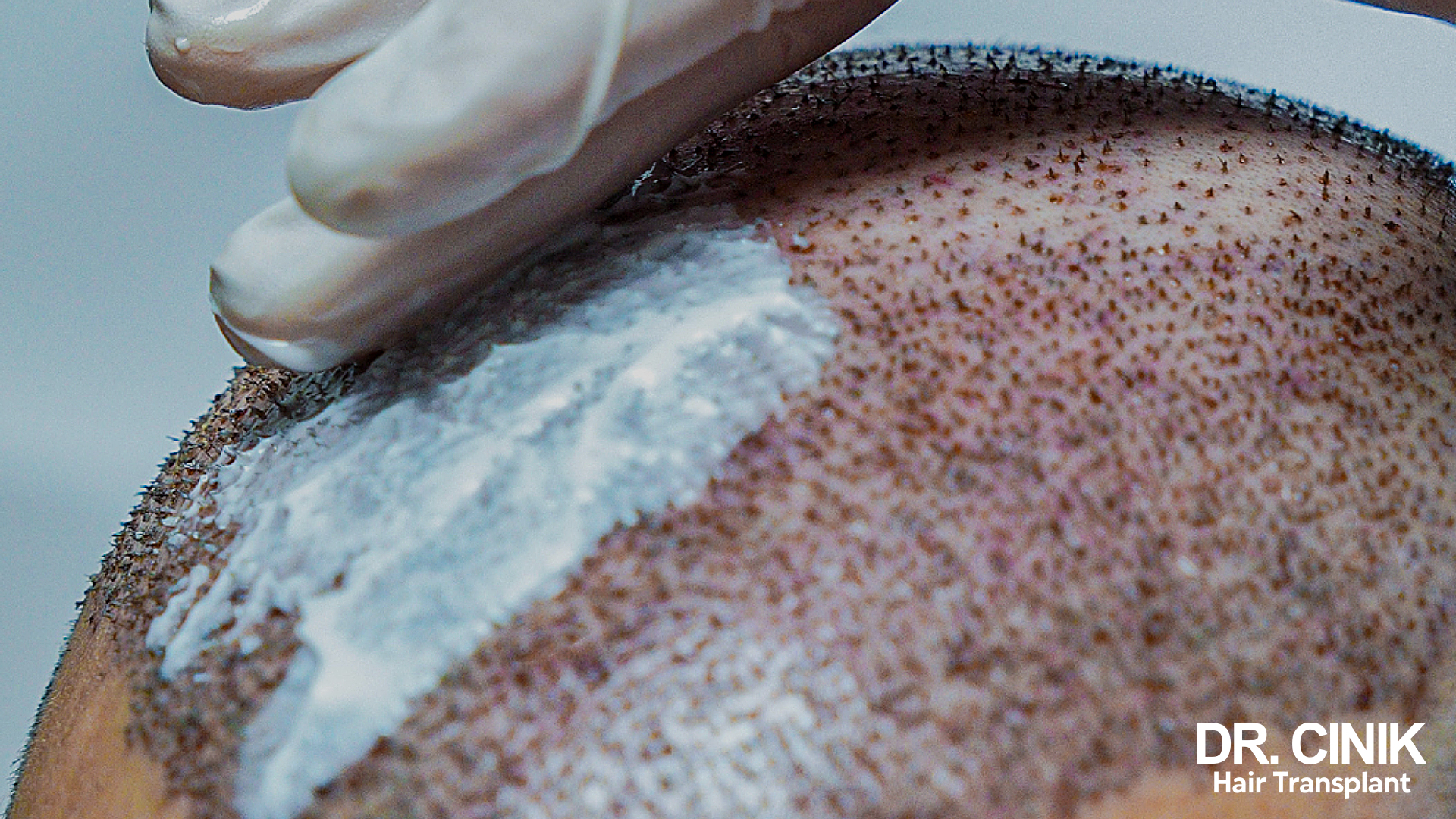
- Precision extraction of follicular units from the donor site using a micropunch with a diameter of 0.8 to 1 mm.
- Maintenance of graft viability by storing each extracted graft in a sterile, chilled nutrient solution.
- Careful placement of follicular units into the prepared incisions on the balding regions that are being restored.
To help ease any nervousness, a mild intravenous sedative may be provided, which allows the patient to remain relaxed while still awake. The complete duration of the surgery typically ranges from 4 to 8 hours, depending on the extent of the area undergoing treatment.
Post-Operative Care and Instructions
The period following a hair transplant is pivotal to guarantee the proper healing and recovery of the re-implanted grafts. Below are the care guidelines and instructions patients should adhere to

Washing the Scalp After a Hair Transplant
Starting the day after surgery, post-operative care is initiated using specially formulated medical shampoos. These shampoos should be applied to the treated areas following a strict protocol to minimise rubbing and encourage proper healing. The steps are as follows:
- Applying Panthenol Foam: Begin by applying panthenol foam to the transplanted regions and leave it on for 30 minutes. Panthenol, laden with provitamin B₅, aids in purging the impurities and loosening crusts without harming the new grafts.
- Rinsing the Foam: Carefully rinse off the foam with tepid water. Steer clear of using the showerhead for this rinse; opt for a jug or bowl instead.
- Shampooing: Employ the clinic-provided shampoo, lathering it onto the scalp with a delicate touch to avoid direct contact with the grafts.
- Final Rinse and Drying: After lathering, rinse thoroughly again with lukewarm water using the jug or bowl. Pat the donor site dry with a clean towel, but allow the implanted area to air dry.
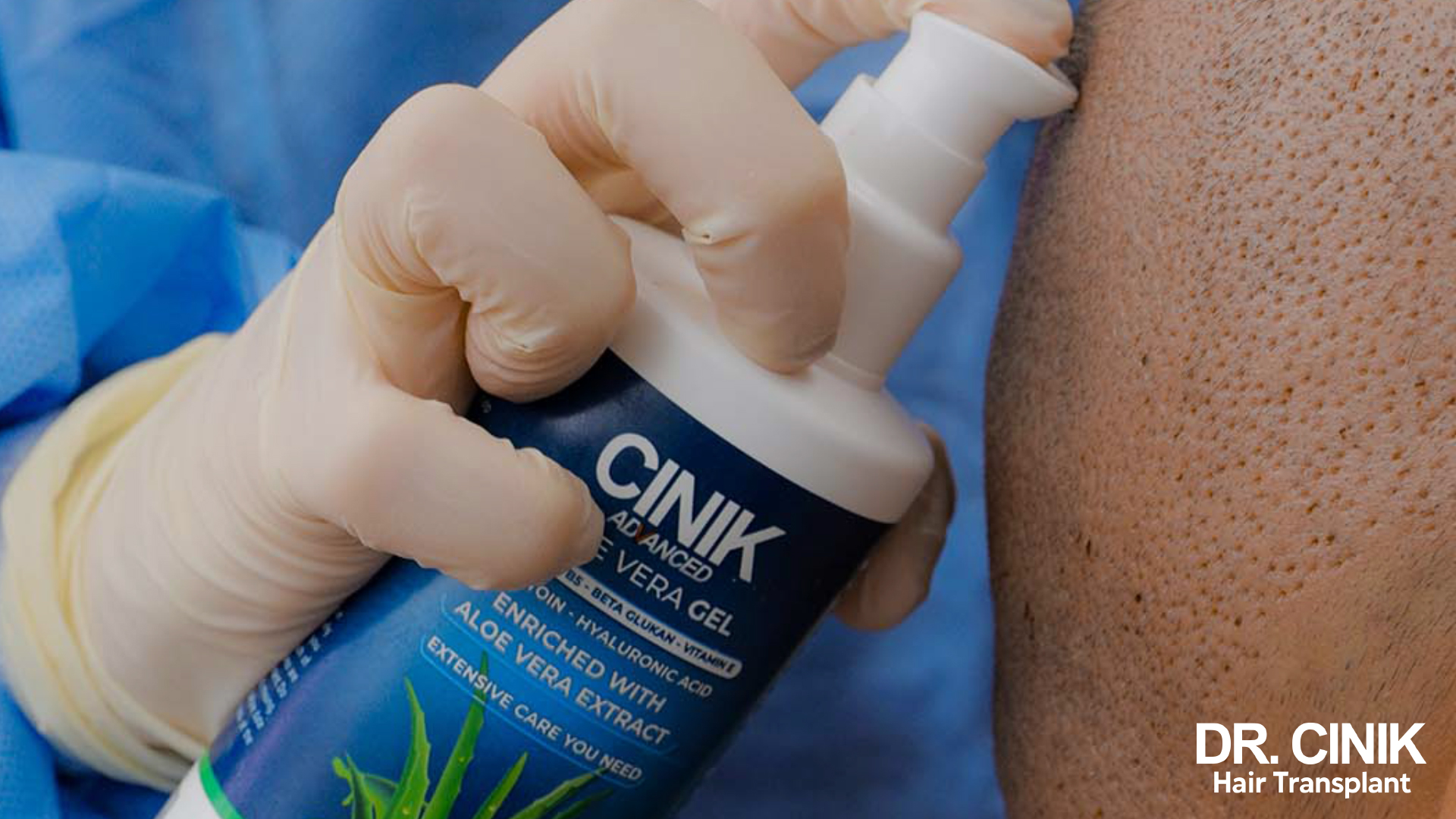
- Applying Aloe Vera Gel: To calm and support the recovery process, lightly apply aloe vera gel on the donor site.
Maintaining pristine cleanliness of the grafted areas is essential for the first three weeks post-operation. Daily shampooing in the morning or evening is advisable for the initial 10 days. Starting from day 11, the cleansing approach should be modified to facilitate the gentle removal of scabs. This involves a similar washing technique but allows the shampoo foam to remain on the scalp for an hour.

Beginning on the 15th day, patients can gradually return to a more typical shower routine, incorporating soft, circular massages to clean the scalp. It remains imperative to handle the grafted area with utmost care. Once 30 days have elapsed, the individual may resume their regular hair care regimen, including using their preferred shampoo.
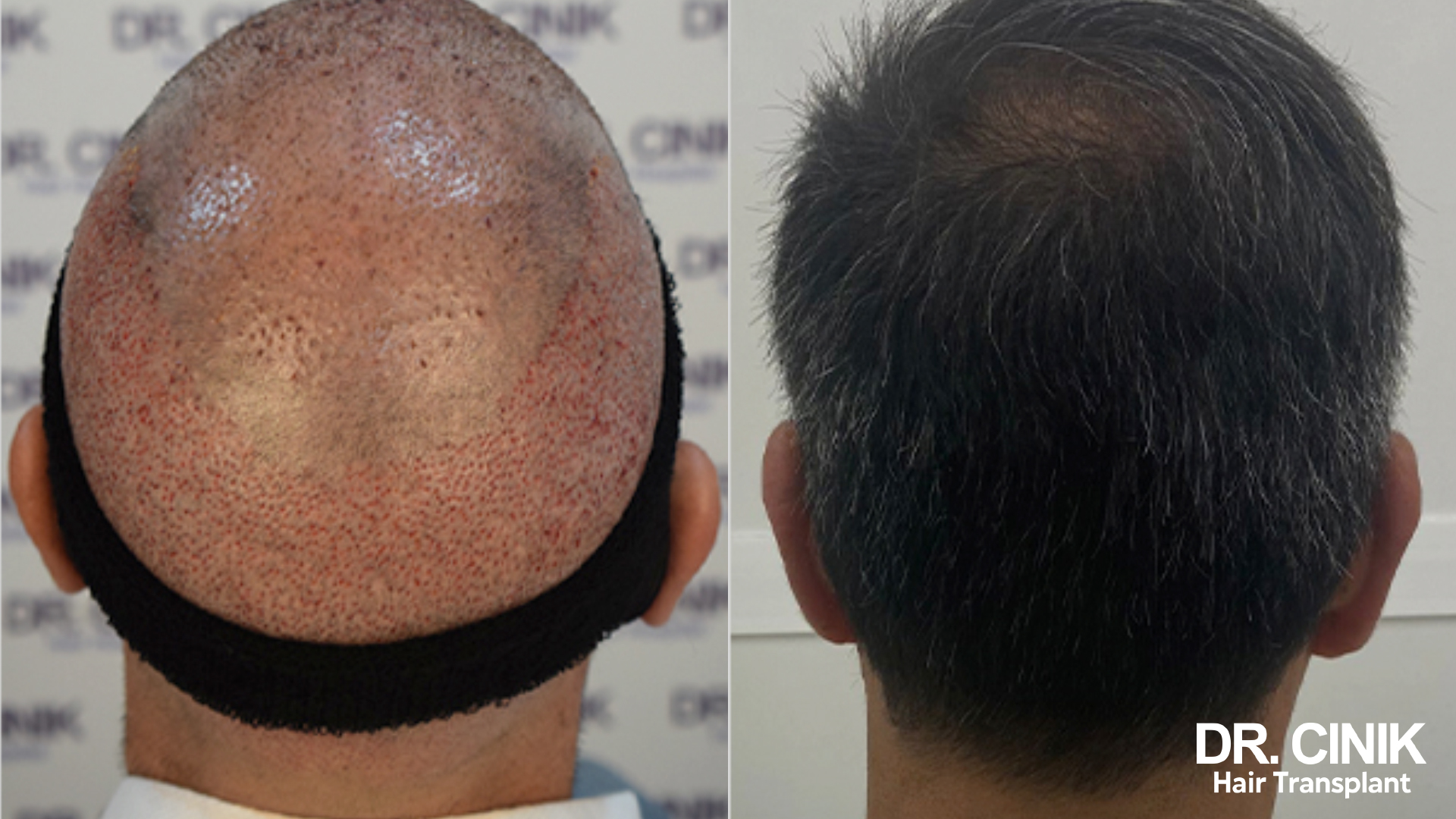
Instructions for Protecting Grafts
Post-transplant care involves several precautions to safeguard the new grafts:
Sleeping After a Hair Transplant
Post-operative sleep care is critical to help the grafts become securely anchored and healed:
- Sleeping Position: For optimal healing, it’s recommended to sleep on your back with the head elevated at about 45 degrees, minimising pressure and friction on the grafted areas. Using a pillow beneath the neck and additional cushions to prop up your body will help maintain this position, keeping your shoulders and head aligned.
- Special Cushions: Utilizing a pregnancy cushion or a U-shaped travel pillow can help prevent rolling onto your side. If needed, consider sleeping in a recliner chair.
- Resuming Normal Sleeping Positions: It’s generally safe to start sleeping on your side after 10 days and on your stomach after 15 days.
Protecting Grafts with Appropriate Headwear
In the initial 10 days following the procedure, it is essential to shield the grafts when going out. You should wear a wide-brimmed hat, which is typically provided by the clinic. It’s important to note that during this period, caps are not an appropriate form of protection.

Sport and Hair Transplants
Post-operative patients must take a break from physical activities to promote optimal healing of the hair grafts. The following stages outline the process of safely resuming sports:
- Healing phase (days 1 to 5): Abstain from all sporting activity to allow the grafts to anchor securely.
- Early consolidation phase (days 6 to 20): Gradual reintroduction to light activity, such as walking at a relaxed pace or engaging in gentle yoga.
- Advanced consolidation phase (3 weeks to 2 months): Start with low-impact exercises like using an elliptical machine and progress to swimming with a cap after the first month.
- Return to normal phase (> 2 months): Slowly incorporate light weightlifting and higher intensity activities, for example, running.
It’s crucial to steer clear of contact, extreme sports, and heavy weightlifting for at least 4 to 6 months. To protect your grafts, wear a headband, remain well-hydrated, and minimize sun exposure.
Sexual Activity Post-Hair Transplant
It is advisable to wait 10 days before resuming any form of sexual activity, which includes masturbation, after a hair transplant. This period is critical to ensure the successful healing of the grafts, which are especially vulnerable during this early stage.
Why is it Important to Pause Sexual Activity?
- Graft Fragility: The grafts need approximately 7 to 10 days to settle securely in their new location.
- Infection Risks: The perspiration associated with sexual activity could heighten the likelihood of infection.
- Vasodilatation Risks: The heightened blood pressure from sexual activity may lead to the reopening of the micro-incisions.
Secure Resumption Tips:
- Ease Into It: After the 10-day hiatus, it’s wise to start with brief, low-intensity sessions.
- Safety Measures: Opt for positions that do not exert pressure on the scalp and sidestep abrupt movements.
- Manage Room Climate: Maintain a cool environment to reduce the likelihood of perspiration.
- Dress and Undress Mindfully: Take extra care while undressing to prevent snagging the grafts.
Normal sexual activities can typically be resumed after 3 weeks, but stay alert for any atypical sensations.
Protecting Your Grafts from the Sun After a Hair Transplant
Post-transplant, guarding the grafts against the sun is paramount; premature or intense UV exposure can interrupt regrowth and may lead to graft failure.

How Do You Protect Yourself from the Sun After a Transplant?
- Healing phase (first 4 to 6 weeks): Minimize sun exposure. Stay indoors or seek shade and don a wide-brimmed hat for any necessary outdoor excursions. Refrain from applying sunscreen to the scalp during this sensitive period.
- Regrowth phase (after 4-6 weeks): Approach sun exposure with caution and progressively increase time in the sun. Ideally, wait 3 months before facing more direct sunlight. Employ SPF 50 sunscreen and continue wearing a wide-brimmed hat during sun exposure.
Adhering to these guidelines will support the successful outcome of your hair transplant and safeguard your grafts from the detrimental effects of sunlight.
Alcohol and Tobacco Consumption After a Hair Transplant
To ensure the best possible outcomes, it’s vital to avoid alcohol and tobacco both before and after a hair transplant.

Alcohol and Hair Transplants: A Cocktail to be Avoided
- Before the transplant: Abstaining from alcohol at least 5 days before the procedure is recommended since alcohol can lessen the effectiveness of local anaesthetics and elevate the risk of bleeding and infection.
- After the transplant: Refraining from alcohol for at least 30 days post-surgery is crucial as it can disrupt the healing process, diminish graft vascularisation, increase inflammation and infection risks, and exacerbate hair shedding.
Tobacco and Hair Transplants
Smoking has been shown to hinder healing and tissue oxygenation, which increases the likelihood of graft rejection or failure.
Styling your hair After a Hair Transplant
Proper styling practices post-hair transplant is crucial to the overall success of the procedure.
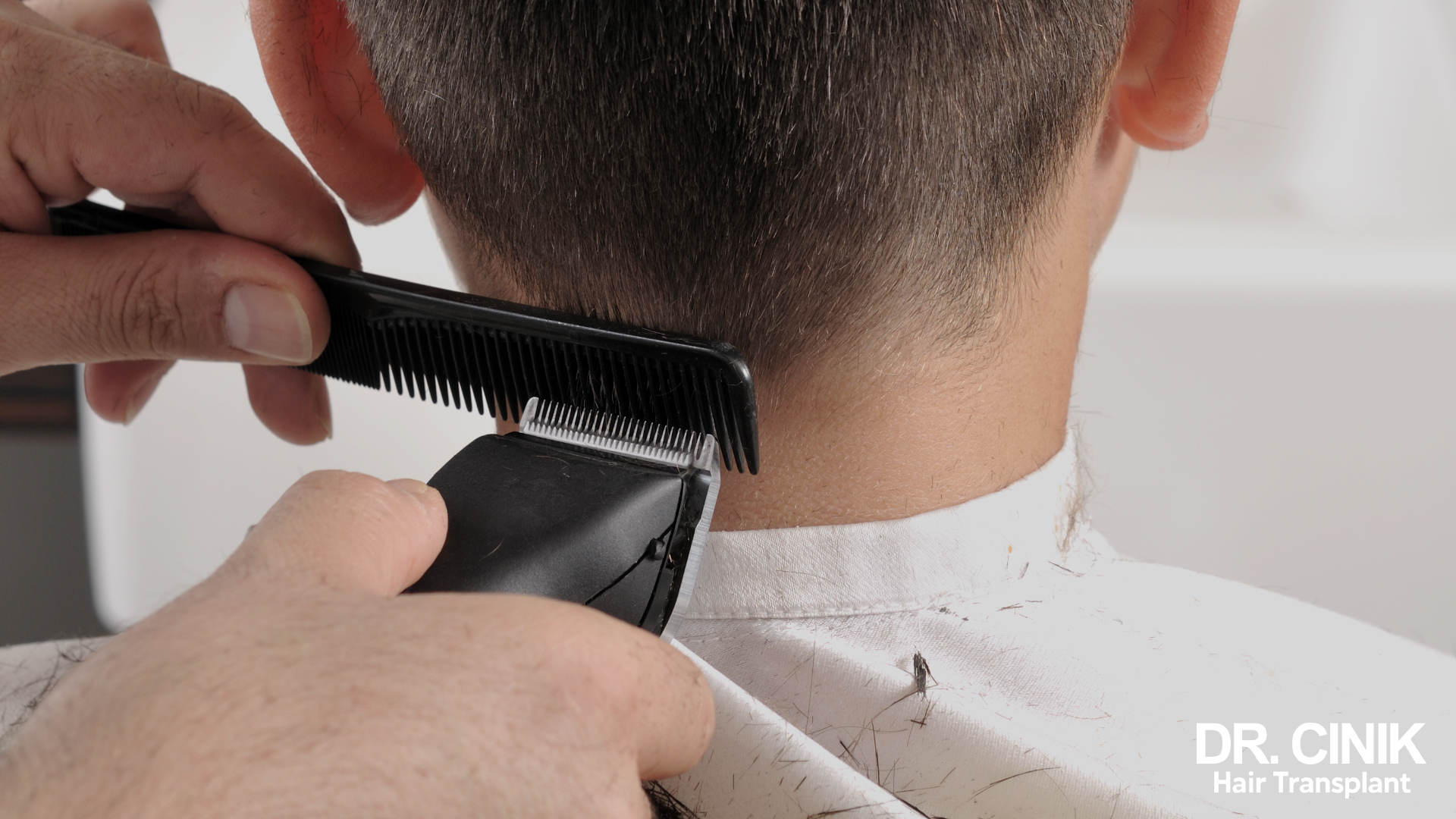
Get a haircut or Shaving Post-Transplant
- Donor Area: You may trim the hair in the donor area, at the back of the head, one-month post-transplant using hair clippers or scissors.
- Grafted Area: For the transplanted region, it is advisable to wait six months before cutting the hair, and scissors are recommended for the first trim.
Choosing a Post-Transplant Hairstyle
To minimise the visibility of growth differences between the donor and transplanted areas, many individuals opt for a very short haircut during the initial 8 to 12 months. As the hair grows out, steer clear of hairstyles that could place excessive tension on the strands, such as tight ponytails.

The Diet to Adopt
Adhering to a healthy, balanced diet that is ample in proteins (such as meat, fish, and eggs), vitamins (from fruits and vegetables), and iron (found in green vegetables and red meat) will aid in promoting the growth of the transplanted hair.
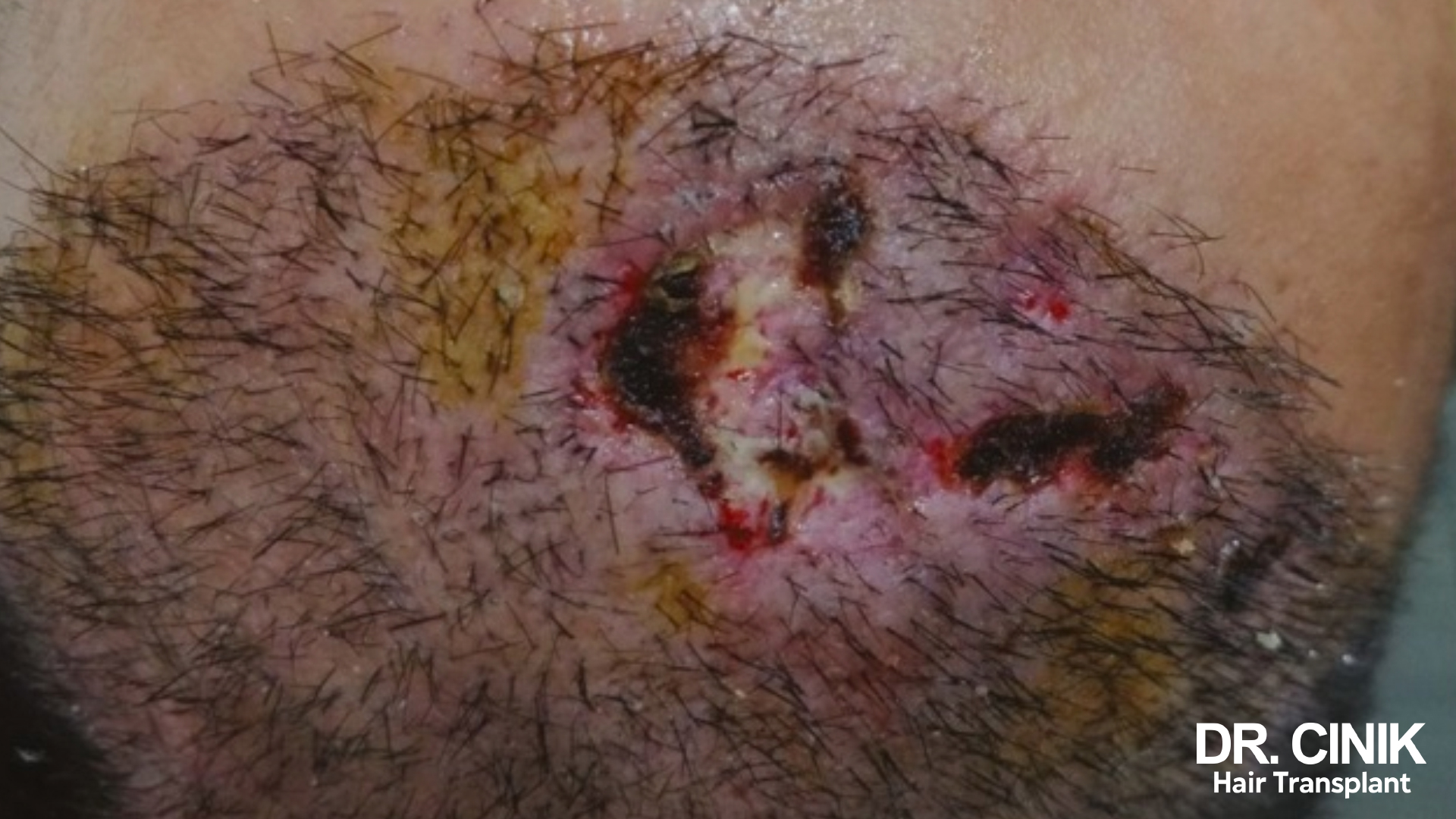
Potential Side Effects and Complications Post-Hair Transplant
Localized Side Effects
- Swelling and Redness typically emerge within the first 10 days post-transplant, impacting both the donor and recipient sites.
- Feelings of Tightness and Itching are frequent around the scars and transplanted zones, but these sensations tend to subside over time.
- Numbness and Temporary Sensation Loss in the surrounding operated areas are a byproduct of the surgical procedure.
- Varying Degrees of Pain might be experienced following the surgery, occasionally necessitating the use of analgesics.
- Shock Loss is a standard, albeit harmless, reaction, with hair often taking several months to regrow completely.
- Bruising Formation can be seen in both the harvesting and implanting regions.
- Scabs Formation occurs at the incision sites, which naturally exfoliate in about 1 to 3 weeks during the healing period.
General side effects
- Marked fatigue and headaches frequently occur following surgery and are typically associated with the operation’s stress.
- Nausea and vomiting: These symptoms after surgery are usually related to the anaesthesia and the medications prescribed.
Rare complications
- Hypertrophic Scars: There’s a risk of developing thickened scars following a FUT graft procedure which might necessitate further treatment.
- Severe Allergic Reactions: Although rare, serious reactions can arise due to anaesthesia.
- Compressive Hematomas: The infrequent development of deep hematomas that demand immediate medical attention.
- Necrotizing Infections: Despite stringent hygiene protocols, skin infections can occur but are extremely rare.
Psychological complications
- Patient Dissatisfaction: Feeling let down by aesthetic results can cause considerable psychological distress.
- Depressive Disorders: Challenging recovery phases post-surgery may sometimes result in depression, necessitating both psychological and medical intervention.
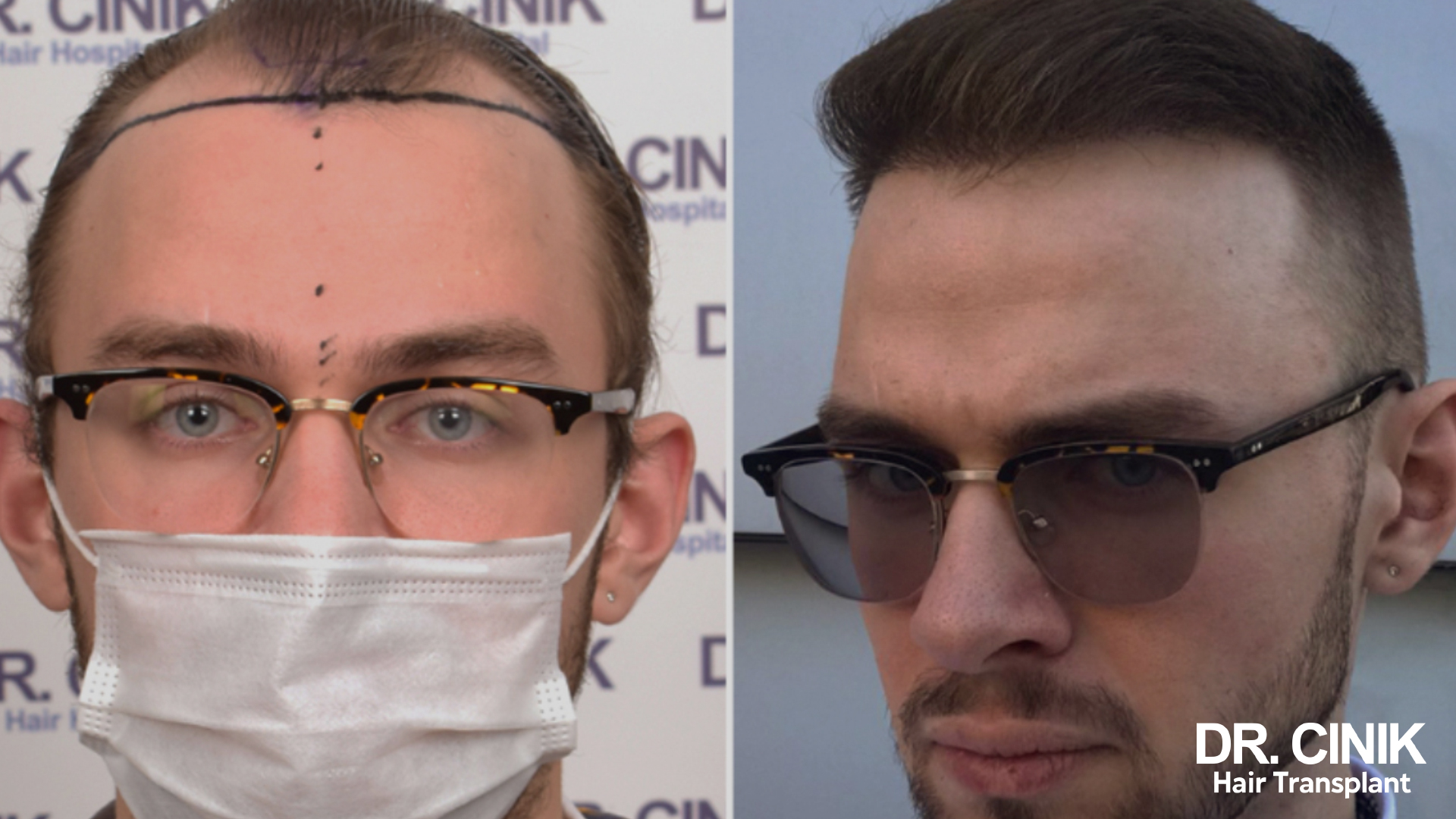
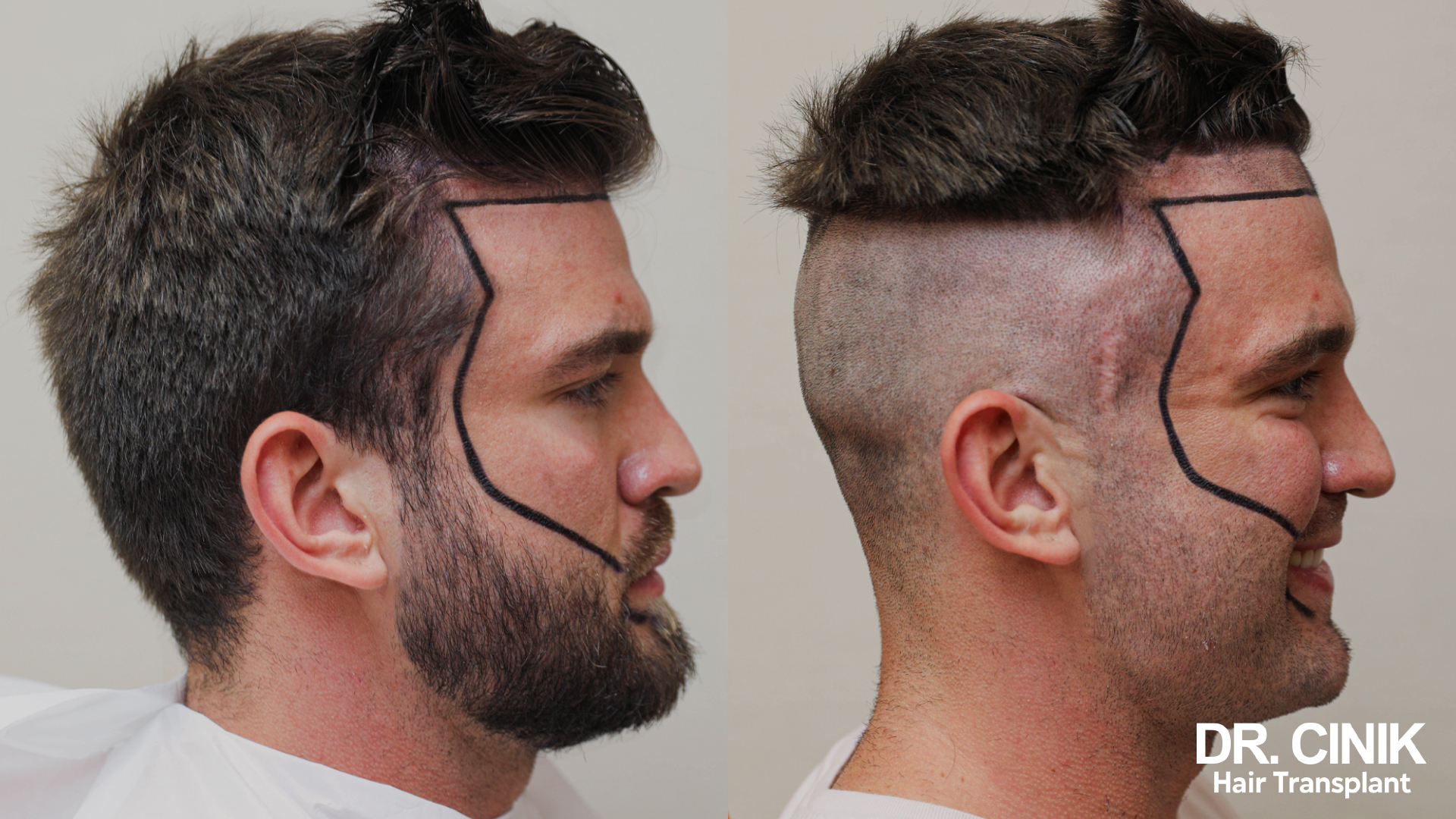
Results of a hair transplant
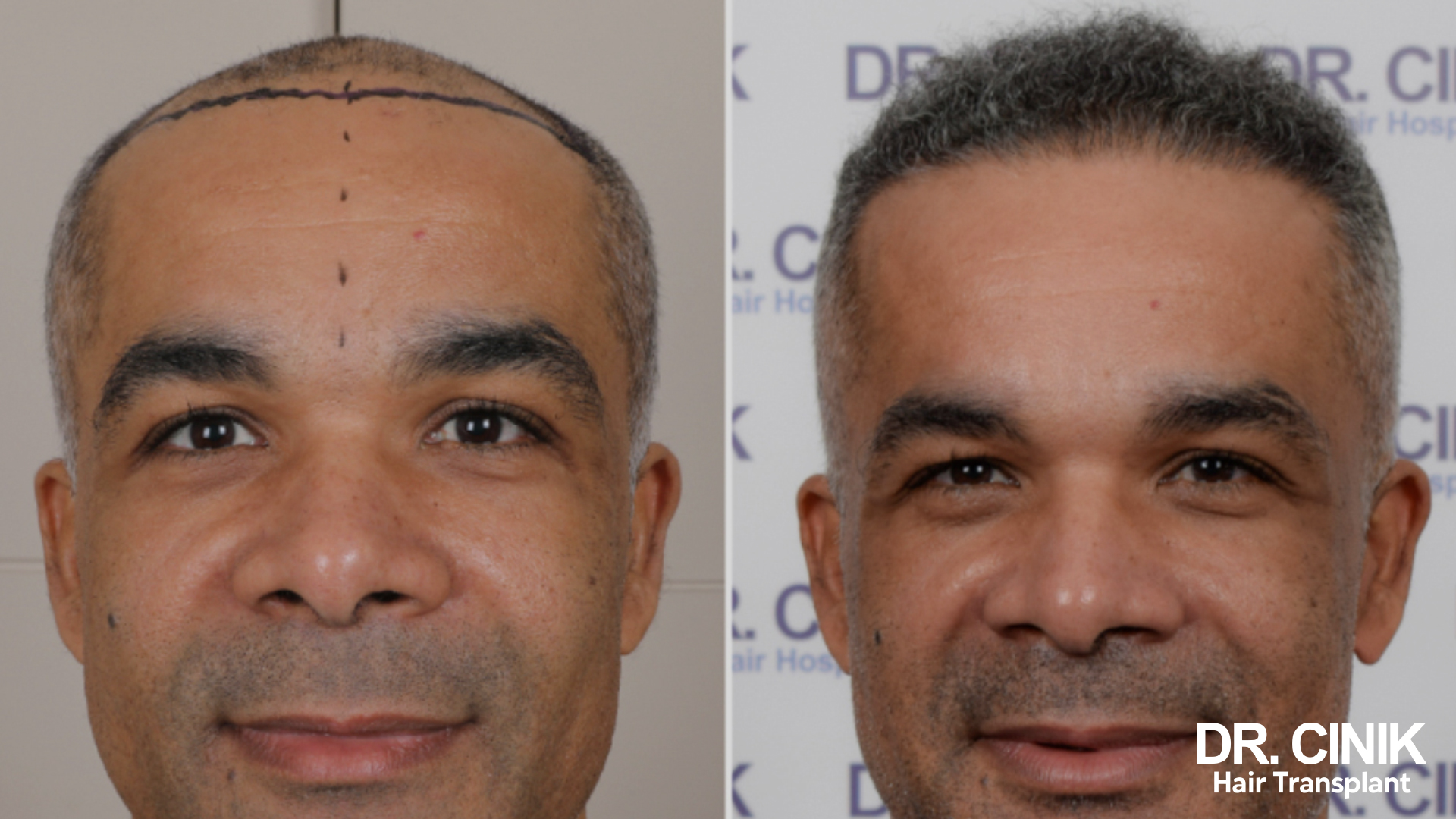
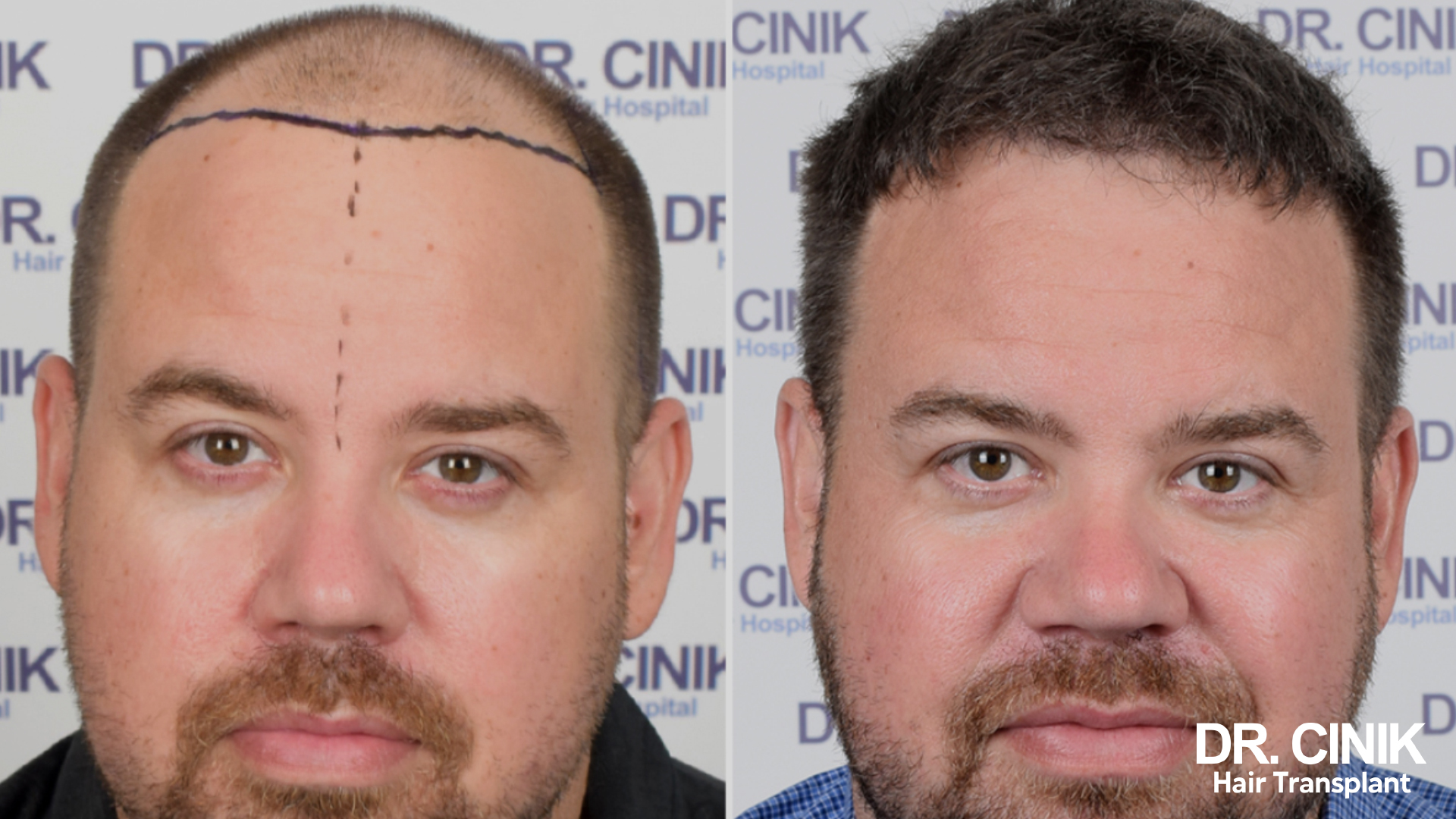
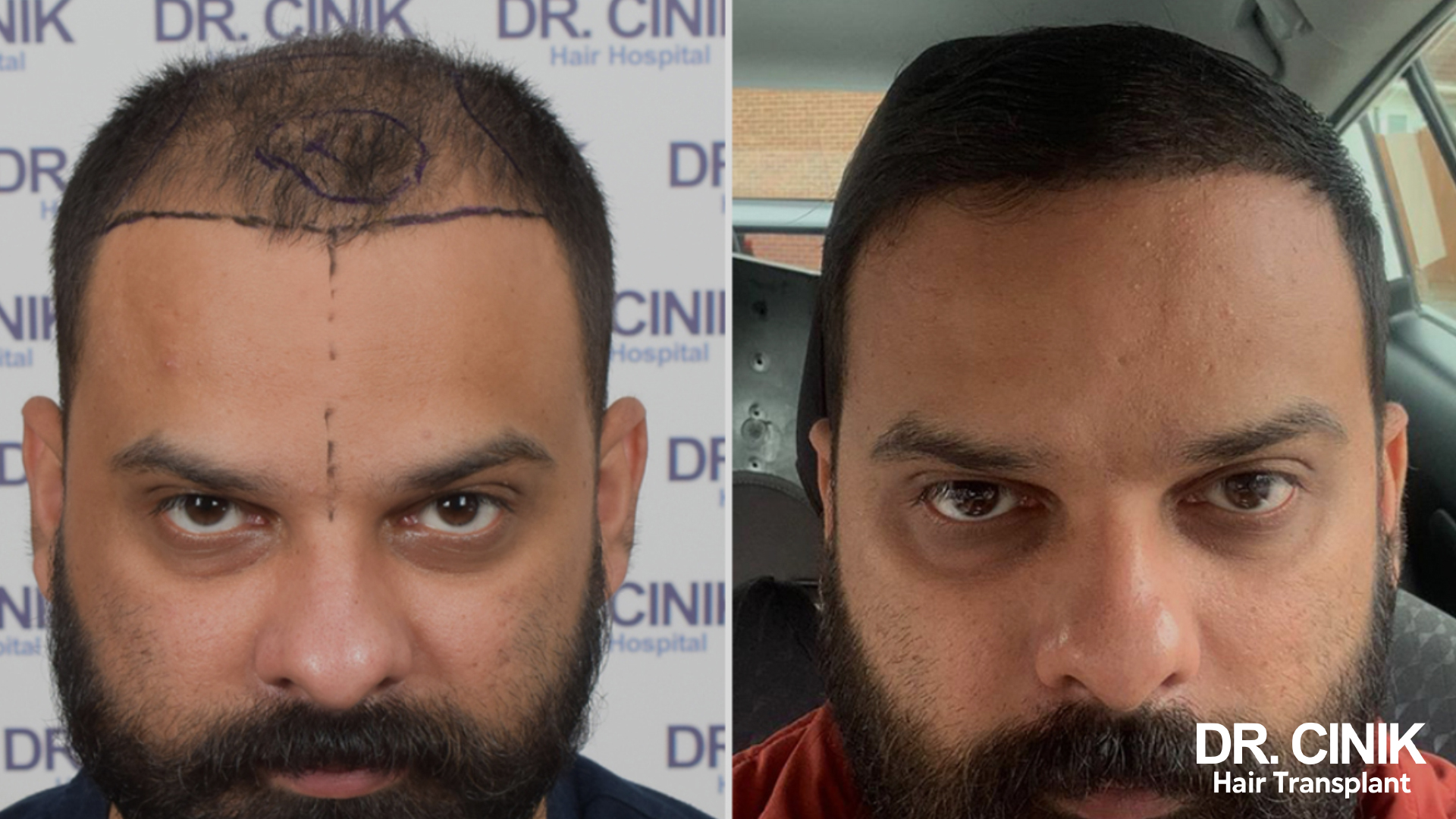
Before and after photos of a hair transplant
In men

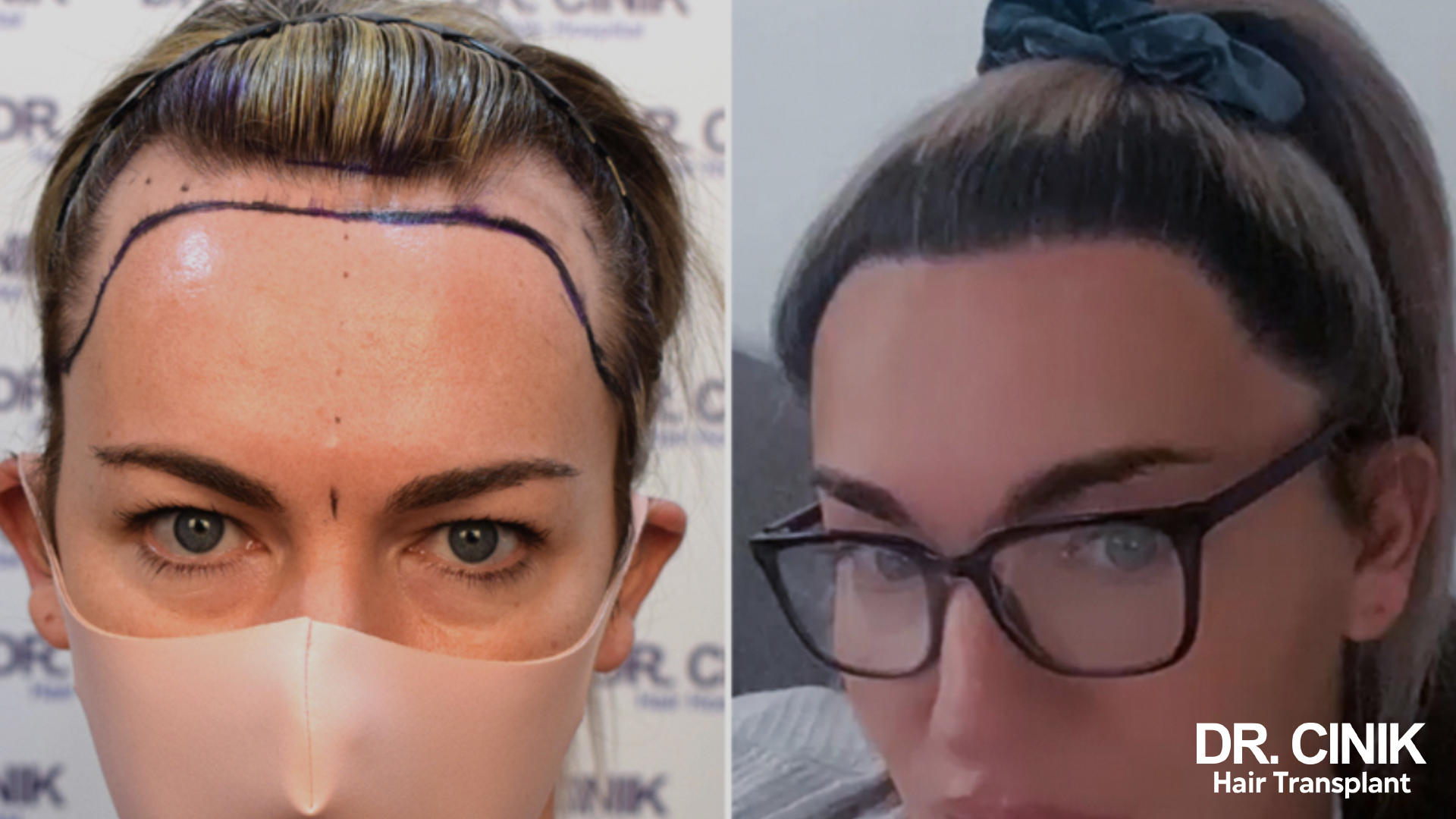
In women
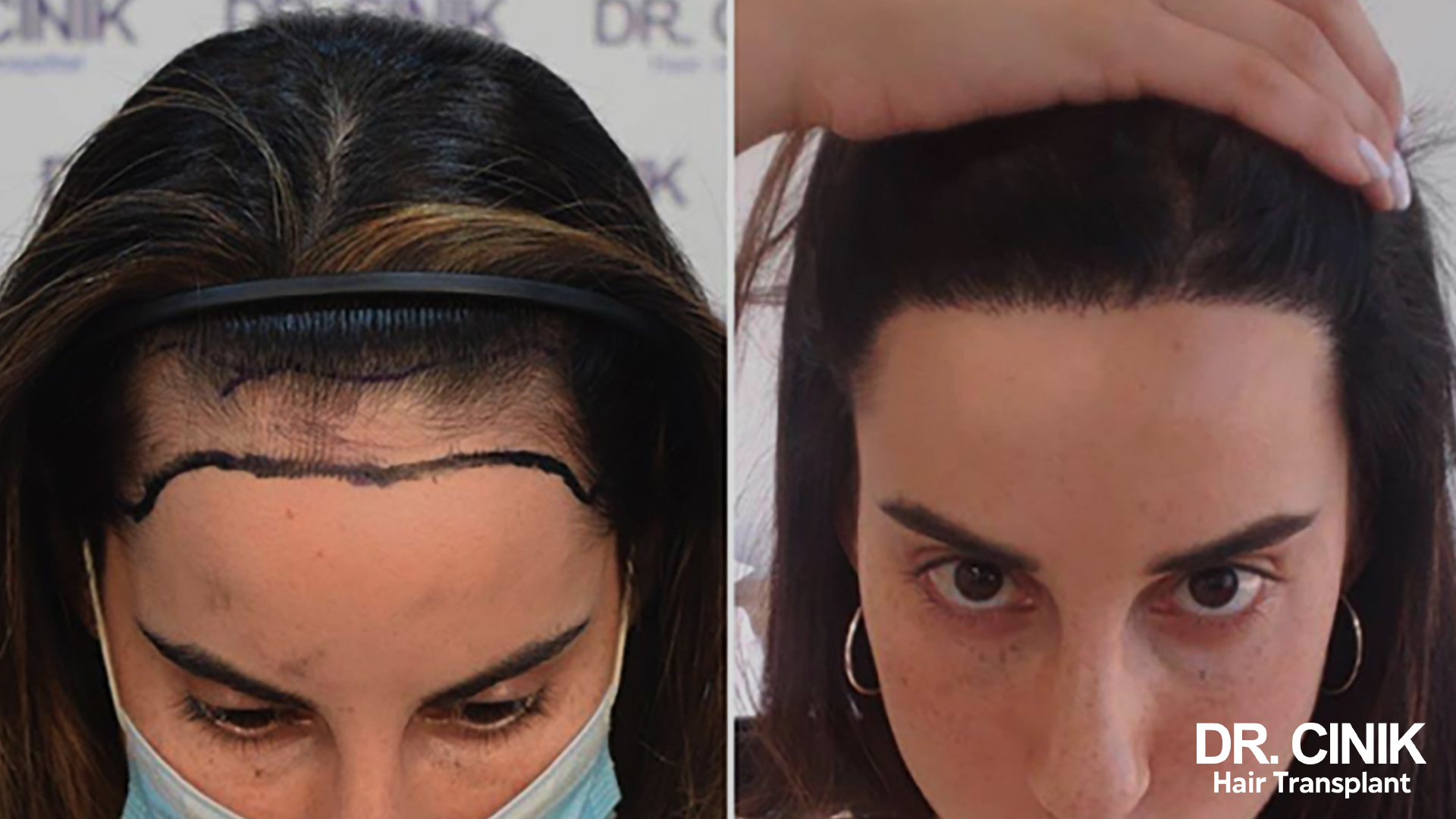
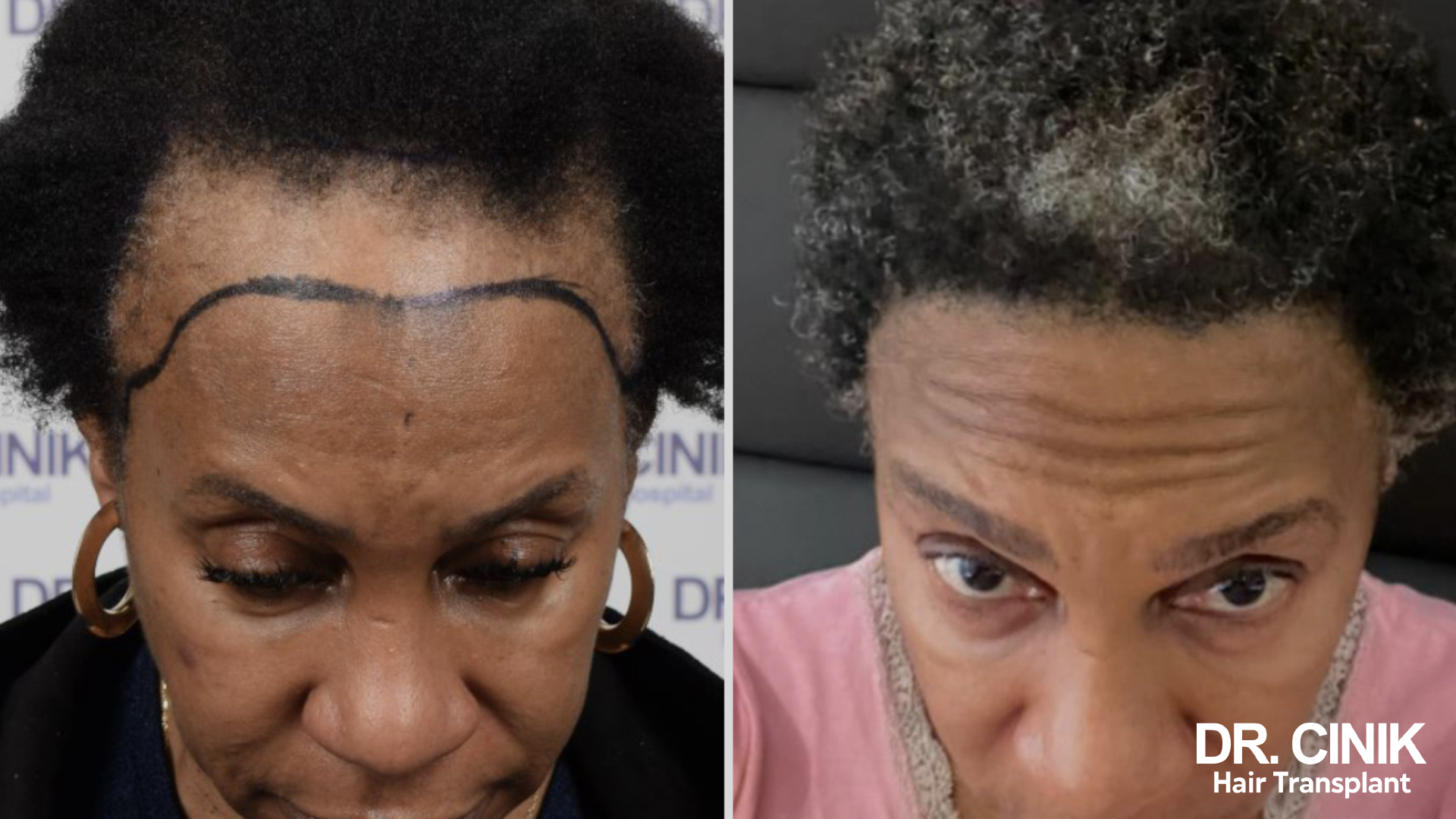
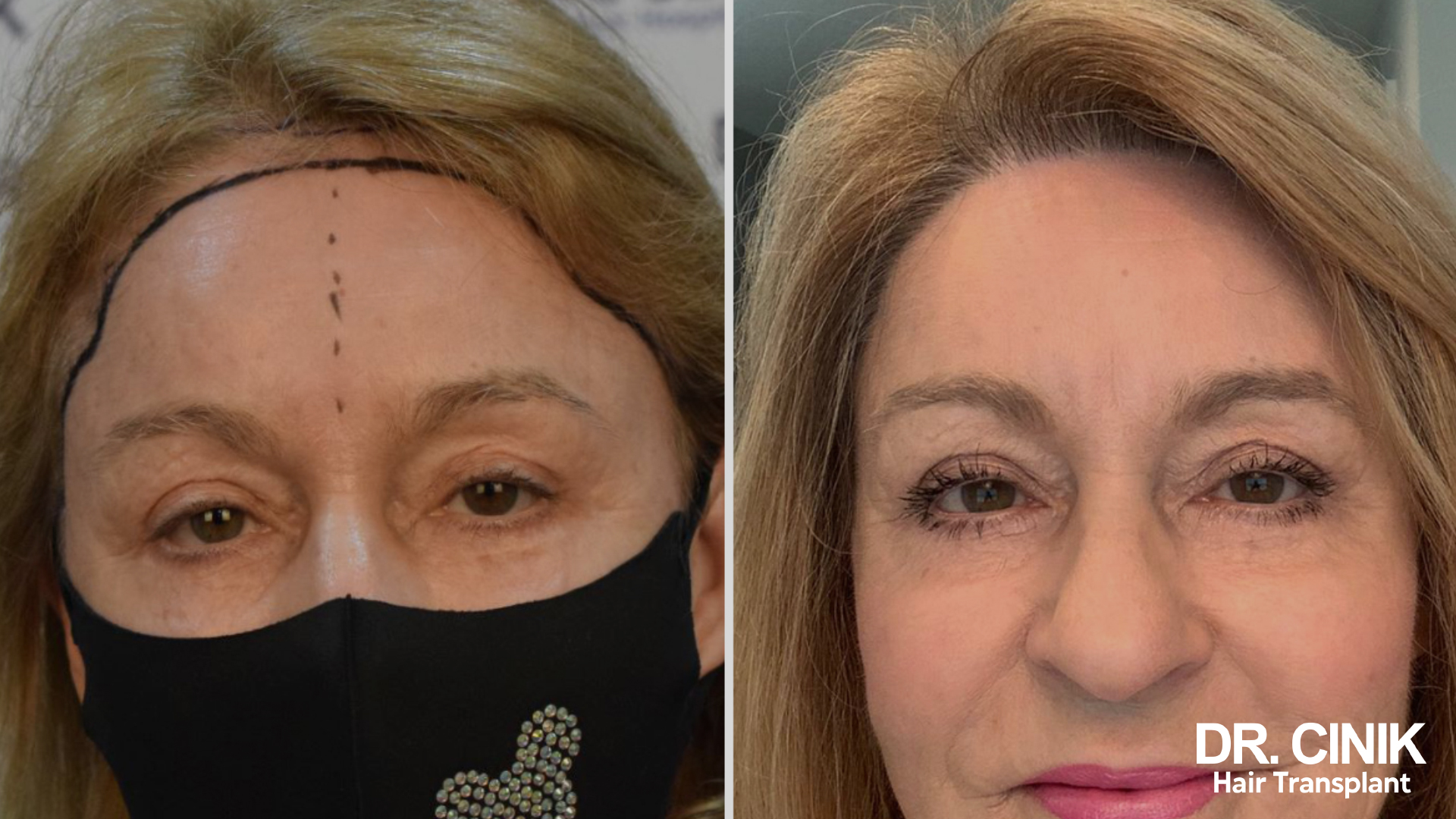

The Stages of Hair Regrowth Following a Transplant
Immediately Post-Transplant
The formation of tiny scabs at the implantation sites and donor area is typical. Patients might experience slight discomfort and swelling.
10 Days Post-Transplant: Healing Phase
The scabs begin to shed naturally. Any swelling recedes, and the grafted region starts to recover.
1 Month Post-Transplant: Shock-Loss Phase
Temporary hair loss may occur in both the grafted and donor areas, a normal response to the surgical process. Hair usually starts to regrow in the weeks to follow.
3 to 4 Months Post-Transplant: Onset of Regrowth
This is when the first transplanted hairs start to emerge. Initially, they may appear fine but gradually thicken over time.
6 Months Post-Transplant: Density Increase
Hair continues to grow in and thicken. At this point, a significant improvement in hair density becomes evident, and patients can start experimenting with different hairstyles.
One Year Post-Transplant: Final Outcome
Full hair density is achieved. The transplanted hair has fully matured and thickened, offering a natural look. Complete regrowth in the vertex area might take a bit longer owing to its less abundant blood supply.
10 Years Post-Transplant: Ageing Alongside You
The grafted hair goes through the natural cycles of growth, aging, and potential greying. These hairs don’t fall out permanently but continue to regenerate as per the customary hair cycle.
Hair Transplant Cost Considerations
Key Factors Affecting Hair Transplant Pricing
Several crucial elements determine the cost of a hair transplant:
- Quality of surgeons and care teams: The expertise and reputation of the professionals are critical.
- Support and care services: The provision of additional services, such as translation or personal care assistance.
- Clinic standards and equipment: The level of technological sophistication and comfort provided.
- Surgical techniques utilized: The range of methods available, including FUE, DHI, and others.
- Location of the clinic: Factors such as accessibility and geographical positioning.
- Post-operative care: The extent and quality of care following the procedure.
Cost Comparisons: France and Turkey
- France: The cost fluctuates with the number of grafts. For instance, 1,500 grafts might set you back €3,900, and the price can climb to approximately €10,300 for a more substantial transplant of 5,000 grafts.
- Turkey: Body Expert provides an all-inclusive package starting at €2,090, which covers up to 5,000 grafts. This comprehensive pricing includes the FUE transplant, on-site support, transportation, PRP treatment, a stay in a 5-star hotel, and meticulous post-operative care.
Price Comparison Tables by Country
Below is a price comparison for an FUE hair transplant based on the number of grafts across different countries:
| Number of Grafts via FUE Method | France | Turkey | Belgium | Switzerland | Tunisia | Mauritius |
| 1,500 | €3,900 | €2,090 | €5,300 | CHF 6,500 | €2,400 | €2,500 |
| 2,000 | €4,800 | €2,090 | €6,500 | CHF 8,000 | €2,400 | €3,100 |
| 2,500 | €5,700 | €2,090 | €7,700 | CHF 9,500 | €2,400 | €3,700 |
| 3,000 | €6,500 | €2,090 | €8,900 | CHF 10,900 | €2,400 | €4,200 |
| 3,500 | €7,400 | €2,090 | €10,100 | CHF 12,300 | €2,800 | €4,800 |
| 4,000 | €8,300 | €2,090 | €11,300 | CHF 13,800 | €2,800 | €5,400 |
| 4,500 | €9,200 | €2,090 | €12,600 | CHF 15,400 | €2,800 | €6,000 |
| 5,000 | €10,300 | €2,090 | €14,000 | CHF 17,100 | €2,800 | €6,600 |
This table serves as a snapshot of the varying prices for FUE hair transplants across several countries, revealing significant differences that can influence a patient’s choice of location for the procedure.
FAQ
Why Opt for a Hair Transplant in Turkey?
Turkey, particularly Istanbul, has emerged as a prime choice for hair transplants, thanks to the synergy of medical excellence, innovative technology, and affordability. Turkish doctors are esteemed for their specialization in hair restoration, bringing to the table extensive training and significant experience with state-of-the-art techniques such as FUE Saphir (Follicular Unit Extraction) and DHI (Direct Hair Implantation). Clinics in Turkey uphold high-quality standards, furnished with contemporary technology and offering comfortable accommodations. They comply with strict health protocols, assuring patient safety and care quality. What’s more, the pricing for hair transplants in Turkey is substantially lower compared to many other countries, ensuring accessibility to high-quality procedures.
Dr. Emrah Cinik exemplifies Turkish excellence in hair transplantation. His more than 20 years of experience and the completion of over 50,000 transplants have earned him international acclaim for his expertise and tailored patient care. Dr. Cinik’s clinic provides all-encompassing packages, which include the surgical procedure, lodging, transport, and if necessary, language assistance, significantly easing the process for international patients.
At What Age Should One Consider a Hair Transplant?
For those contemplating a hair transplant, the preferred age range is typically 30 to 40 years. Within this timeframe, hair loss is more likely to have stabilized, which allows for a more accurate assessment of the area needing treatment and the expected transplant outcomes. Undergoing the procedure before hair loss has stabilized may lead to inconsistent or unsatisfactory results, and might result in the necessity for additional transplants if baldness continues to advance.
Is Shaving Necessary Before a Hair Transplant?
Shaving the head is generally required before undergoing a hair transplant to enhance the surgeon’s visibility and to decrease infection risks. However, in certain instances and with the surgeon’s agreement, a hair transplant without full shaving — or with partial shaving — might be an option. This is usually considered for distinct cases, like minor hair loss, or for patients with long hair who prefer to conceal the donor area post-transplant.
Can I Have a Hair Transplant If I’m Afraid of Needles?
If the thought of needles makes you uneasy, consider a hair transplant at Dr. Emrah Cinik’s clinic, which offers needle-free anaesthesia. This state-of-the-art process delivers anaesthetic without traditional needles, by spraying it under high pressure onto the scalp and numbing it prior to injections. While it significantly reduces discomfort, be aware that it may not completely replace needles in all scenarios.
Is a Beard Transplant Possible?
Absolutely, beard transplants are a viable option increasingly sought by men wanting to enhance their beard’s thickness or address sparseness. Similar to hair transplants, this procedure adapts the technique to facial hair.
Are Women Candidates for Hair Transplantation?
Oui, la greffe de cheveux est tout à fait possible chez la femme, et elle est de plus en plus courante. Cette procédure est une solution efficace pour les femmes souffrant d’alopécie androgénétique, d’alopécie cicatricielle ou d’alopécie de traction.
How Is the Number of Grafts for Implantation Determined?
To ascertain the appropriate number of grafts for a hair transplant, various elements are considered:
- Extent of Baldness: The surgeon assesses the bald or thinning areas to determine the size of the surface that needs coverage.
- Density of the Donor Area: A key factor is the hair density in the donor region—the higher the density, the more grafts can be harvested for the transplant.
- Hair Characteristics: The type of hair, including its thickness, colour, and texture, plays a role in the number of grafts needed. For instance, covering an area with thick, dark hair might require fewer grafts compared to fine, light-coloured hair.
- Patient’s Aesthetic Goals: Desired hair density and style preferences, as envisioned by the patient, are taken into account.
- Age and Hair Loss Progression: The patient’s age and the extent of hair loss, based on the Norwood-Hamilton scale, are critical factors. Anticipating future hair loss is essential, especially when hair loss is actively progressing, which may call for multiple transplant sessions to preserve donor areas.
- Chosen Transplant Technique: The transplant method, whether it’s FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) or DHI (Direct Hair Implantation), affects the quantity of grafts achievable in a single procedure.
Before the surgery, a comprehensive hair analysis (trichogram) is performed to help the surgeon estimate the number of grafts required to meet the patient’s expectations.
 en
en