Finasteride 1mg (Propecia) for Treating Androgenetic Alopecia
Summary
Millions of individuals globally suffer from androgenetic alopecia, impacting their physical appearance and emotional well-being. Amidst a sea of products claiming to cure baldness, finasteride 1mg (Propecia) stands out as a scientifically validated prescription medication that effectively slows down hair loss. However, the drug is also associated with potentially serious side effects, making it controversial.
This comprehensive article examines the chemical makeup of finasteride 1mg (Propecia), its functioning mechanism, and its effectiveness. Additionally, we will cover potential side effects and precautions you should consider. We also highlight alternative solutions like hair transplants, which offer the most lasting results.
What is Finasteride 1mg (Propecia)?
Finasteride 1mg (Propecia) is renowned for its efficacy in treating hair loss, specifically male pattern baldness. In this segment, we will delve into the drug’s chemical structure, how it functions, and its primary medical applications.
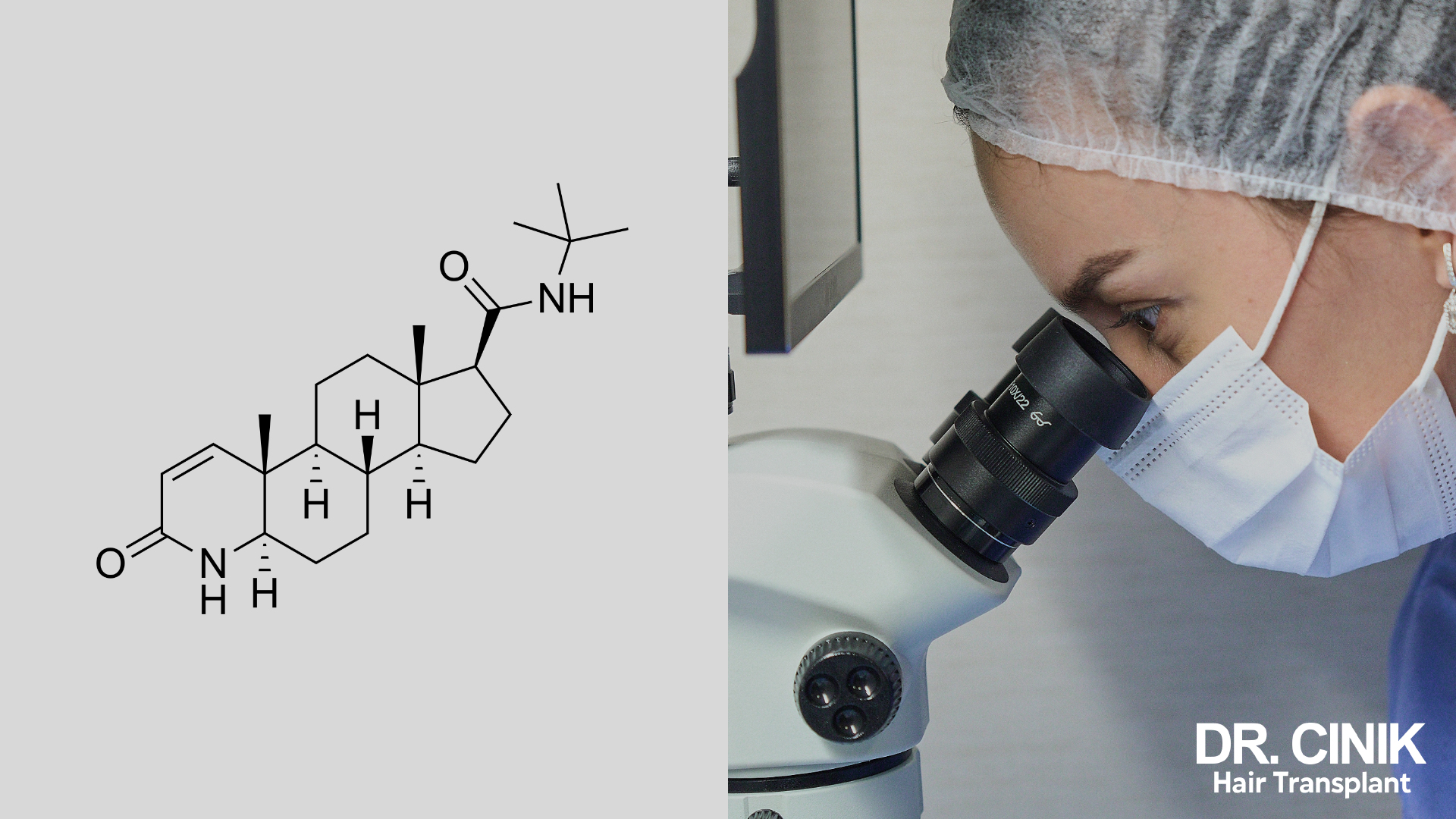
Chemical Composition
Finasteride is an inhibitor of 5-alpha reductase, an enzyme that transforms testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). The chemical formula of finasteride is C₂₃H₃₆N₂O₂. It typically comes as film-coated tablets for oral administration but is also available as a topical cream.

Mechanism of Action
The drug’s primary function is inhibiting testosterone conversion to DHT. DHT is an androgen hormone that plays a key role in causing androgenetic alopecia. It accelerates the hair growth cycle and depletes the hair follicles, eventually resulting in permanent hair loss. By blocking the action of 5-alpha reductase, finasteride lowers DHT production, thereby slowing or even reversing hair loss.
Difference Between Chibro-Proscar and Propecia
Both Chibro-Proscar and Propecia contain the active ingredient finasteride, but they differ in dosage. Propecia, containing 1mg of finasteride, is specifically designed for treating androgenetic alopecia and is generally prescribed for men aged 18 to 41 who are in the early stages of hair loss. On the other hand, Chibro-Proscar, which contains a higher dose of 5mg of finasteride, is primarily used for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It’s essential to note that using Chibro-Proscar for hair loss, due to its higher finasteride content, elevates the risk of experiencing side effects.
Efficacy of Finasteride 1mg (Propecia) in Treating Androgenetic Alopecia
In this section, we explore how effective finasteride 1mg (Propecia) is in treating androgenetic alopecia, considering both oral and topical applications and its potential benefits for women.
Oral Administration
According to a pilot study conducted in Japan, oral finasteride effectively treated androgenetic alopecia in 59.5% of the patients, categorising the results as excellent or good.

Topical Application
Topical formulations of finasteride, usually in the form of a cream, aim to minimise the complications associated with oral administration. A survey of existing studies indicated that topical finasteride showed positive outcomes and a favourable safety profile in treating male androgenetic alopecia.
Efficacy in Women
The preferred treatment for female pattern hair loss (FPHL) is Minoxidil. Several studies have examined the possible efficacy of finasteride as an alternative treatment. However, these studies are limited due to finasteride’s potential teratogenic effects. Although some results appear promising, more clinical research is needed to confirm both the efficacy and safety of finasteride for women.

Side Effects of Finasteride
The NHS details several serious side effects associated with finasteride use.
Psychological Side Effects
Finasteride may lead to psychological issues such as anxiety, depression, and suicidal thoughts. Importantly, these symptoms could persist even after discontinuing the medication.

Sexual Side Effects
There are also reported sexual side effects, including erectile or ejaculation issues, testicular discomfort, and reduced libido. Some users have also reported issues related to infertility and diminished sperm quality.
Other Adverse Effects
Finasteride can cause additional serious side effects, such as severe allergic reactions, breast tenderness and enlargement (gynaecomastia), and nipple discharge.
How to Prevent Side Effects
Medical Consultation Before Starting Treatment
Before initiating any treatment with finasteride, consult your healthcare provider for a comprehensive medical evaluation. This is especially important if you have a history of psychological conditions like depression or anxiety.
Regular Medical Supervision During Treatment
Frequent consultations with your doctor are recommended while you are on treatment to monitor for any undesirable effects closely.
Inform Your Social Circle
Informing your family and friends that you are taking finasteride can be useful. They can serve as an additional support system, helping to identify any changes in your behaviour or mood.
Discontinue Treatment if Necessary
If you experience mood changes or sexual difficulties, consult your healthcare provider immediately. If advised, you may need to cease treatment.

Alternatives to Finasteride 1mg (Propecia) for Hair Loss Treatment
If finasteride isn’t suitable for you or you’re concerned about potential side effects, there are various other options for addressing hair loss.

Minoxidil
Initially developed to treat hypertension, Minoxidil is now available in topical solutions or foam for scalp application. While generally less effective than finasteride, it has the advantage of fewer side effects. It may, however, cause scalp irritation and, in rare instances, facial hair growth.

Natural Therapies
Natural treatments like castor oil and Saw Palmetto are also available. Castor oil, applied directly to the scalp, promotes hair growth. Saw Palmetto functions similarly to finasteride by inhibiting DHT, a hormone connected to hair loss.
Advanced Hair Treatments
Modern treatments such as PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma), Low-Intensity Laser, and Regenera Activa offer advanced solutions. PRP uses the patient’s own blood to encourage hair growth. Low-intensity lasers use light beams to stimulate hair follicles. Regenera Activa employs stem-cells to rejuvenate the scalp. These treatments generally require multiple sessions, and their effectiveness can vary.
Hair Transplants
Considered the most effective and permanent solution for hair loss, hair transplants come in various forms: DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) and FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction). These procedures involve extracting hair follicles from a donor area and implanting them in areas of hair loss. Though cost-prohibitive for some, the results are permanent and natural-looking.